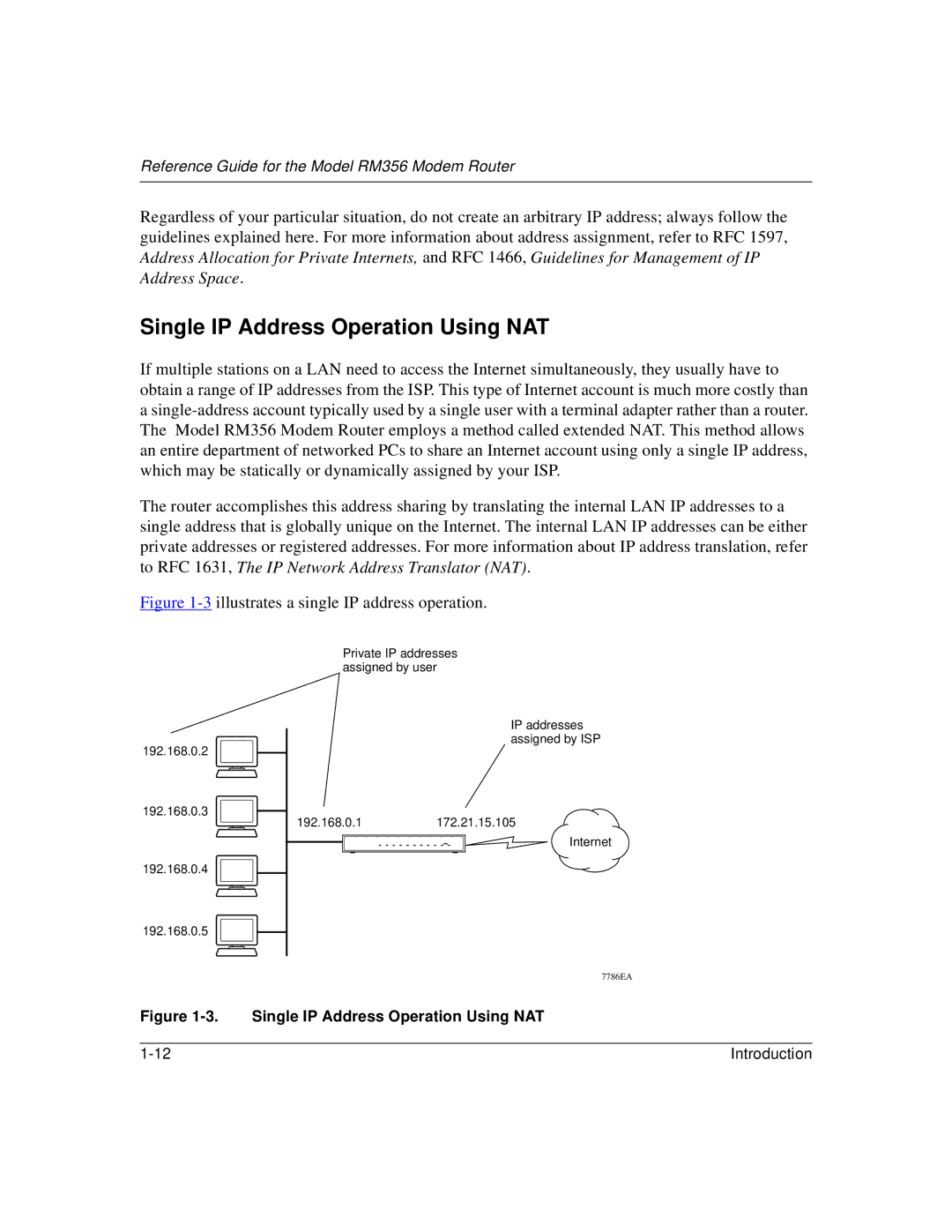
RM356 specifications
Bay Technical Associates RM356 is a state-of-the-art remote monitoring solution designed for a wide range of industries. It is particularly suited for companies requiring a reliable system for tracking and monitoring operations in real-time. This advanced device combines innovative technologies to deliver unparalleled functionality and performance.One of the standout features of the RM356 is its robust data acquisition capabilities. The device can interface with various sensors and equipment, enabling it to collect critical data from multiple sources. This real-time data collection allows for immediate analysis and facilitates informed decision-making. The RM356 supports various protocols and standards, making it highly compatible with existing infrastructure.
Another significant characteristic of the RM356 is its advanced communication technology. Equipped with both wired and wireless communication options, including LTE, Wi-Fi, and Ethernet, it ensures seamless connectivity in various environments. This versatility enables businesses to monitor operations remotely, reducing the need for on-site presence and enhancing operational efficiency.
The RM356 also incorporates cutting-edge analytics and reporting tools. Its built-in software allows users to visualize data through intuitive dashboards, making it easier to identify trends and anomalies. These analytics capabilities help organizations optimize processes and address potential issues before they escalate, ultimately improving productivity and reducing operational costs.
Security is a top priority for the RM356. The unit comes with robust encryption and authentication measures to ensure that the data it collects remains secure from unauthorized access. This feature is especially critical for industries handling sensitive information or operating in regulated environments.
Additionally, the RM356 is designed with user-friendliness in mind. Its installation process is straightforward, with comprehensive setup guides available for quick deployment. Once operational, users can easily navigate the system interface, allowing for efficient monitoring and management of their operations.
With its combination of advanced features, reliable communication, data analytics, and strict security measures, Bay Technical Associates RM356 stands out as an excellent choice for businesses looking to enhance their monitoring capabilities. Whether in manufacturing, logistics, energy, or other sectors, the RM356 is poised to deliver improved outcomes and support organizations in their quest for operational excellence.