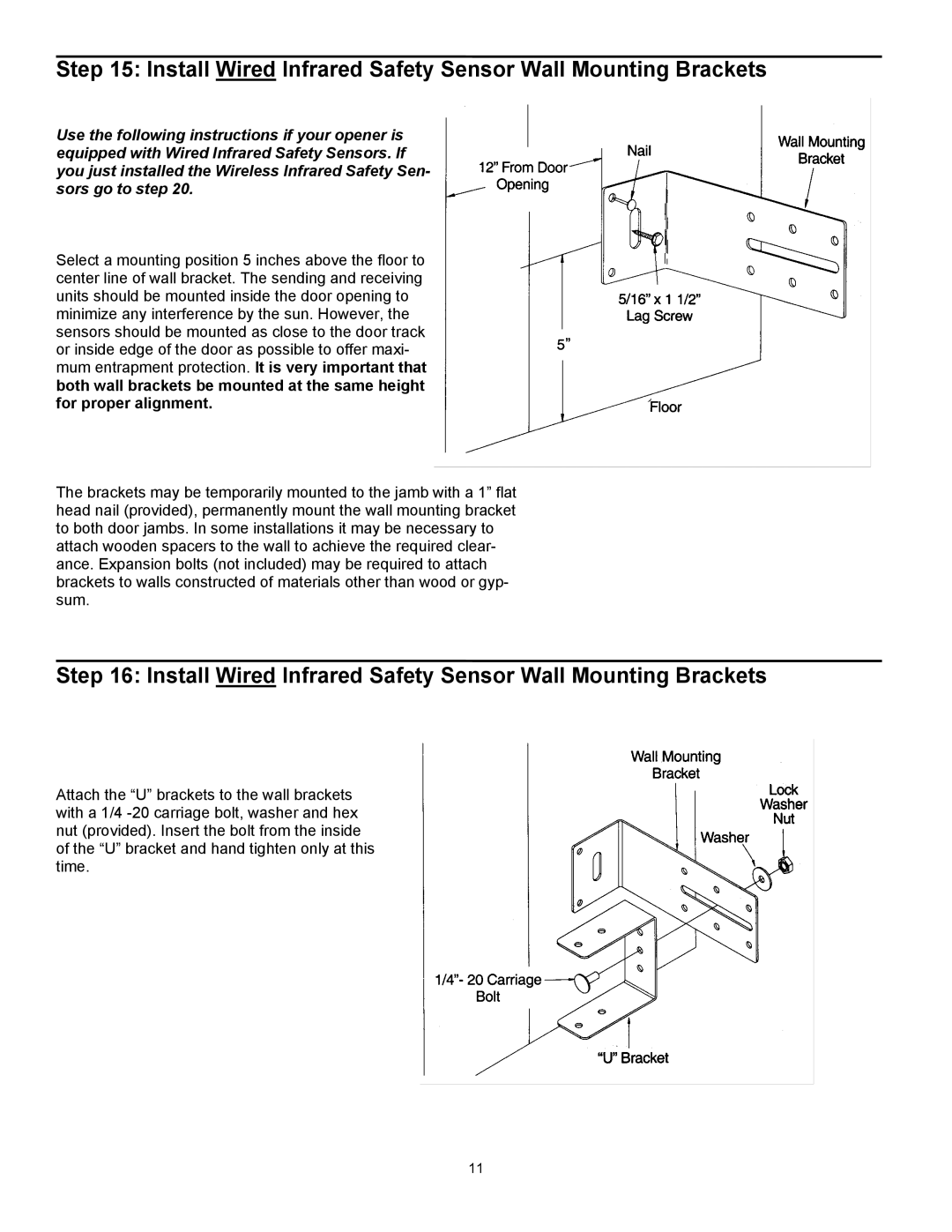
3316, 3314, 3214, 3414 specifications
Quantum 3414, 3316, 3214, and 3314 represent a series of cutting-edge technologies that have emerged in the field of quantum computing and advanced materials science. Each of these models offers unique features and capabilities designed to push the boundaries of computational power and efficiency.The Quantum 3414 is distinguished by its robust architecture and high-performance qubit system. It utilizes superconducting qubits, which provide exceptional coherence times and operational fidelity. This model is particularly well-suited for complex algorithm implementations, making it an attractive choice for researchers focused on quantum simulations and machine learning applications. Its innovative design integrates quantum error correction mechanisms that enhance reliability and reduce error rates.
Following closely, the Quantum 3316 emphasizes versatility and scalability. This model introduces a modular approach to quantum systems, enabling users to expand their computational resources as their needs grow. It features a hybrid quantum-classical architecture, allowing for greater flexibility in algorithm execution while leveraging classical computing's strengths. The 3316 is ideal for industries looking to optimize operational efficiency through quantum-enhanced processes.
The Quantum 3214 focuses on user accessibility and simplified integration into existing technological ecosystems. This model is equipped with an intuitive interface and user-friendly programming capabilities, catering to both seasoned quantum developers and newcomers. The 3214 also adopts cutting-edge quantum networking technologies, facilitating the remote connection of quantum systems for collaborative research and development.
Lastly, the Quantum 3314 combines power and compactness. Though smaller in form factor, this model does not compromise on performance. It employs advanced cryogenic technology to maintain optimal operating conditions for qubits, thus enhancing thermal stability and minimizing noise. The 3314 is particularly suitable for environments where space is limited yet high performance is essential, such as academic laboratories and research institutions.
Overall, the Quantum 3414, 3316, 3214, and 3314 each present a variety of sophisticated features tailored to specific applications within the quantum domain. From research and development to practical industrial applications, these models signify a significant leap forward in harnessing quantum technologies for future advancements. Their unique characteristics make them valuable tools for overcoming the challenges faced in the ever-evolving landscape of computing and science.