Hardware Maintenance Manual Types 6826, 8317, 8318,
Page
Hardware Maintenance Manual Types 6826, 8317, 8318,
Second Edition December
Contents
Iv Hardware Maintenance Manual
About this manual
Important Safety Information
Hardware Maintenance Manual
General Checkout
Set Power-On Self-Test to Enhanced
Hardware Maintenance Manual
General information
Features
Expansion
Specifications
Available options
IBM Setup Utility program
Diagnostics
First IBM Setup Utility screen is shown here
Create Recovery/Repair Diskette Disk to Disk Solution Only
Product Recovery Program menu
Running diagnostics tests
Diagnostics
Diagnostics program download
Navigating through the diagnostics programs
Fixed disk advanced test Fdat
Test results
Other Test Features
Quick and Full erase hard drive
Viewing the test log
Installing external options
Installing Options
Obtaining device drivers
Locating connectors on the rear of the computer
Removing the cover
Removing the bezel
Locating components
Accessing system board components and drives
Identifying parts on the system board
Installing memory
What to do next
Installing PCI adapters
Installing a drive in the disk drive tray
Replacing the hard disk drive
Connecting a diskette drive
Installing a cable lock
Changing the battery
Replacing the cover and connecting the cables
Erasing a lost or forgotten password clearing Cmos
Installing Options
Hardware Maintenance Manual
Replacing a microprocessor
Removing the retention bar and PCI riser card
System board
Power supply
FRU Removals
Hardware Maintenance Manual
Check/Verify FRU/Action
Hard disk drive boot error
Power Supply Errors
Error FRU/Action
Check the power-on switch for continuity Power-on Switch
Diagnostic error codes
Hardware Maintenance Manual
Symptom-to-FRU Index
Hardware Maintenance Manual
005-025-XXX Video card, if installed
005-00X-XXX Video card, if installed
005-010-XXX Video card, if installed 005-011-XXX
005-024-XXX Video card, if installed
005-198-XXX If a component is called out, make sure
005-199-XXX Go to the ″Undetermined problems″
005-2XX-XXX Video card, if installed 005-3XX-XXX
006-199-XXX Go to the ″Undetermined problems″
011-001-XXX Remove external serial device, if
Diagnostic Error Code FRU/Action 011-000-XXX No action
011-027-XXX Run Setup, enable port
011-199-XXX Go to the ″Undetermined problems″
Hardware Maintenance Manual
015-002-XXX Remove USB devices and re-test
015-034-XXX Reboot the system
