HP-UX IPSec version A.02.00 Administrator’s Guide
Manufacturing Part Number J4256-90009 June
Legal Notices
Contents
Configuring HP-UX IPSec
Contents
Using Certificates with HP-UX IPSec
Troubleshooting HP-UX IPSec
Viii
HP-UX IPSec and IPFilter
HP-UX IPSec and HP-UX Mobile IPv6
HP-UX IPSec and MC/ServiceGuard
Xii
HP-UX IPSec and Linux
Migrating from Previous Versions of HP-UX IPSec
Glossary
Xvi
Tables
Xviii
Figures
Figure C-2. Example 1 telnet BA
Intended Audience
New and Changed Documentation in This Edition
Xxii
Publishing History
What’s in This Document
HP-UX IPSec and HP-UX Mobile IPv6 Use this chapter to learn
Related Documents
Typographical Conventions
HP Encourages Your Comments
OpenSSL Copyright Notice
Xxvi
Xxvii
Xxviii
HP-UX IPSec Overview
HP-UX IPSec Overview
Introduction
Introduction
Authentication Header AH
Symmetric Key Authentication
Transport Mode
Transport and Tunnel Modes
Host a
AH in Transport Mode
Tunnel Mode
AH in Tunnel Mode
Encapsulating Security Payload ESP
ESP Encryption
Symmetric Key Cryptosystem
ESP header can be used in transport mode or tunnel mode
ESP Encryption in Transport Mode
ESP in Tunnel Mode
IP data or payload e.g., TCP or UDP packet
ESP with Authentication and Encryption
Authenticated ESP
Nested ESP in AH
IPv6
Security Associations SAs and IKE Phases
Internet Key Exchange IKE
Generating Shared Keys Diffie-Hellman
SA Establishment
IKE Primary Authentication
10 Diffie-Hellman Key Generation
Re-using Negotiations
IKE Preshared Key Authentication
IKE Automatic Re-keying
Digital Signatures
Manual Keys
HP-UX IPSec Topologies
Host-to-Host Topology
Host-to-Gateway Topology
Host-to-Host Tunnel Topology
13 Host-to-Host Tunnel Topology
Gateway-to-Gateway Topology
14 IPSec Gateway-to-Gateway Topology
HP-UX IPSec Configuration and Management Features
HP-UX IPSec Configuration and Management Features
HP-UX IPSec Configuration and Management Features Chapter
Installing HP-UX IPSec
Installing HP-UX IPSec
Security Certificate Configuration Utility Requirements
HP-UX IPSec Product Requirements
Disk Requirements
Chapter
Loading the HP-UX IPSec Software
Do not run the HP-UX IPSec product when the system is booted
Setting the HP-UX IPSec Password
Re-establishing the HP-UX IPSec Password
Ipsecadmin -newpasswd
Completing Post-Installation Migration Requirements
Configuring HP-UX IPSec
Configuring HP-UX IPSec
Maximizing Security
Bypass List
Strong End System Model
Ndd -set /dev/ip ipstrongesmodel
General Syntax Information
Argument Delimiters
Line Continuation Character \
Batch File Processing
Batch File Syntax
Ipsecconfig delete
Profile File
Using a Profile File with a Batch File
Profile File Structure
Creating a Customized Profile File
Dynamic Configuration Updates
Dynamic Deletions
Configuration Overview
Start-up options
Configuration Overview
Configuring Host IPSec Policies
Default Host IPSec Policy
Policy Order and Selection
Ipsecconfig add host hostpolicyname
Automatic Priority Increment
