Managing Serviceguard Extension for SAP Version B.05.00
Page
Table of Contents
SGeSAP Cluster Administration 137
SAP Supply Chain Management
SAP Master Data Management MDM 111
List of Figures
Page
List of Tables
Page
Printing History
About this Manual
Related Documentation
INSTNR, INR
Designing SGeSAP Cluster Scenarios
General Concepts of SGeSAP
Mutual Failover Scenarios Using the Two Package Concept
Mutual Failover Scenarios Using the Two Package Concept
Robust Failover Using the One Package Concept
Follow-and-Push Clusters with Replicated Enqueue
Replicated Enqueue Clustering for Abap and Java Instances
Applications/sap/enqor/SID ersINSTNR
Dedicated NFS Packages
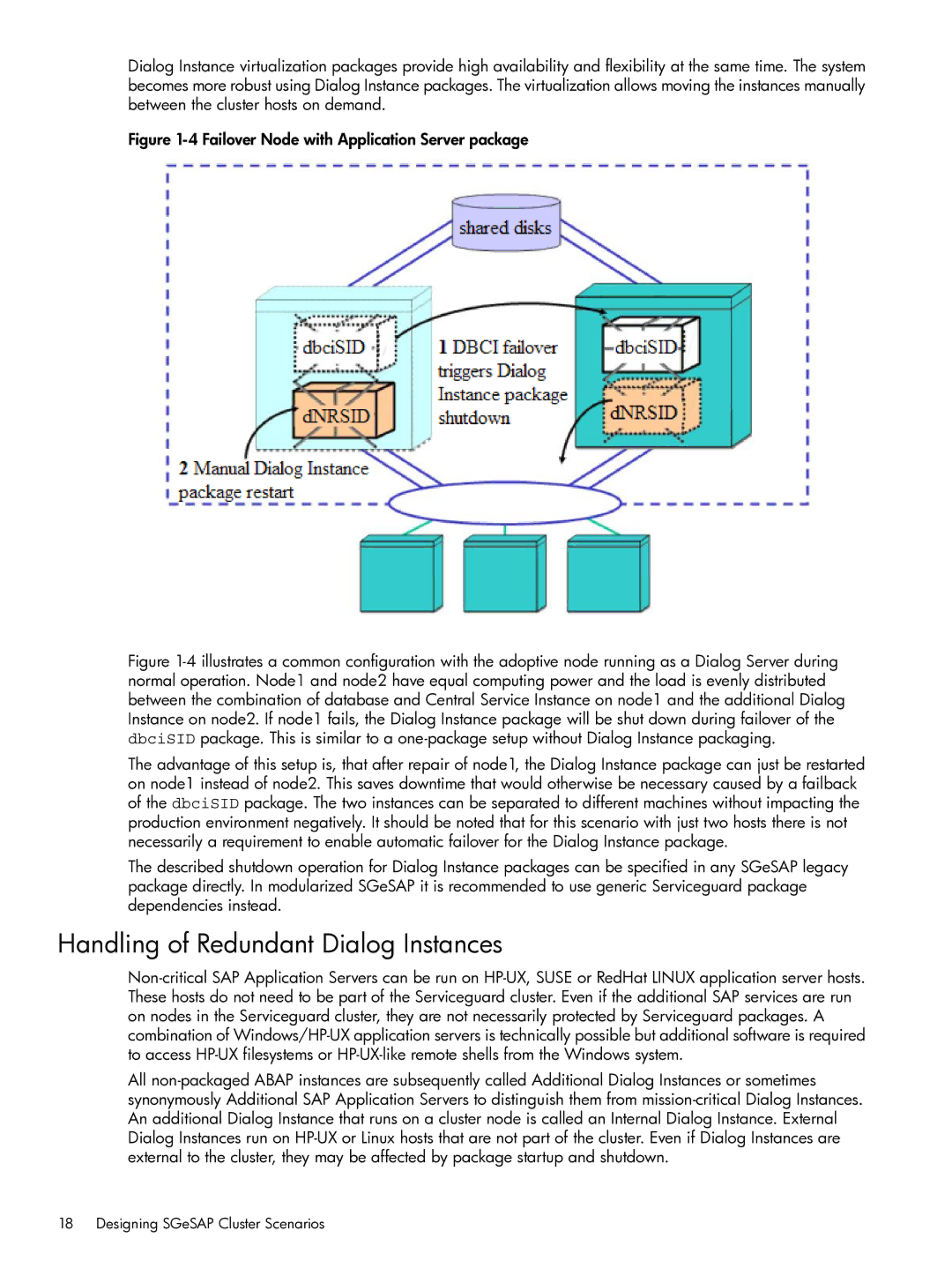
Handling of Redundant Dialog Instances
Dedicated Failover Host
Replicated Enqueue Clustering for Abap and Java Instances
Planning the Storage Layout
SAP Instance Storage Considerations
Option 1 SGeSAP NFS Cluster
Common Directories that are Kept Local
Directories that Reside on Shared Disks
System and Environment Specific Volume Groups
Option 2 SGeSAP NFS Idle Standby Cluster
Option 3 SGeSAP CFS Cluster
Database Instance Storage Considerations
Directories that Reside on CFS
$ORACLEHOME/common/nls/admin/data
Oracle Single Instance Rdbms
Oracle Real Application Clusters
File System Layout for NFS-based Oracle Clusters
Maxdb Storage Considerations
Globals IndepData=/sapdb/data IndepPrograms=/sapdb/programs
Sapnfs
Planning the Storage Layout
Step-by-Step Cluster Conversion
Pgname = pkgtypeINSTNRSID
Step-by-Step Cluster Conversion
SAP Pre-Installation Considerations
SAP Preparation
SAP Netweaver High Availability
Cmmakepkg -m sgesap/db Cmmakepkg -m sgesap/ci
Cmmakepkg -m sgesap/sapinstance -m ... /sap.config
Cmmakepkg -m sgesap/db -m sgesap/ci
Cmmakepkg -m sgesap/scs Cmmakepkg -m sgesap/ers
Page
SAPINSTMASTERDVD/IMXOS/SAPINST/UNIX/OS
Replicated Enqueue Conversion
Create a new mountpoint
Volume group needs to be created for the Ascs instance
Splitting an Abap Central Instance
Su sidadm Mkdir /usr/sap/SID/ASCSINSTNR
If the used SAP kernel has a release older than
Sapsystemname =SID
Instancename =ASCSINSTNR
SAPSYSTEM=INSTNR2
SAPLOCALHOST=DRELOC
Volume group needs to be created for the ERS instance
Creation of Replication Instance
Su sidadm Mkdir /usr/sap/SID/ERSINSTNR
Mkdir -p exe/servicehttp/sapmc
Sapstartsrv Sapcontrol Servicehttp
Scsid = INR
PF = $DIRPROFILE/SIDERSINSTNRAREPRELOC
HP-UX Configuration
Directory Structure Configuration
Cluster Filesystem Configuration
Ls -d /usr/sap/???/*INSTNR
