537EX Chipset
Developer’s Manual
Intel Confidential
Contents
Figures
Tables
Revision History
Date Revision Description
001 Initial release
Introduction
Controllerless Modem Driver Overview
Windows 95 and Windows
Unimodem
V.90/V.92 and V.34 Data Modes
Tapi
Intelsdb.VXD
Modem Connection Overview
DCE-to-DCE Data Rates for Each Mode
AT Commands Overview
DTE-to-DCE Data Rates for Each Mode
DCE-to-ISP Data Rates for V.90 Mode
DTE-Modem Data Rate Response Codes
Sending Commands
Delayed Call
Numeric Text
Dial Modifier
Command Function
AT Escape Sequences
Dialing digits
Data Mode Command Summary
Command Function Default Range Reported By &Vn
Intel Confidential
Intel Confidential
Intel Confidential
+ESR
+EB
+ESA
+ETBM
44/V.42/V.42 bis MNP Command Summary
Processes flow control characters and passes to local
Fax Identity Command Summary
Fax Class 1 Command Summary
IS-101 Voice Command Summary
Voice DTE→DCE Character Pairs
Response Hex Code Function
DEL
Voice DTE →DCE Character Pairs
Voice DTE←DCE Character Pairs
ESC
Register Summary
Register Function Default Range Units Reported by &Vn
Dial Modifiers
Ascii
Register Function Default Range Units
Using AT Commands to Access the S-Registers Sn?, Sn=x, ?
Modem Responses and Command Echo En, Vn, Xn, Wn, Qn
Modem Setup Host Modem Response Command
Disable Enable
Data Reporting Wn Mapping
DTE
Resets and then configures the modem to Nvram user profile
AT Commands Product Information
Establishing a Modem Connection A, D, DS = n, S0
Product Identification Information
Online Command Mode Escape Codes, On
Hanging Up Hn, S10, Zn, &D2
Modem-to-Modem Connection Data Rates
Intel Confidential
Modem-on-Hold Incoming Voice Call in Data Mode
Modem-on-Hold Initiating a Voice Call in Data Mode
Intel Confidential
Supported Modulation Types
Carrier Description
Diagnostic Testing S18, &Tn
Local Analog Loopback AT&T1
Local Analog Loopback With Self-Test AT&T8
Local Modem or Test Modem
AT Escape Sequences
Time-Independent Escape Sequence
Licensing Requirements for Hayes Escape Sequence
Example
Data Mode Command Descriptions
Command Default Description
Hayes* Escape Sequence
Echo disabled
Previously stored in the Nvram with the AT&Zn=x command
Host in either online or off-line command mode
Echo enabled
ATI2
DTE
Sn=x
Numeric or verbose form
Command
Modem dials a telephone number touch tone dialing
Numeric form
Resets the modem and recalls user profile
Disconnecting
Subsequent commands to be ignored
DCD or Rlsd signal
Stored Profile
AT&V0
Active Profile
Telephone Numbers
Select profile
S-register configurations into the Nvram user profile ‘n’
Command to see the stored telephone number
= 0-9 a B C D # * T P R W @
Command Default
Indication Definition
+EB
Secondary channel operation, and vice versa
CRC generation and checking disabled
Nrzi encoding and decoding disabled
12/V.34
+ESR
+ETBM
+IFC
+GMR
+GSN
+ILRR=m
= carrier,carrier,…carrier
+MS command description
+MA? will display a list of enabled alternative modulations
If +MS = ,0,, no alternative modulations will be available
BELL212
Carrier Description
BELL103
+MS=m See ‘m’