Action PASSDISCARDtransformlist -flags flags
Ipaddr/prefix/portnumberservicename
Hostpolicyname
Source and -destination
Ipsecconfig Service Names
Service Port Protocol Name
Ipsecconfig Service Names
Protocolprotocolid
Default ALL
Priorityprioritynumber
Tunneltunnelpolicyname
Action
Transformname/lifetimeseconds/lifetimekbytes
Ipsecconfig Transforms
Transformname
Transform Name Description
Ipsecconfig Transforms
ESP3DES
Ipsecconfig add host Flags
Flags flags
Flag Description
Host IPSec Policy Configuration Examples
Configuring Host IPSec Policies
Configuring Tunnel IPSec Policies
Ipsecconfig add tunnel tunnelpolicyname
Default None
Tunnelpolicyname
Tsource and -tdestination tunneladdress
Ipaddr/prefix/portnumberservicename
Subnet address filter
TCP UDP Icmp ICMPV6 Igmp
Actiontransformlist
Tunnel IPSec Policy Configuration Example
Lifetimeseconds
Lifetimekbytes
Configuring Tunnel IPSec Policies
Configuring IKE Policies
Lifelifetimeseconds -maxqmmqmaxquickmodes
Add ike ikepolicyname
Ikepolicyname
Remoteipaddr/prefix
Authenticationauthenticationtype
Acceptable Values
Group
Hash MD5SHA1
Lifelifetimeseconds
Maxqmmaxquickmodes
Ipsecconfig add IKE Command Examples
Default
Configuring Preshared Keys Using Authentication Records
Configuring IKE ID Information with Preshared Keys
Remote Multi-homed Systems
Ipsecconfig add auth authname
Remoteipaddr/prefix -presharedpresharedkey
Add auth authname
Authname
Ipaddr/prefix
Authentication Record Configuration Examples
However, HP strongly recommends that you configure an
Unique preshared key
Presharedkey
Configuring Preshared Keys Using Authentication Records
Configuring Certificates
Configuring the Bypass List Local IPv4 Addresses
Logical Interfaces
Example
Ipsecconfig add bypass ipaddress
Maximizing Security
Bypass List Example
Node1 Node2
Bypass Configuration Example
Add bypass ipaddress
Ipaddress
Ipsecconfig batch batchfilename -nocommit
Verify Batch File Syntax
Ipsecconfig batch batchfilename
Ipsecconfig show all
Ipsecadmin -status
Ipsecreport -cache
Ipsecreport -all
108
Configuring HP-UX IPSec to Start Automatically
Ipsecconfig add startup -autoboot on
Add startup -autoboot on
110
Baltimore Configuration Files
VeriSign Configuration Files
112
Using Certificates with HP-UX
114
Overview
Security Certificates and Public Key Cryptography
Public Key Distribution
Digital Signatures
IKE Public Key Distribution
Requirements
Using VeriSign Certificates
Overview
VeriSign Certificate Tasks
VeriSign PKI Data Flow
Step
Verifying Prerequisites
Configuring Web Proxy Server Parameters
Ipsecmgr
Export DISPLAY=displaydevice0.0
Registering the Administrator
Requesting and Receiving Certificates
124
Chapter 125
Using Baltimore Certificates
Baltimore Certificate Tasks
Chapter 127
Requesting the Baltimore Certificate
Configuring the Baltimore Certificate
130
Chapter 131
132
Chapter 133
Configuring Authentication Records with IKE IDs
Chapter 135
Determining the IPv4 Address in the SubjectAlternativeName
VeriSign SubjectAlternativeName
