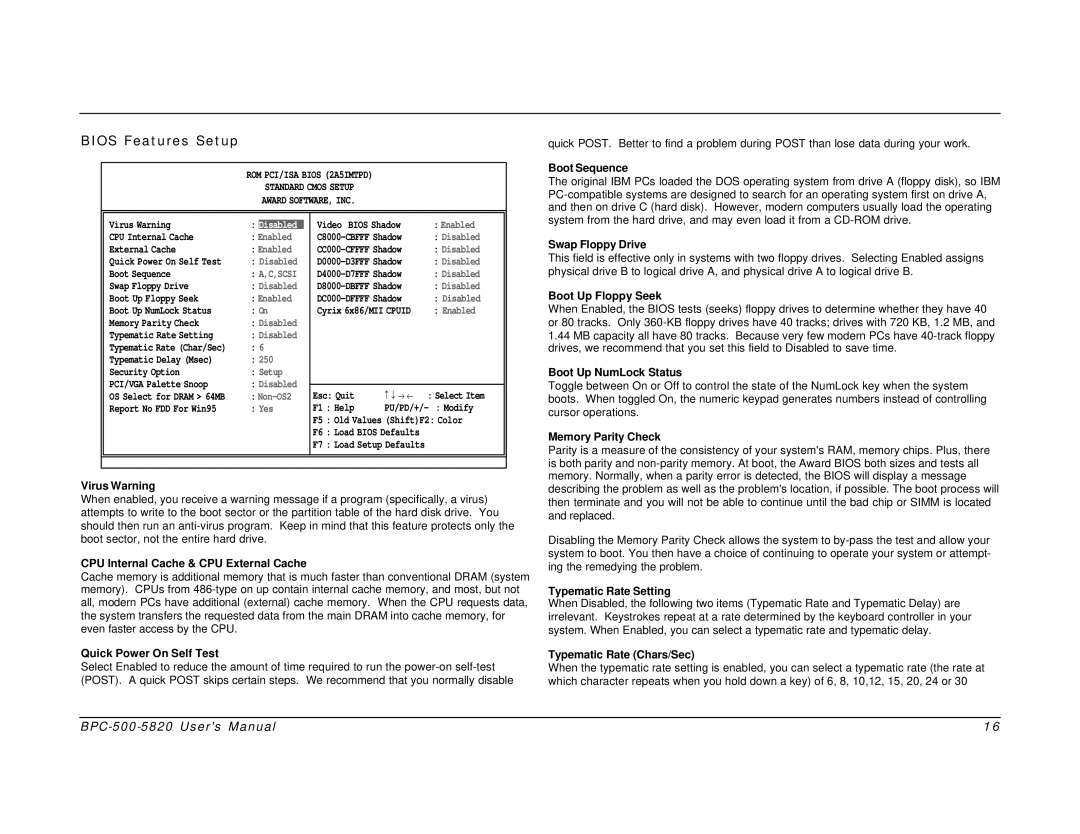
BIOS Features Setup
ROM PCI/ISA BIOS (2A5IMTPD)
STANDARD CMOS SETUP
AWARD SOFTWARE, INC.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Virus Warning | : | Disabled |
| Video BIOS Shadow | : Enabled | |
CPU Internal Cache | : Enabled |
| : Disabled | |||
External Cache | : Enabled |
| : Disabled | |||
Quick Power On Self Test | : Disabled |
| : Disabled | |||
Boot Sequence | : A,C,SCSI |
| : Disabled | |||
Swap Floppy Drive | : Disabled |
| : Disabled | |||
Boot Up Floppy Seek | : Enabled |
| : Disabled | |||
Boot Up NumLock Status | : On |
| Cyrix 6x86/MII CPUID | : Enabled | ||
Memory Parity Check | : Disabled |
|
|
|
| |
Typematic Rate Setting | : Disabled |
|
|
|
| |
Typematic Rate (Char/Sec) | : 6 |
|
|
|
| |
Typematic Delay (Msec) | : 250 |
|
|
|
| |
Security Option | : Setup |
|
|
|
| |
PCI/VGA Palette Snoop | : Disabled |
|
|
|
| |
| Esc: Quit |
| : Select Item | |||
OS Select for DRAM > 64MB | : |
| − ↓ → ← | |||
Report No FDD For Win95 | : Yes |
| F1 : Help | |||
|
|
|
| F5 : Old Values (Shift)F2: Color | ||
|
|
|
| F6 : Load BIOS Defaults |
| |
|
|
|
| F7 : Load Setup Defaults |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Virus Warning
When enabled, you receive a warning message if a program (specifically, a virus) attempts to write to the boot sector or the partition table of the hard disk drive. You should then run an
CPU Internal Cache & CPU External Cache
Cache memory is additional memory that is much faster than conventional DRAM (system memory). CPUs from
Quick Power On Self Test
Select Enabled to reduce the amount of time required to run the
quick POST. Better to find a problem during POST than lose data during your work.
Boot Sequence
The original IBM PCs loaded the DOS operating system from drive A (floppy disk), so IBM
Swap Floppy Drive
This field is effective only in systems with two floppy drives. Selecting Enabled assigns physical drive B to logical drive A, and physical drive A to logical drive B.
Boot Up Floppy Seek
When Enabled, the BIOS tests (seeks) floppy drives to determine whether they have 40 or 80 tracks. Only
1.44MB capacity all have 80 tracks. Because very few modern PCs have
Boot Up NumLock Status
Toggle between On or Off to control the state of the NumLock key when the system boots. When toggled On, the numeric keypad generates numbers instead of controlling cursor operations.
Memory Parity Check
Parity is a measure of the consistency of your system's RAM, memory chips. Plus, there is both parity and
Disabling the Memory Parity Check allows the system to
Typematic Rate Setting
When Disabled, the following two items (Typematic Rate and Typematic Delay) are irrelevant. Keystrokes repeat at a rate determined by the keyboard controller in your system. When Enabled, you can select a typematic rate and typematic delay.
Typematic Rate (Chars/Sec)
When the typematic rate setting is enabled, you can select a typematic rate (the rate at which character repeats when you hold down a key) of 6, 8, 10,12, 15, 20, 24 or 30
16 |