Installation Step IS049
Non-CFS Directory Structure Conversion
Mkdir /usr/sap/SID.new
Maxdb Database Step SD040
Installation Step IS050
Filename localcopy checkexist
Open the password file, /etc/passwd, on the primary side
Cluster Node Synchronization
Open the groupfile, /etc/group, on the primary side
Look at the service file, /etc/services, on the primary side
Copy the sidadm home directory to the backup nodes
Su orasid Mkdir -p /oracle/SID Exit
STARTPROFILE=STARTDVEBMGSINRprimary
STARTPROFILE=STARTDVEBMGSINRsecondary
Su sqddbsid Mkdir -p /sapdb/DBSID
Cluster Node Configuration
Mkdir /dev/vgdbSIDmknod /dev/vgdbSID/group c 64
Mkdir -p /usr/sap/tmp
Iddsa Iddsa.pub
Swlist grep ssh
Ssh-keygen -t dsa
Ssh hostN date Ssh -l sidadm hostN date
Hosts filesNOTFOUND=continue UNAVAIL=continue TRYAGAIN=ns
External Application Server Host Configuration
Configure /etc/nsswitch.conf to avoid problems
Set -u
Modular Package Configuration
DB=ORACLE
DBRELOC=0.0.0.0
Sapsystem C11
Modular Package Configuration
Step-by-Step Cluster Conversion
Example entries for the package configuration file
Sapextinstance DVEBMGS10 Sapextsystem QAS
Sbin/init.d/sapinit referenced by /sbin/rc3.d/S###sapinit
Cmapplyconf -P ./sap.config
Created configuration files need to be edited
Legacy Package Configuration
Serviceguard Configuration
Mkdir -p /etc/cmcluster/SID
Servicename ciC11disp
Servicename ciC11ms
Servicefailfastenabled YES Servicehalttimeout
Touch /etc/cmcluster/SID/debug
Resourcename /applications/sap/enqor/C11ascs
Applications/sap/enqor/SIDersinstnr
ENQORSCSPKGNAMEC11=foobar ENQORREPPKGNAMEC11=foorep
SGeSAP Configuration
Specification of the Packaged SAP Components
Distribute the package setup to all failover nodes
NFSRELOC=0.0.0.0
DNAME0=D
CINAME=DVEBMGS CINR=00
AREPNAME=ERS AREPNR=01 AREPRELOC=0.0.0.0
DNAME1=D
JCIRELOC=0.0.0.0
Configuration of Application Server Handling
JCINAME=SCS JCINR=01
REPNAME=ERS REPNR=00
Page
$STARTWITHPKG, $STOPWITHPKG, $RESTARTDURINGFAILOVER
Restart Stop Start
ASTREAT0=$RESTARTDURINGFAILOVER ASPLATFORM0=SG-PACKAGE
ASPSTART=1
WAITOWNAS=1
Optional Parameters and Customizable Functions
WAITOWNAS=2
WAITOWNAS=0
SAPROUTERSTART0=1 SAPROUTERPORT0=-S3299
RFCADAPTERSTART=1
RFCADAPTERCMD=runadapter.sh
Global Defaults
SAPCCMSRSTART=1
SAPSTARTSRVSTART=1 SAPSTARTSRVSTOP=1
Legacy Package Configuration
JMSSERVBASE=3600
HA NFS Toolkit Configuration
EXEDIR= /usr/sap/SID/SYS/exe/runU
Packagename sapnfs
Export/sapmnt/SID Export/usr/sap/trans
Auto FS Configuration
HANFSSCRIPTEXTENSION=pkgtype