Syntax
Add auth authname -remoteipaddr/prefix
Ltypelocalidtype
Lvalue localid
Rtyperemoteidtype
Ridremoteid
CN=commonName,O=organization,C=country,OU=organizationUnit
Examples
Add auth Black -remote 10.10.10.10 -ltype IPV4 \ -lid
Retrieving the Certificate Revocation List CRL
VeriSign
Baltimore
Manually Retrieving a CRL for VeriSign or Baltimore
144
Troubleshooting HP-UX IPSec
146
Authenticate Each Peer’s Identity
Authenticate Identities
IPSec Operation
Establishing Security Associations SAs
Establish ISAKMP/MM SA
Establish IPSec/QM SAs
Internal Processing
Outbound Processing
Outbound Data Query the Kernel Policy Engine
Query the Policy Manager Daemon
Establish an ISAKMP/MM SA
Add IPSec/QM SAs to the Kernel SA Database
Inbound Data AH or ESP Packet
152
Clear Text Packet
Establishing Tunnel Security Associations
Processing Inbound Tunnel Packets
154
Troubleshooting Utilities Overview
Getting General Information
Getting SA Information
Getting Policy Information
Ipsecreport -host configured
Ipsecconfig show gateway
Configured
Ipsecconfig show tunnel
Viewing and Configuring Audit Information
Getting Interface Information
Enabling and Disabling Tracing
Troubleshooting Procedures
Checking Status
Ipsecreport -all -file filename
Chapter 161
Isolating HP-UX IPSec Problems from Upper-layer
Ipsecadmin -traceon tcp udp igmp all
Checking Policy Configuration
Using ipsecpolicy
Examining the Policy Cache and Policy Entries
Configuring HP-UX IPSec Auditing
Audit Level
Ipsecadmin -maxsize maxauditfilesize
Dynamically Setting Audit Parameters
Ipsecadmin -al auditlevel -au auditdirectory
Audit Files and Directory
Configuring Startup Audit Parameters
Ipsecconfig add startup -autoboot Onoff
Viewing Audit Files
Auditlvlauditlevel -auditdirauditdirectory
Where entityname is one of the following names
Filtering Audit File Output by Entity
Recorded by specified entities
Ipsecreport -audit auditfile -entity entityname
Reporting Problems
Output from ipsecadmin -status Output from ipsecreport -all
Chapter 169
Troubleshooting Scenarios
Problem
HP-UX IPSec Incorrectly Passes Packets
Symptoms
Solution
HP-UX IPSec Attempts to Encrypt/Authenticate and Fails
Ipsecreport -mad Ipsecreport -audit file
Additional Information
Ipsecreport -audit /var/adm/ipsec/auditdateinfo.log
ISAKMP/MM SA Negotiation Fails Main Mode
Processing failed, MM negotiation timeout
Chapter 175
Isakmp Primary Authentication with Preshared Key Fails
Isakmp Primary Authentication Fails with Certificates
ISAKMP/MM SA Negotiation Succeeded, IPSec/QM SA
Details
Manual Keys Fail
Invalid Sadbadd
Streams Logging Messages and Additional Audit File Entries
Nettl -ss
Nettl -log e d -e streams
Netfmt /var/adm/nettl.LOG000 mylogoutput
HP-UX Will Not Start ipsecadmin -startFails
Ipsecadmin -auditlvl warning
182
Corrupt or Missing Configuration Database
Ipsecmigrate -s oldconfigfile -d newconfigfile
Using the Skeleton Database File
Autoboot is Not Working Properly