015-040-XXX Run setup and check for conflicts
015-199-XXX Go to the ″Undetermined problems″
018-197-XXX Make sure the component that is called
018-199-XXX Go to the ″Undetermined problems″
018-195-XXX PCI card
018-196-XXX Press F3 to review the log file
025-02X-XXX IDE signal cable 025-03X-XXX
020-199-XXX Go to the ″Undetermined problems″
025-00X-XXX IDE signal cable 025-01X-XXX
025-027-XXX IDE signal cable
030-03X-XXX Scsi signal cable 030-04X-XXX
Diagnostic Error Code FRU/Action 025-199-XXX
030-00X-XXX Scsi signal cable 030-01X-XXX
030-027-XXX Scsi signal cable
035-195-XXX Information
035-199-XXX Go to the ″Undetermined problems″
071-00X-XXX Run Setup 071-01X-XXX
071-04X-XXX Run Setup
071-25X-XXX Speakers
071-199-XXX Go to the ″Undetermined problems″
080-199-XXX Go to the ″Undetermined problems″
071-198-XXX If a component is called out, make sure
086-035-XXX Mouse
Diagnostic Error Code FRU/Action 086-032-XXX Mouse
086-040-XXX Run Setup
086-199-XXX Go to the ″Undetermined problems″
170-0XX-XXX Flash system
170-199-XXX Go to the ″Undetermined problems″
170-250-XXX Power supply 170-251-XXX
170-000-XXX No action
175-250-XXX Check fans 175-251-XXX
175-199-XXX Go to the ″Undetermined problems″
185-278-XXX Assure Asset Security Enabled
175-198-XXX If a component is called out, make sure
Hi-Capacity Cartridge Drive error
Diagnostic Error Code FRU/Action
CD-ROM Drive error
Check power supply voltages
2 1st 64K RAM parity test failed
Beep symptoms
Beeps Description
3-1 1st 64K RAM test failed
Hardware Maintenance Manual
Symptom/Error FRU/Action
No-beep symptoms
See Undetermined problems on
Post error codes
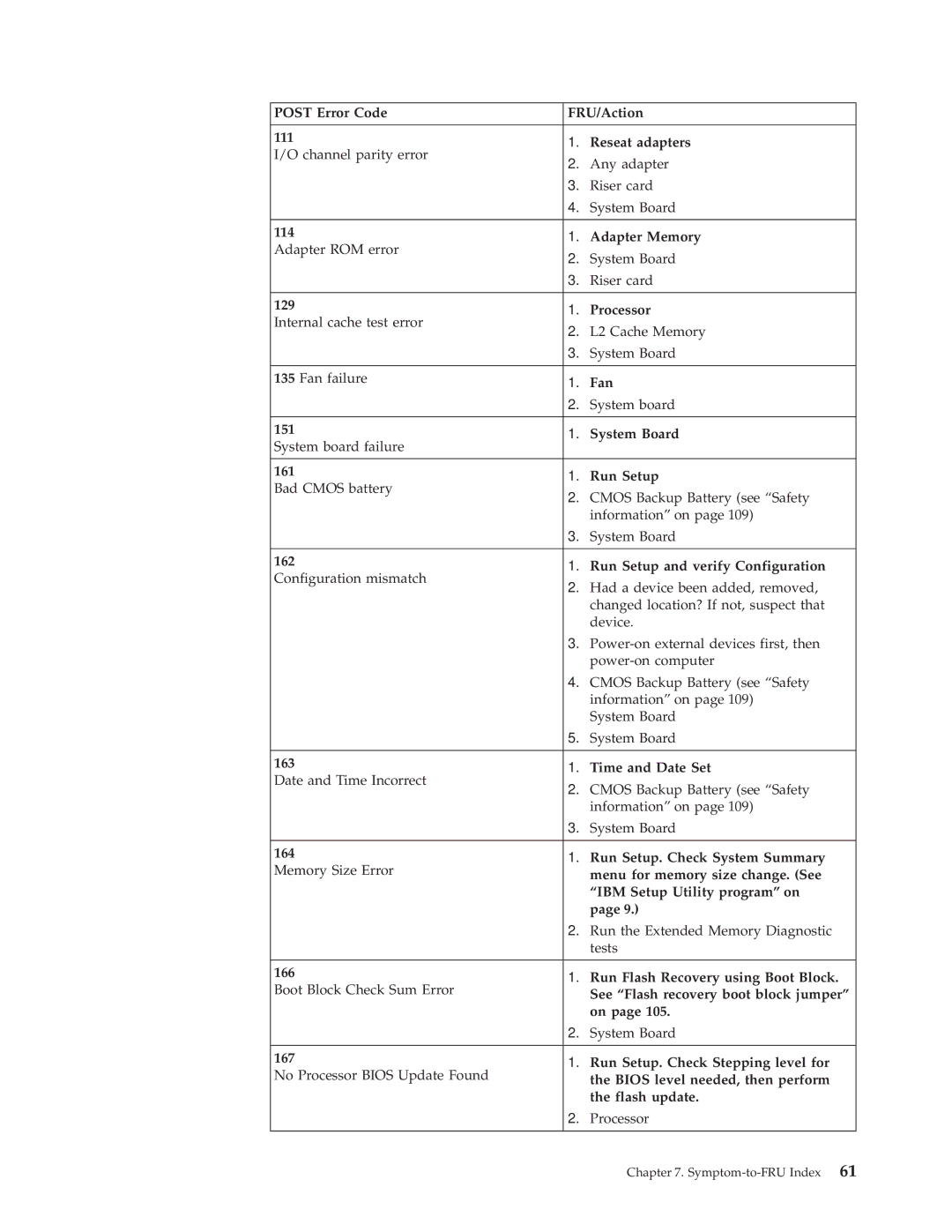
164 Run Setup. Check System Summary
Post Error Code FRU/Action 111 Reseat adapters
161 Run Setup
162 Run Setup and verify Configuration
Not listed above
Configuration settings
Post Error Code FRU/Action 303 Mouse
Video Adapter if installed
604 Run Setup and verify diskette
9XX
1406 Run Enhanced Diagnostics
Post Error Code FRU/Action 1207 Communications Cable
1404 Run Enhanced Diagnostics
1405 Run Enhanced Diagnostics
209X Diskette Drive
Post Error Code FRU/Action
180X Run Setup and verify PCI/ISA
1962 Press F1 to repeat boot sequence
Symptom-to-FRU Index
Hardware Maintenance Manual
Symptom-to-FRU Index
Hardware Maintenance Manual
Dbcs Japanese Display Adapter/A
185XXXX
20104 Memory Module DRAM, Vram
Post Error Code FRU/Action 200XX Image Adapter/A
