AAppendix: How Infrared Thermometry Works
Blackbody
When thermal radiation falls on an object, part of the energy is transmitted through the object, part is reflected and part is absorbed. A blackbody is defined as an ideal object that absorbs all the radiation incident upon it. The best example of a real object that acts like a blackbody is a small hole drilled deep into a large opaque cavity. Thermal radiation entering the cavity is internally reflected and has little chance of escaping the cavity before it is fully absorbed.
Emissivity is defined as the ratio of energy radiated by an object to that of the energy radiated by a blackbody. By definition, the emissivity of a blackbody is 1. Most objects are considered gray objects with an emissivity between 0 and 1. Various emissivities for common materials are shown in Appendix B.
Spectral Distribution
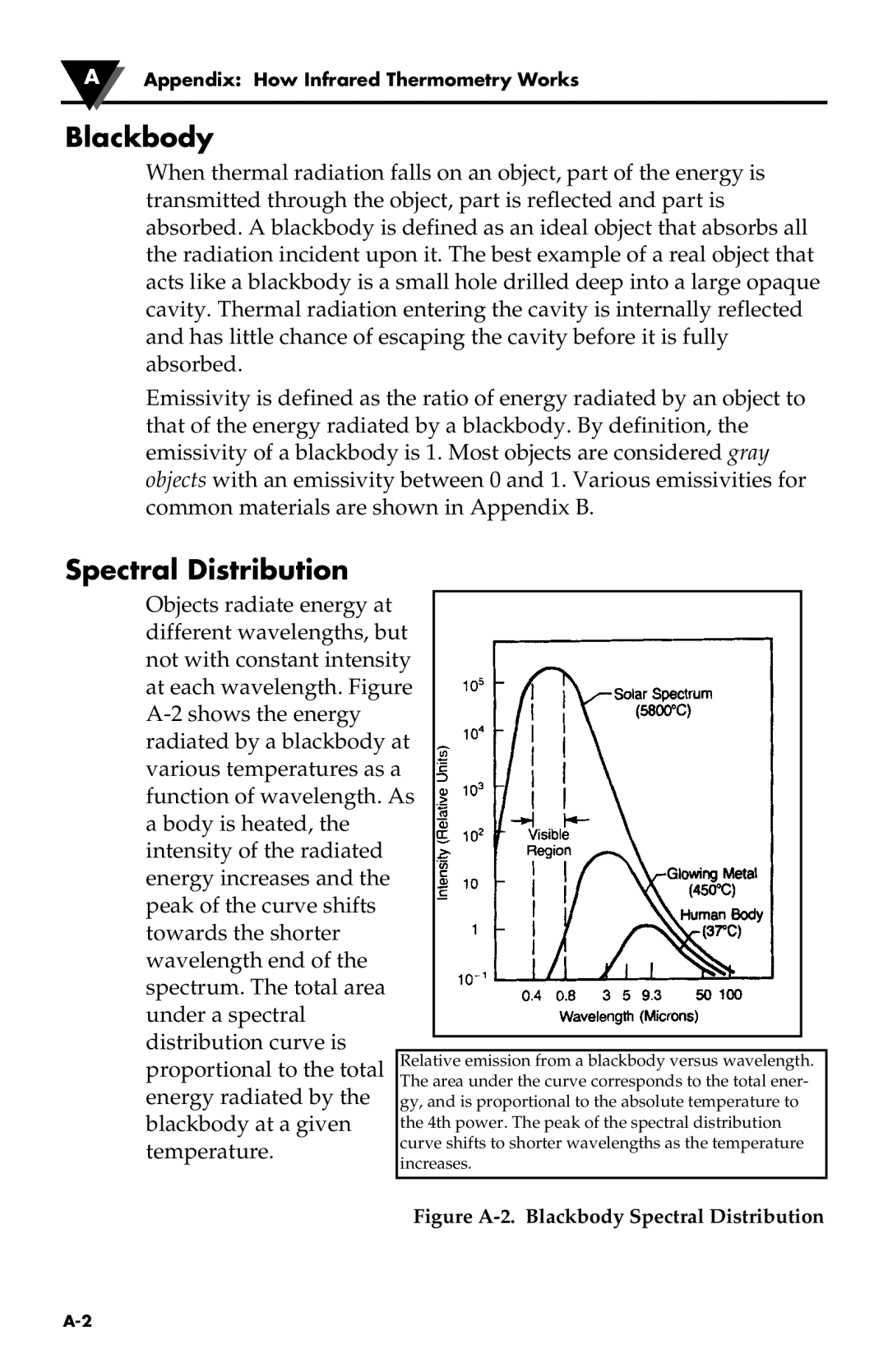
Objects radiate energy at different wavelengths, but not with constant intensity at each wavelength. Figure