Administrator Cannot Get a Local VeriSign Certificate
186
Security Policy Database Limit Exceeded Kernel
188
HP-UX IPSec and IPFilter
190
IPFilter and IPSec Basics
IPFilter and IPSec
IPFilter Scenario One
192
IPSec UDP Negotiation
IPFilter Scenario Two
194
When Traffic Appears to be Blocked
Scenario Three
Allowing Protocol 50 and Protocol 51 Traffic
Packet with Encrypted TCP Data
Packet with IPSec-Encrypted TCP Data
Protocol 51 traffic, then IPSec traffic will not get through
Scenario Four
IPSec Gateways
HP-UX IPSec and HP-UX Mobile
200
Mobile Node and Home Address
Care-of Address
Correspondent Nodes
Home Agent
Home Agents and Basic Operation
Mobile IPv6 Basic Operation Correspondent Node to Mobile
Node
Route Optimization
Mobile IPv6 Basic Operation Mobile Node to Correspondent
Mobile IPv6 Route Optimization
Securing Mobile IPv6 with HP-UX IPSec
Acknowledgement messages
Prefix Discovery Messages
Binding Messages Between the Home Agent and Mobile Node
Chapter 205
Payload Packets Routed Through the Home Agent
Chapter 207
Understanding Gateway IPSec Policies
Gateway IPSec Policies
Using Manual Keys
Configuration Procedure
Using the HP-UX Strong Random Number Generator
Troubleshooting Manual Key Problems
210
Syntax
Inand -outmanualkeysaspecification
Sourcehomeagentaddr
Actiontransformname
Chapter 213
2B, 2C Home Agent Mobile Node
Mobile IPv6 Home Test Init and Home Test Packets
Return Routability Messages Configuring
Gateway IPSec Policy for Home Agent
Correspondent Node Segments
216
Tunnel rrtunnelname -action Forward -flags MIPV6
Tunnelrrtunnelname
218
Chapter 219
220
Chapter 221
222
Protocol ALL -priority prioritynumber
Action Forward -flags MIPV6
224
Tunnelpayloadtunnelname
Ipsecconfig add tunnel payloadtunnelname
Mobile IPv6 Configuration Example
Binding Messages
Return Routability Messages
3ffe83fffef71111
Optional Prefix Discovery Messages
Gateway IPSec Policy for Home Agent Mobile Node Segments
Return Routability Tunnel IPSec Policy
Optional Payload Messages Routed Through the Home Agent
Payload Gateway IPSec Policies
Add gateway mn2222payloadtocn \
Protocol ALL -pri 300 -action Forward -flags MIPV6
Payload Tunnel IPSec Policy
Batch File Template
232
Chapter 233
234
HP-UX IPSec
236
MC/ServiceGuard Cluster
Using HP-UX IPSec with MC/ServiceGuard
Package Clients Not Using HP-UX IPSec A.01.07 or Later
Chapter 239
MC/ServiceGuard Heartbeat Requirement Recommendation
Configuration Steps
242
Configuring a Common HP-UX IPSec Password
Configuring HP-UX Host IPSec Policies for MC/ServiceGuard
Determining MC/ServiceGuard Cluster Information
Configuring Host IPSec Policies for Package Addresses
Private Dedicated Heartbeat Networks
10.0.0.0/8
Cluster Node IPSec Policies for Quorum Server
1238
Address or Server Wildcard
Cluster Node IPSec Policies for Remote Command Execution
Quorum Server IPSec Policies
Server Address Address or Wildcard
Source IP Destination Protocol Address IP Address Port
Address or Command Wildcard Client address
514