Rotary Switch Circuit Board
20101 to Printer/Scanner Option
Symptom-to-FRU Index
Hardware Maintenance Manual
Miscellaneous error messages
Check startup sequence
See Power Supply Errors on
External Device Self-Test OK?
Undetermined problems
Hardware Maintenance Manual
Item # Machine Type
Parts listing
46M 61M CHJ CJJ CKJ CLJ
41M 42M CAJ CBJ CCJ CDJ CEJ CFJ CGJ 41J 42J 23J
Recovery CDs Win XP- Home
Recovery CDs Win2K
Recovery CDs Win XP- Pro
34J 35J 36J 37J 38J 17J CAJ CBJ CCJ CDJ CEJ CFJ CGJ
Keyboards Standard PS/2 Black
Keyboards RAK III Lite
Power Cords
FRU# CRU?
Keyboards PS/2 Fullwidth ID Black
Power Cords
Line Cord model 22G 71G 32G
Recovery CDs Win XP- Pro
Keyboards PS/2 Fullwidth ID Black
Line Cord model 31G 31A 31M
74G CTO CAU CBU CCU CDU 32M 41S 41P 41D
23V 23H 24C 24B 24H CTO CAU CBU CCU CDU CEU
Recovery CDs Win2K
Recovery CDs Win XP- Home
Recovery CDs Win XP- Pro
CFU CGU
FRU# CRU?
Line Cord model 23A 41A 1AA 47A 64A
Hardware Maintenance Manual
Passwords
Security features
Alert on LAN
Bios levels
Vital product data
Desktop Management Interface DMI
Flash recovery boot block jumper
Flash BIOS/VPD update procedure
Hardware Maintenance Manual
Automatic Hardware Power Management features
Power management
Automatic configuration and power interface Acpi Bios
Advanced Power Management
Hardware Maintenance Manual
General safety
Safety information
Electrical safety
Safety inspection guide
Handling electrostatic discharge-sensitive devices
Grounding requirements
Safety notices multi-lingual translations
To Connect To Disconnect
Do not
Related service information
Para Conectar Para Desconectar
Perigo
Precaución
Fonte de energia elétrica
Related service information
Hardware Maintenance Manual
Related service information
Hardware Maintenance Manual
Related service information
Hardware Maintenance Manual
Related service information
Hardware Maintenance Manual
Connexion Déconnexion
Faites-vous aider pour soulever ce produit
Courant
Kabel anschlieβen Kabel lösen
Vorsicht
≥18 kg ≥32 kg ≥55 kg
Achtung
Per collegare Per scollegare
Pericolo
≥18 kg ≥32 kg ≥55 kg
Siano scollegati dalla sorgente di alimentazione
Hardware Maintenance Manual
Related service information
Hardware Maintenance Manual
Para la conexin Para la desconexiín
Peligro
Tome medidas de seguridad al levantar el producto
Precaución
Send us your comments
Problem determination tips
IBM
Trademarks
Page
Part Number 59P7580