Outlet
Bypass Valve
Piston
Inlet
Figure 3 Basic Piston Prover
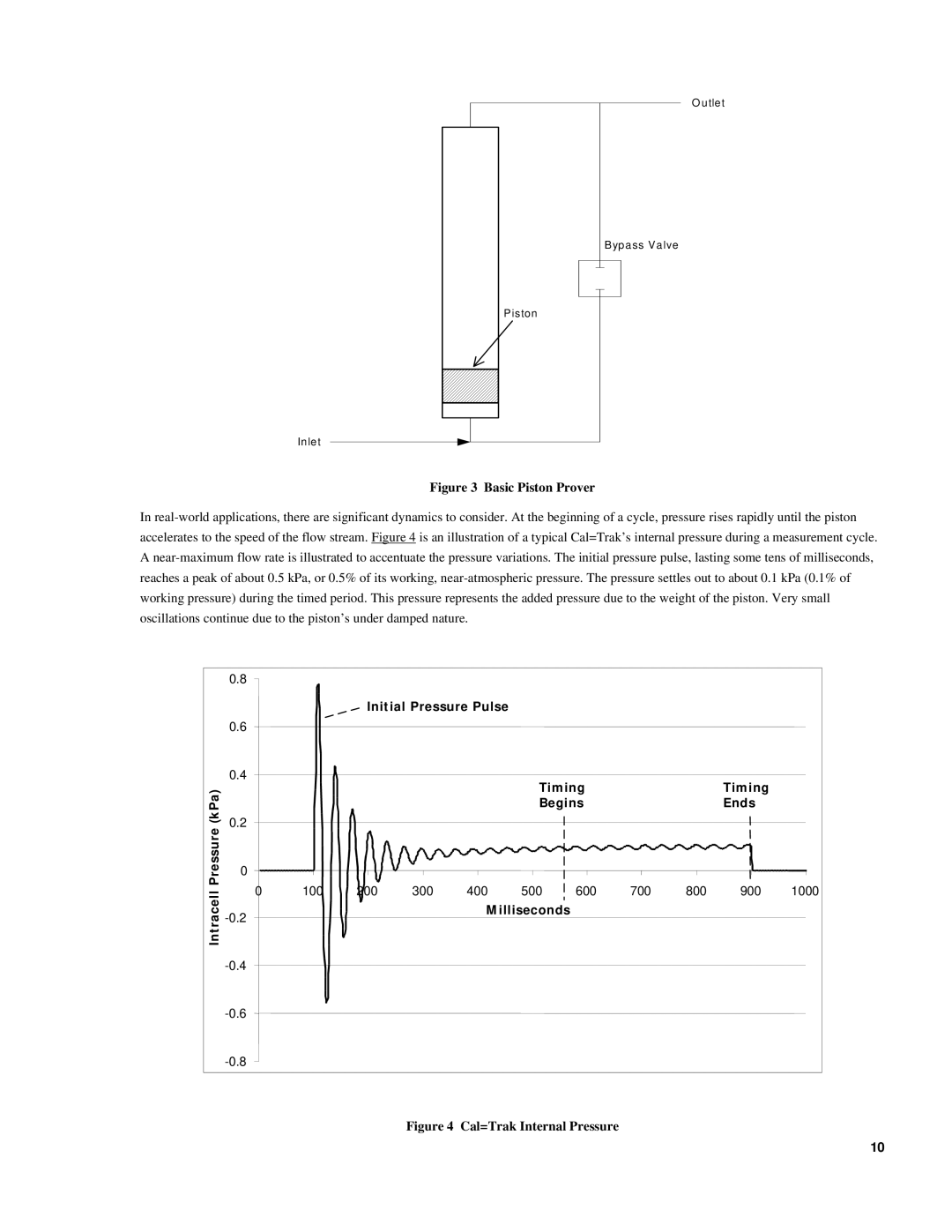
In real-world applications, there are significant dynamics to consider. At the beginning of a cycle, pressure rises rapidly until the piston accelerates to the speed of the flow stream. Figure 4 is an illustration of a typical Cal=Trak’s internal pressure during a measurement cycle. A near-maximum flow rate is illustrated to accentuate the pressure variations. The initial pressure pulse, lasting some tens of milliseconds, reaches a peak of about 0.5 kPa, or 0.5% of its working, near-atmospheric pressure. The pressure settles out to about 0.1 kPa (0.1% of working pressure) during the timed period. This pressure represents the added pressure due to the weight of the piston. Very small oscillations continue due to the piston’s under damped nature.
| | 0.8 | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | Initial Pressure Pulse | | | | | | |
| | 0.6 | | | | | | | | | | |
| | 0.4 | | | | | Timing | | | Timing | |
| (kPa) | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | Begins | | | Ends | |
| 0.2 | | | | | | | | | | |
| Pressure | | | | | | | | | | |
| 0 | | | | | | | | | | |
| 0 | 100 | 200 | 300 | 400 | 500 | 600 | 700 | 800 | 900 | 1000 |
| Intracell |
| -0.2 | | | | M illiseconds | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | -0.4 | | | | | | | | | | |
| | -0.6 | | | | | | | | | | |
| | -0.8 | | | | | | | | | | |
Figure 4 Cal=Trak Internal Pressure
10