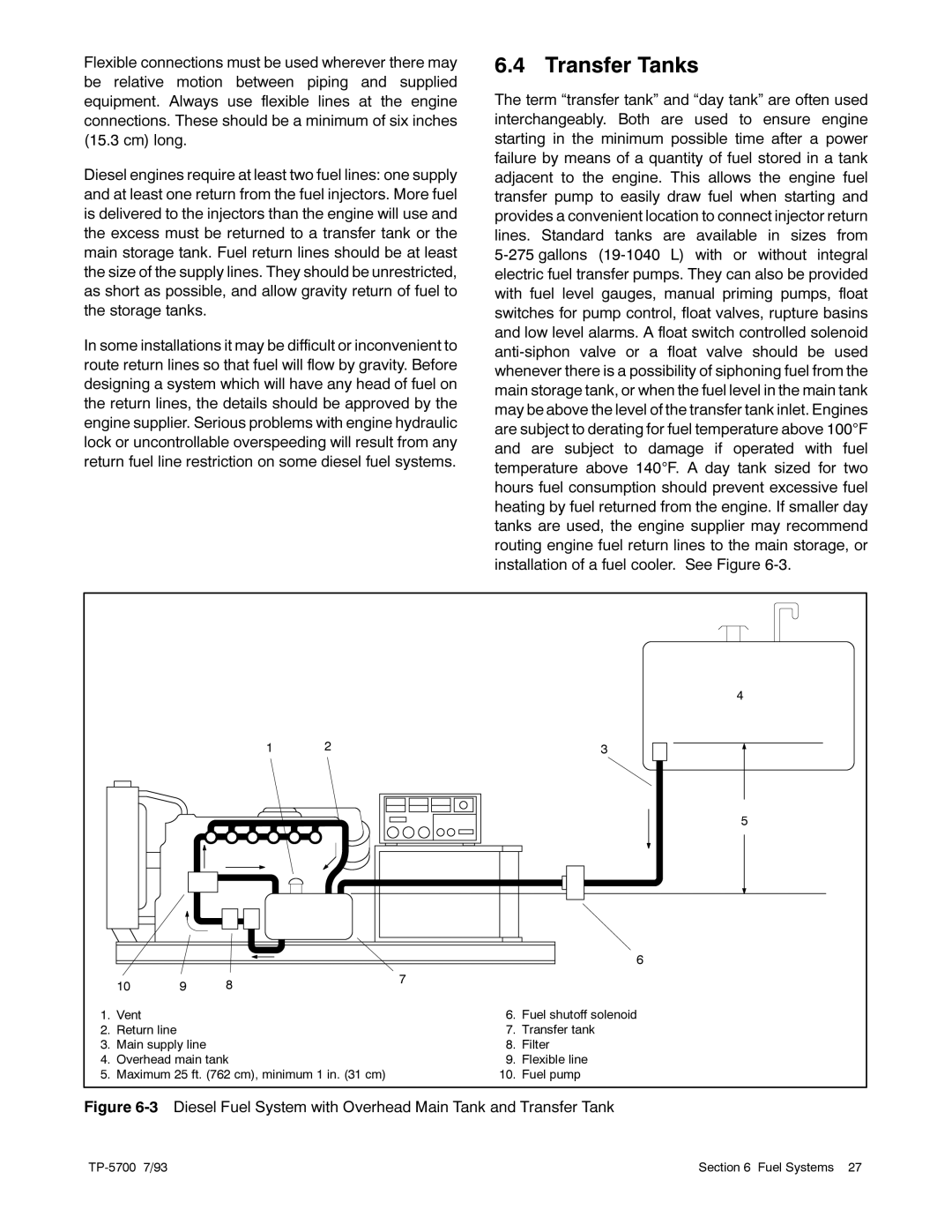
20--2800 kW specifications
The Kohler 20-2800 kW generator series is renowned for its exceptional performance and reliability, making it a prime choice for various industrial and commercial applications. Designed for continuous and backup power generation, these generators are capable of providing robust energy solutions for facilities that demand high capacity and efficiency.One of the standout features of the Kohler 20-2800 kW series is its advanced technology integration. Kohler utilizes the latest in digital control systems, ensuring precise monitoring and management of generator functions. The generator's control panel provides real-time data on power output, fuel consumption, and operating conditions, allowing operators to make informed decisions quickly.
In terms of fuel efficiency, the Kohler generators are engineered to minimize operational costs while maximizing performance. The series includes options for both diesel and natural gas, offering flexibility depending on user requirements and availability. The efficient fuel consumption not only supports cost savings but also aligns with environmental standards, reducing emissions during operation.
Durability and reliability are key characteristics of this generator series. Kohler buildings are constructed using high-quality materials and components that withstand harsh environmental conditions. System redundancy features and robust cooling systems ensure that the generators can operate continuously without failure, making them ideal for critical power needs.
The Kohler 20-2800 kW series also includes noise-reducing technology, making them suitable for installations in noise-sensitive environments. With options for acoustic enclosures, these generators comply with local noise regulations while delivering powerful performance.
Safety features are integrated into the generator design, including automatic shutdown systems for over-speed, low oil pressure, and high water temperature, ensuring that the equipment operates safely during emergencies.
The modular design of the Kohler 20-2800 kW allows for easy installation and maintenance. Access points for service and diagnostics are strategically placed for convenience, reducing downtime and improving efficiency in upkeep.
Overall, the Kohler 20-2800 kW generator series stands out as a dependable powerhouse, combining advanced technology, fuel efficiency, durability, and safety features to meet the demands of various industries. Whether for data centers, manufacturing facilities, or large commercial buildings, Kohler's commitment to quality and innovation makes these generators an exemplary choice for reliable power generation.