Value Description
+PHSW=
+PMHF
+PMHR
Enable Short Phase
Conjunction with the +PSS command
Enable Short Phase 1 and Short Phase
Disable short Phase 1 and Short Phase
Mode Features
Operating Modes
Resulting +ES Connection Types
44/V.42/V.42 bis and MNP Data Modem Command Descriptions
+ES Settings Answer Modem
+ES=1, 0 +ES=4, 4 +ES=3, 0 +ES=3, 2
\Bn
\Kn
+DS=m
+DR=m
Direction
Max string
3768
+EFCS=m
+ER=m
Display messages when +ER =
Decimal value and the format is as follows
+ER Lapm
Non-error control operation
Setting is ignored if origrqst=6
Control during non-error control operation
+ES=m
Fax Identity Command Descriptions
Fax Identity Commands
Fax Class 1 Commands
+FMFR?/+FMI
Mod Selection Table
Value Modulation Speed bps
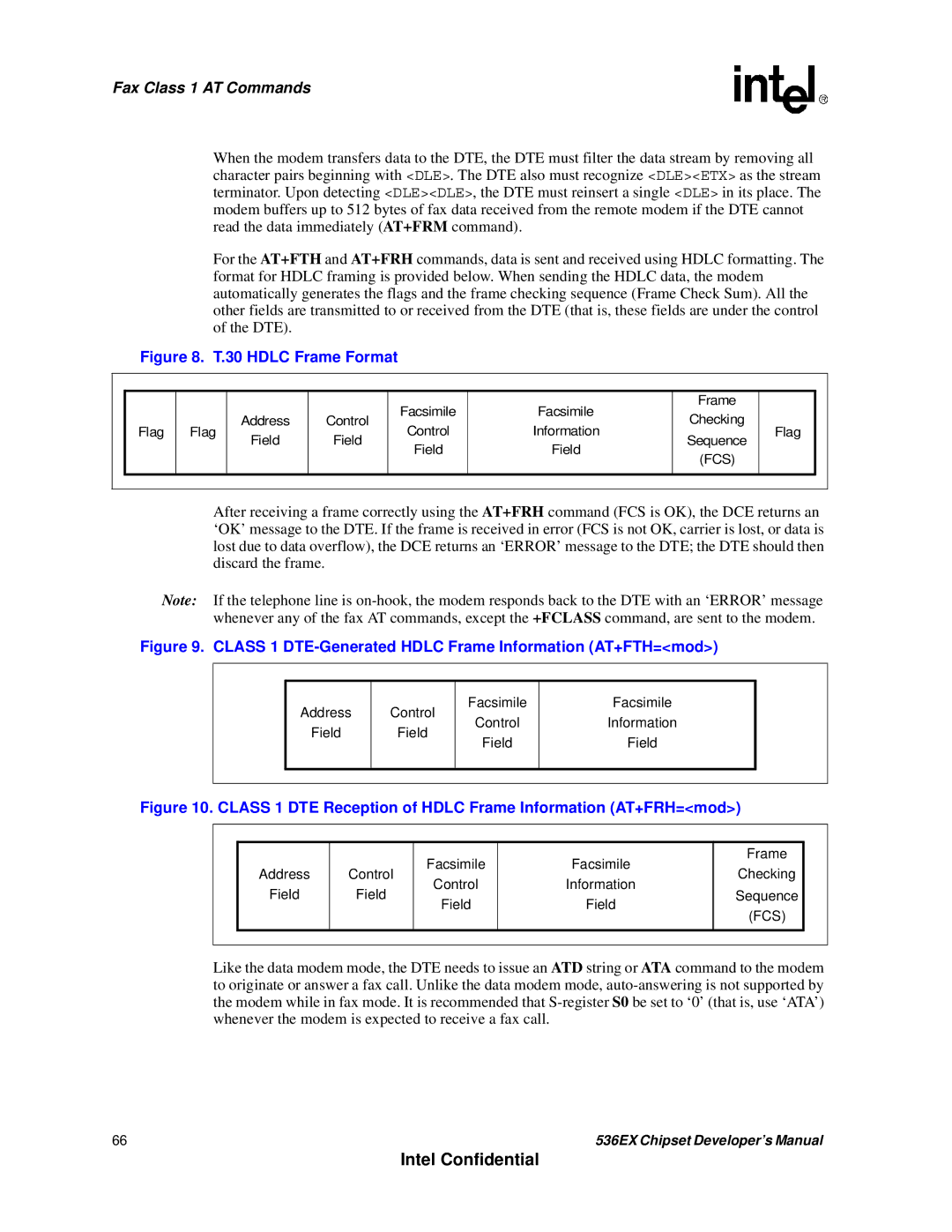
30 Hdlc Frame Format
Class 1 DTE-Generated Hdlc Frame Information AT+FTH=mod
Fax Mode Command Descriptions
+FCLASS?
+FCLASS
+FRH=m
+FRS=m
+FTH=m
IS-101 Voice Mode AT Commands
Voice Mode Command Descriptions
Dtmf Detection Reporting
Relay Control
+FLO=m
Enable report Function
+VDR=m See ‘m’
Event Description
Defaults = ‘C’, BB860980, BFE63883, BB863EE0
Caller ID report Command Reserved Distinctive ringing All
+VEM=m See ‘m’
EIGHT-DIGIT HEX Code B B 8 6 3 E E
EX Value BIT Value Event
HEX Digit Location
Local telephone, or speaker
128 Nominal transmit level
+VIP
Preassigned Voice I/O Labels
Label
+VLS=m
Voice I/O Primitive Codes
Relay/Playback Control
Primitive Code Description
+VRX
+VSD=m See ‘m’
+VSM=m
+VSM=? command to obtain supported sampling rates
141 AD3 3-bit Adaptive differential pulse code modulation
Range 4800, 7200, 8000, and 11025 samples/second
Hard Disk
Cml
Serial
Compression
100
Factory default is ‘0’
100 Default value 1 second
Range 5-255 units of 0.01 seconds
Specified by +VTD=m
Dual tones may be sent using the following format
+VTS=m None
This sends a 500 ms period of silence
Command Default Description
Register Command Descriptions
S10
Range Seconds Default 0 seconds
Escape sequences
S16
S25
S21
S22 118
S30
Sleep mode is disabled by setting S33 to ‘0’
Modem exits sleep mode whenever the host reads or writes to
Modem or when a ring signal is detected
Inactive state when
Caller ID Tags for Formatted Reporting
Tag Description
Ring
Uart Emulation in the Controllerless Modem
Uart Emulation in Intelsdb.VxD
Uart
THR
RBR
Parallel Host Interface Uart Register Bit Assignments
Uart Register Definitions
Scratch Register SCR
Modem Status Register MSR
Line Status Register LSR
Bit Framing error
OE Overrun Error-Not supported
Stack
Modem Control Register MCR
IER Interrupt Enable register
Procedure is as follows
Line Control Register LCR
Fifo Control Register FCR
Bit
Interrupt Identity Register IIR
Interrupt Control Functions
ID1 ID0
Transmitter Holding Register THR
Interrupt Enable Register IER
ID bit 2 for Fifo mode
Dlab =
Programmable Data Rates
Receiver Buffer Register RBR
Divisor Latch Registers DLM and DLL
Data Rate Divisor Number Divisor Latch Hex
16C550A Uart Fifo Operation
Fifo Interrupt Mode Operation
Fifo Polled Mode Operation
102
536EX Chipset Developer’s Manual 103