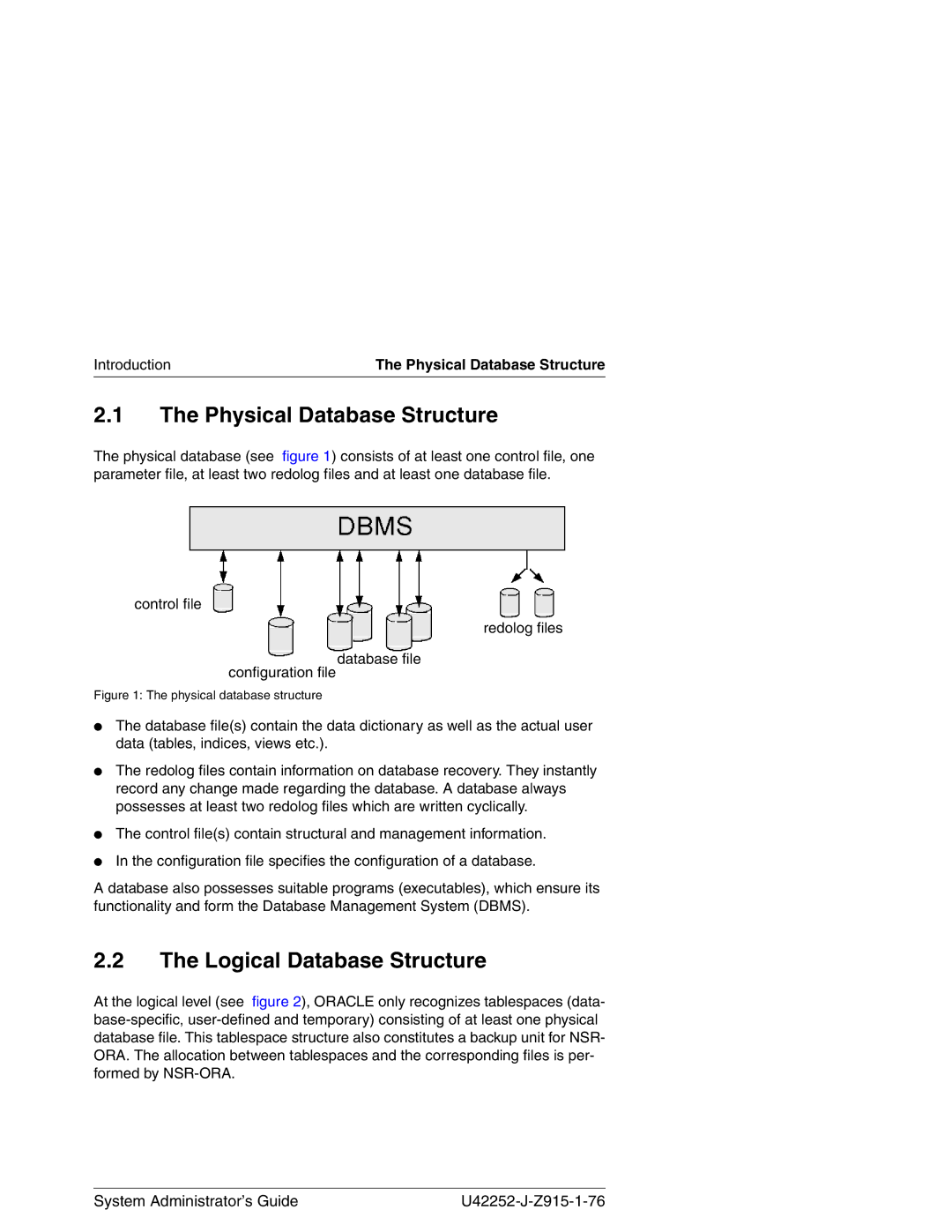
NSR-ORA V3.2 specifications
The 3Com NSR-ORA V3.2 is a versatile networking solution designed to enhance connectivity and streamline data management across various enterprise environments. With the rapid evolution of digital communication, 3Com recognized the need for a robust system that caters to the demanding requirements of today's businesses. The NSR-ORA V3.2 is specifically engineered to provide optimal performance, scalability, and reliability.One of the standout features of the NSR-ORA V3.2 is its integrated network processing capabilities. This device employs advanced multi-layer switching technology that significantly boosts data throughput while maintaining low latency. This is particularly advantageous for organizations that rely on real-time data transmission for critical applications, such as VoIP and video conferencing. The ability to process large volumes of data efficiently ensures that businesses can operate seamlessly without disruptions.
Another key characteristic of the NSR-ORA V3.2 is its support for a wide range of networking protocols. The device is compatible with both IPv4 and IPv6, allowing businesses to transition smoothly to newer network architectures without the need for significant reconfiguration. This dual-stack capability not only enhances network flexibility but also future-proofs investments as organizations look to scale and adapt their digital infrastructure.
Security is at the forefront of the NSR-ORA V3.2's design. The device incorporates advanced security features such as firewall protection, intrusion detection, and secure VPN capabilities. These components work together to safeguard sensitive information and ensure that data integrity is maintained across the network. In addition to these features, the device offers comprehensive management tools, allowing network administrators to monitor performance and manage access controls more effectively.
The NSR-ORA V3.2 also excels in its interoperability with various devices and platforms, making it an ideal choice for enterprises that utilize a mix of legacy systems and modern technologies. Its compatibility with both wired and wireless networks provides businesses with the flexibility to design an infrastructure that meets their specific operational needs.
In summary, the 3Com NSR-ORA V3.2 is a powerful networking solution that combines advanced processing capabilities, robust security features, and a high degree of compatibility with diverse systems. Its emphasis on performance and scalability makes it a compelling choice for organizations seeking to enhance their network infrastructure in an ever-evolving digital landscape.