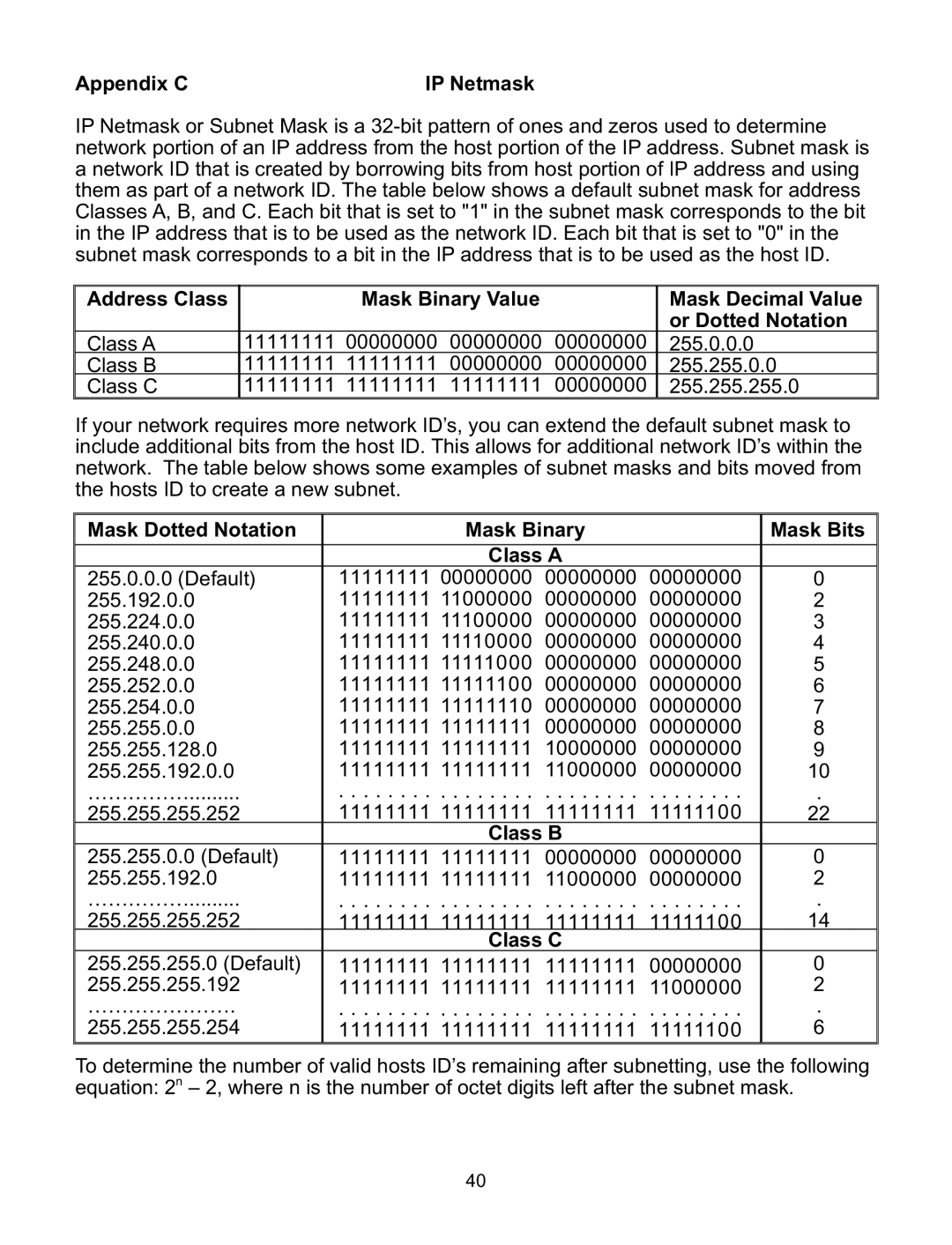
Appendix C | IP Netmask |
IP Netmask or Subnet Mask is a
Address Class | Mask Binary Value |
| Mask Decimal Value | |
|
|
|
| or Dotted Notation |
Class A | 11111111 00000000 | 00000000 | 00000000 | 255.0.0.0 |
Class B | 11111111 11111111 | 00000000 | 00000000 | 255.255.0.0 |
Class C | 11111111 11111111 | 11111111 | 00000000 | 255.255.255.0 |
If your network requires more network ID’s, you can extend the default subnet mask to include additional bits from the host ID. This allows for additional network ID’s within the network. The table below shows some examples of subnet masks and bits moved from the hosts ID to create a new subnet.
Mask Dotted Notation | Mask Binary |
| Mask Bits | |
|
|
|
| |
| Class A |
|
| |
255.0.0.0 (Default) | 11111111 00000000 | 00000000 | 00000000 | 0 |
255.192.0.0 | 11111111 11000000 | 00000000 | 00000000 | 2 |
255.224.0.0 | 11111111 11100000 | 00000000 | 00000000 | 3 |
255.240.0.0 | 11111111 11110000 | 00000000 | 00000000 | 4 |
255.248.0.0 | 11111111 11111000 | 00000000 | 00000000 | 5 |
255.252.0.0 | 11111111 11111100 | 00000000 | 00000000 | 6 |
255.254.0.0 | 11111111 11111110 | 00000000 | 00000000 | 7 |
255.255.0.0 | 11111111 11111111 | 00000000 | 00000000 | 8 |
255.255.128.0 | 11111111 11111111 | 10000000 | 00000000 | 9 |
255.255.192.0.0 | 11111111 11111111 | 11000000 | 00000000 | 10 |
…………… | . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . | . | ||
255.255.255.252 | 11111111 11111111 | 11111111 | 11111100 | 22 |
| Class B |
|
| |
255.255.0.0 (Default) | 11111111 11111111 | 00000000 | 00000000 | 0 |
255.255.192.0 | 11111111 11111111 | 11000000 | 00000000 | 2 |
…………… | . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . | . | ||
255.255.255.252 | 11111111 11111111 | 11111111 | 11111100 | 14 |
| Class C |
|
| |
255.255.255.0 (Default) | 11111111 11111111 | 11111111 | 00000000 | 0 |
255.255.255.192 | 11111111 11111111 | 11111111 | 11000000 | 2 |
…………………. | . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . | . | ||
255.255.255.254 | 11111111 11111111 | 11111111 | 11111100 | 6 |
To determine the number of valid hosts ID’s remaining after subnetting, use the following equation: 2n – 2, where n is the number of octet digits left after the subnet mask.
40