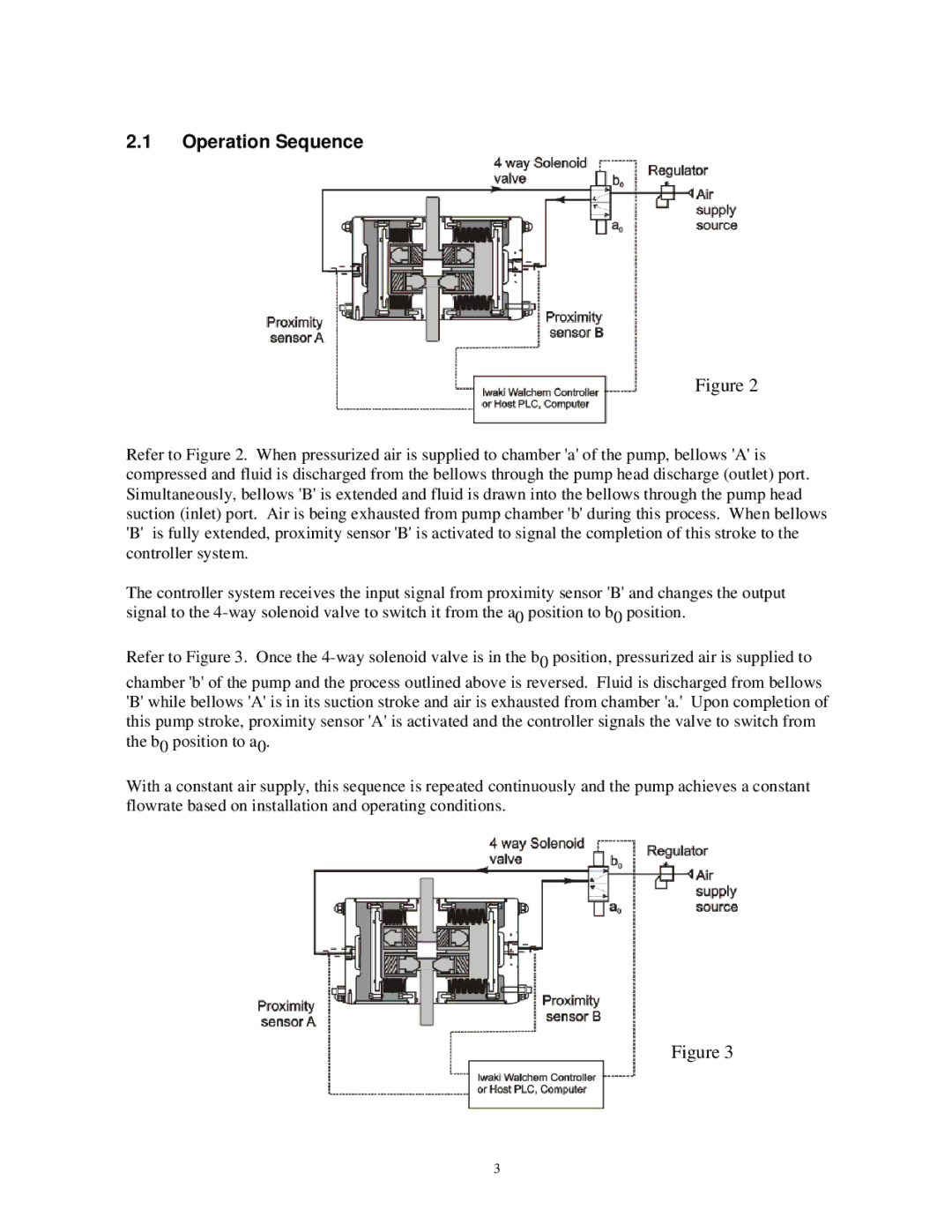
2.1Operation Sequence
Figure 2
Refer to Figure 2. When pressurized air is supplied to chamber 'a' of the pump, bellows 'A' is compressed and fluid is discharged from the bellows through the pump head discharge (outlet) port. Simultaneously, bellows 'B' is extended and fluid is drawn into the bellows through the pump head suction (inlet) port. Air is being exhausted from pump chamber 'b' during this process. When bellows 'B' is fully extended, proximity sensor 'B' is activated to signal the completion of this stroke to the controller system.
The controller system receives the input signal from proximity sensor 'B' and changes the output signal to the
Refer to Figure 3. Once the
With a constant air supply, this sequence is repeated continuously and the pump achieves a constant flowrate based on installation and operating conditions.
Figure 3
3