Configuring Host IPSec Policies for ServiceGuard Manager
Command Address Client address Or wildcard
Cluster Node Host IPSec Policies for ServiceGuard Manager
ServiceGuard Manager Host IPSec Policies
Source IP Destination Protoco Address IP Address Port
Cluster Node Host IPSec Policies for COM
COM System Host IPSec Policies
Summary MC/ServiceGuard Port Numbers Protocols
MC/ServiceGuard Port Numbers and Protocols
Port Protocols Service
5303
Chapter 255
256
Configuring HP-UX IPSec IKE policies
Cluster IKE policies
Cluster Client IKE policies
Configuring Authentication Records for Preshared Keys
Preshared Key Configuration on Cluster Nodes
Preshared Key Configuration on Client Nodes
Preshared Keys Configuration on Cluster Nodes
Preshared Keys Configuration on Client1
Preshared Keys Configuration on Client2
Remote IP Address Key
260
Configuring Authentication Records for Certificates
Authentication Records and IKE ID Information
Cluster Clients
Chapter 263
IKE ID Configuration on Cluster Nodes
IKE ID Configuration on Client1 and Client2
Verifying and Testing the HP-UX IPSec Configuration
Ipsecpolicy -sa 15.1.1.1 -da
Configuring HP-UX IPSec Start-up Options
Distributing HP-UX IPSec Configuration Files
268
Configuring MC/ServiceGuard
Cluster Configuration
Package Configuration
Package Control Script
Monitor Script Polling Interval
Starting HP-UX IPSec MC/ServiceGuard
Adding a Node to a Running Cluster
272
HP-UX IPSec and Linux
274
Chapter 275
Configuration Example
Product Specifications
Appendix a
IPSec RFCs
RFC 3776 Mandatory Support
RFC Number RFC Title
280
Product Restrictions
Isakmp Limitations
IPv4 Icmp Messages
IPv6 Icmp Messages
Authentication Algorithms
HP-UX IPSec Transforms
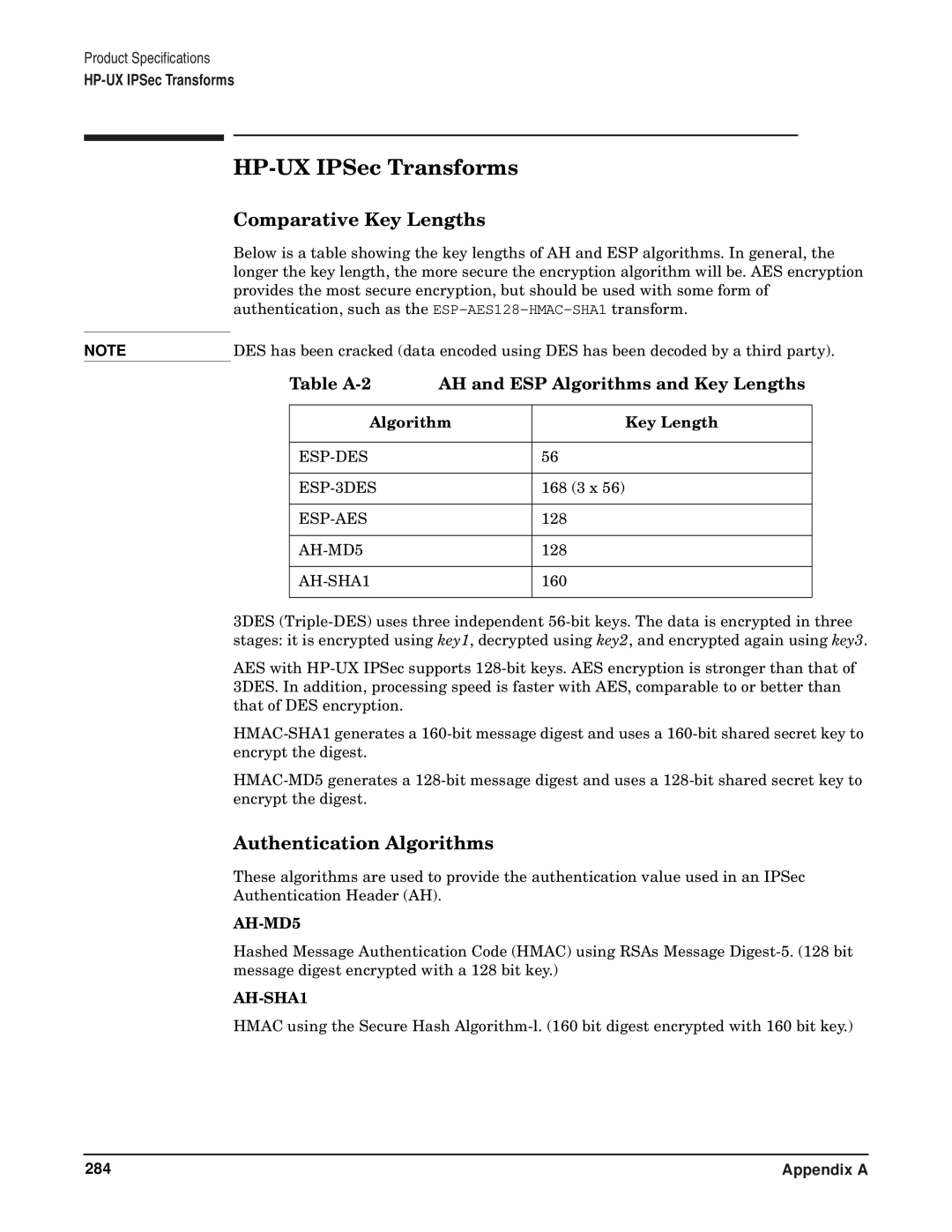
Comparative Key Lengths
Algorithm Key Length
Encryption Algorithms
ESP-DES
Transform Lifetime Negotiation
Migrating from Previous Versions
Appendix B
Pre-Installation Migration Instructions
MD5 Version Compatibility
Migrating from Versions Prior to A.01.03
Ipsecreport -auditauditfilename -fileoutputfilename
Not Re-using Configuration Files
Post-Installation Migration Instructions
Configuration File
Usr/sbin/ipsecmigrate -s configfile -d newconfigfile
Ipsecadmin -start
292
HP-UX IPSec Configuration Examples
Appendix C
Example 1 telnet Between Two Systems
Apple Configuration
Figure C-1 Example 1 telnet AB
Banana Configuration
Authentication Record with Preshared Key
IKE Policy
298
Example 2 Authenticated ESP with Exceptions
Figure C-3 Example 2 Network IPSec Policy with Exceptions
Carrot Configuration
Ipsecconfig Batch File Entries
Authentication Record
Blue Configuration
Example 3 Host to Gateway
Host IPSec Policy
Priority 100 -action Pass -tunnel torouter
Tunnel IPSec Policy
Add auth torouter -rem 16.6.6.6 -psk Hello
Dog Configuration
Cat Configuration
Example 4 Manual Keys
Glossary
Asymmetric keys, public/private keys
Diffie-Hellman
Encapsulating Security Payload ESP
Glossary 307
Preshared Key
Numerics
309
310
311
312
313
314