Sapmnt/SID Usr/sap/trans
AUTOMASTER=/etc/automaster AUTOOPTIONS=-f $AUTOMASTER
AUTOMASTER=/etc/automaster AUTOMOUNTOPTIONS=-f $AUTOMASTER
AUTOMOUNTDOPTIONS= -L AUTOFS=1
NFSCLIENT=1 NFSSERVER=1 NUMNFSD=4 NUMNFSIOD=4
Database Configuration
Additional Steps for Oracle
Perform the following step as sidadm
Perform the following steps as orasid
If you use more than one SAP system inside of your cluster
Lsnrctl start LISTENERSID1/2
Additional Steps for Maxdb
Additional steps for Oracle 9i Rdbms
Additional steps for Oracle 10g Rdbms
SAP Application Server Configuration
Rdisp/enqname = relocciSIDinstnr
SAP Abap Engine specific configuration steps
Cdpro
Sapmnt/SID/profile/SIDINSTNAMEINR
Saplocalhostsidinstnr
SID/dbhost = relocdb
Batch jobs can be scheduled to run on a particular instance
SAP J2EE Engine specific installation steps
Rdisp/starticman=TRUE
Icm/hostnamefull=relocatibleip
Admin/host/SID relocdb
Jdbc/pool/SID/Url jdbcoraclethin@relocdb1527SID
Page
SAP Supply Chain Management
More About Hot Standby
Planning the Volume Manager Setup
Option 1 Simple Clusters with Separated Packages
Option 2 Non-MAXDB Environments
Option 3 Full Flexibility
Maxdb Storage Considerations
Option 4 Hot Standby liveCache
LiveCache Installation Step LC010
HP-UX Setup for Options 1, 2
Synchronize the /etc/group and /etc/passwd files
Mkdir /sapdb
Do the following to continue
Copy file /etc/opt/sdb to the second cluster node
Mkdir -p /sapdb/data Mkdir /sapdb/LCSID
Hosts filesNOTFOUND=continue UNAVAIL=continue \ TRYAGAIN=ns
HP-UX Setup for Option
If you use DNS
HORCCMRCF=1 HORCMINST=0
SGeSAP Modular Package Configuration
Cmmakepkg -m sgesap/livecache lcLCSID.config
Packagename lcLCSID
SGeSAP Modular Package Configuration
Cp /opt/cmcluster/sap/*.functions /etc/cmcluster
SGeSAP Legacy Package Configuration
Create standard package control and configuration files
Packagetype Failover
Cold Admin Warm Online
LCPRIMARYROLE=primarynode LCSECONDARYROLE=secondarynode
AVOIDWWIDCHECK=1
Livecache Service Monitoring
LCCOPYMECHANISM=BUSINESSCOPY
LCSTANDBYRESTART=1
APO Setup Changes
Su lcsidadm Dbmcli -ux SAPLCSID,password -ul
Mv .XUSER.62 .XUSER.62.ORG Default key
# dbmcli on hostname Lcsid quit
General Serviceguard Setup Changes
For option
Sapdb/programsrelocsapnfss/export/sapdb/programs
Last step is to reconfigure the cluster with cmapplyconf1m
Master Data Management Overview
Master Data Management User Interface Components
MDM Server Components
SAP Netweaver XI components
MDM SGeSAP File System Layout
Installation and Configuration Considerations
Prerequisites
Oracle/MDM
Multiple MDM Serviceguard packages FOUR+ONE
Single or Multiple MDM Serviceguard Package Configurations
Single MDM Serviceguard Package ONE
Opt/MDM
Run ioscan and insf to probe/install new disk devices
Mkdir -p /oracle/MDM
Mkdir -p /export/home/mdmuser Mkdir -p /home/mdmuser
Mkdir -p /opt/MDM
Installation and Configuration Considerations
Nodename
Runscripttimeout Notimeout
Haltscripttimeout Notimeout
Runscript /etc/cmcluster/MDMNFS/mdmNFS.control.script
Scp -rp /etc/cmcluster/MDMNFS clunode2/etc/cmcluster/MDMNFS
Scp -p /etc/auto.direct clunode2/etc/auto.direct
Sbin/init.d/nfs.client stop Sbin/init.d/nfs.client start
Runscript /etc/cmcluster/MDM/mgroupMDM.control.script
Haltscript /etc/cmcluster/MDM/mgroupMDM.control.script
Runscript /etc/cmcluster/MDM/mdbMDM.control.script
Haltscript /etc/cmcluster/MDM/mdbMDM.control.script
Runscript /etc/cmcluster/MDM/mdsMDM.control.script
Haltscript /etc/cmcluster/MDM/mdsMDM.control.script
Runscript /etc/cmcluster/MDM/mdssMDM.control.script
Runscript /etc/cmcluster/MDM/mdisMDM.control.script
Haltscript /etc/cmcluster/MDM/mdisMDM.control.script
Haltscript /etc/cmcluster/MDM/mdssMDM.control.script
Runscript /etc/cmcluster/MDM/masterMDM.control.script
Haltscript /etc/cmcluster/MDM/masterMDM.control.script
Ssh -X clunode1 -l oramdm
Sidmdm
KITS/ora9208/Disk1/runInstller Specify File Locations
Setup Step MDM218
SAP Master Data Management MDM
MDM = Description = Addresslist =
Connectdata = Server = Dedicated Servicename = MDM
Listener = Descriptionlist = Description = Addresslist =
Sidlistlistener = Sidlist = Siddesc = Globaldbname = MDM
Installation and Configuration Considerations
Create a /home/mdmuser/mdss directory
Global
SAP Master Data Management MDM
Single Serviceguard package configure sap.config
MDMLISTENERNAME=LISTENER
MDMUSER=mdmuser
MDMMONITORINTERVAL=60
MDMPASSWORD= MDMREPOSITORYSPEC=
MDMMDSRELOC=172.16.11.96
MDMMGROUPDEPEND=mdb mds mdis mdss
Cmapplyconf -P /etc/cmcluster/MDM/mdsMDM.config
Servicefailfastenabled no Servicehalttimeout
Vi /etc/cmcluster/MDM/mdsMDM.config Servicename mdsMDMmon
Cmrunpkg mgroupMDM Cmhaltpkg mgroupMDM
Cmrunpkg masterMDM Cmhaltpkg masterMDM
Change Management
System Level Changes
SGeSAP Cluster Administration
SAP Software Changes
Swlist -l bundle T2357BA T2803BA
Upgrading SAP Software
Mixed Clusters
Swlist -l bundle B7885BA T2803BA
Cd /sapmnt/SID Ln -s /sapmnt/SIDexelocal exe
Cd /sapmnt/SID Mv exe exepa
Cd /sapmnt/SID Mkdir exeipf
Cd /sapmnt Ln -s /sapmnt/SID/exepa /sapmnt/SIDexelocal