Troubleshooting
What is the difference between 802.11b, 802.11g, 802.11a, and
Currently there are four levels of wireless networking standards, which transmit data at very different maximum speeds. Each is based on the designation 802.11(x), so named by the IEEE, the board that is responsible for certifying networking standards. The most common wireless networking standard, 802.11b, transmits information at 11Mbps; 802.11a and 802.11g work at 54Mbps; and
at 108Mbps.
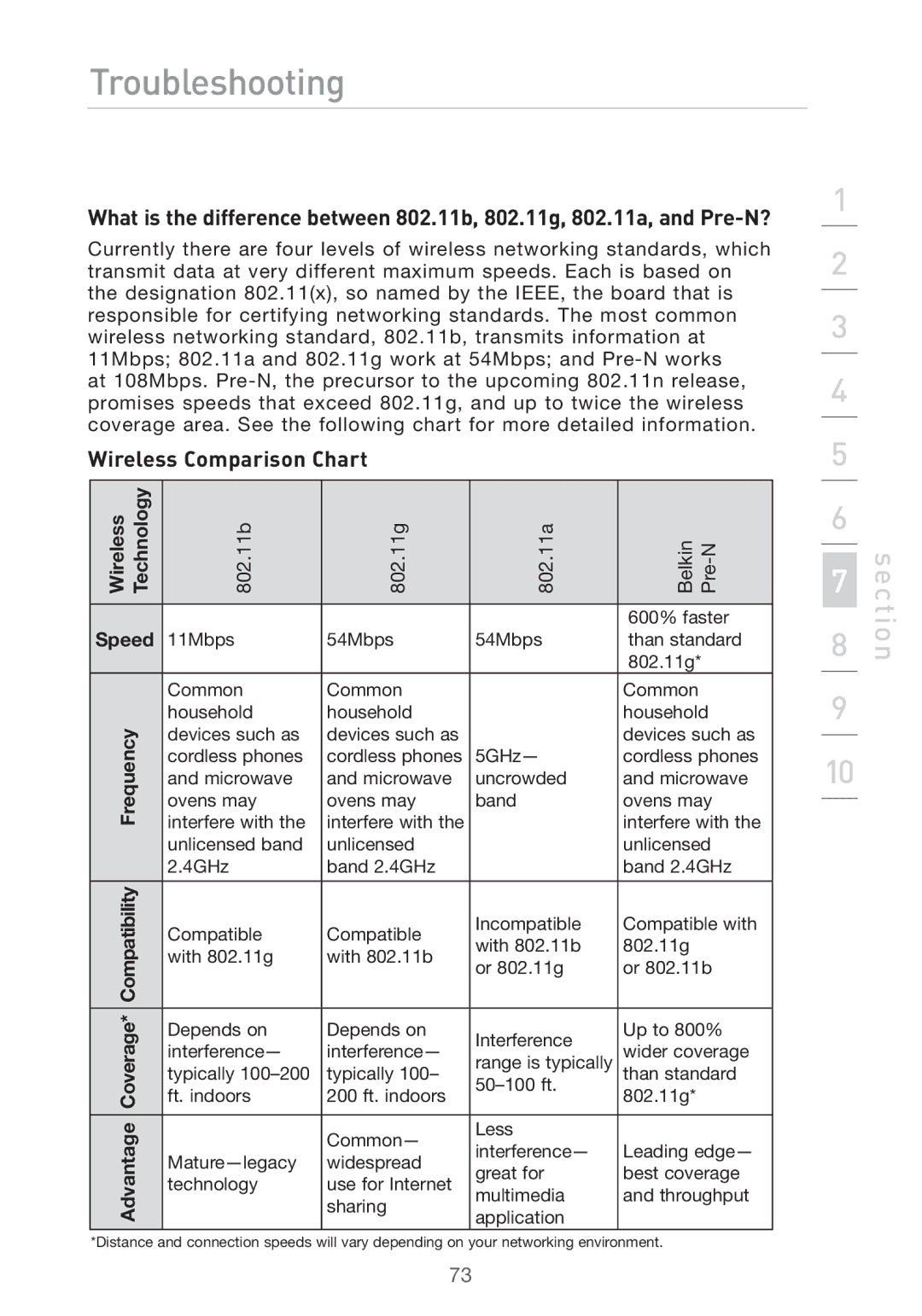
Wireless Comparison Chart
Wireless Technology | 802.11b | 802.11g | 802.11a | Belkin | |
|
|
|
|
| |
Speed |
|
|
| 600% faster | |
11Mbps | 54Mbps | 54Mbps | than standard | ||
|
|
|
| 802.11g* | |
| Common | Common |
| Common | |
| household | household |
| household | |
Frequency | devices such as | devices such as |
| devices such as | |
cordless phones | cordless phones | 5GHz— | cordless phones | ||
| |||||
| and microwave | and microwave | uncrowded | and microwave | |
| ovens may | ovens may | band | ovens may | |
| interfere with the | interfere with the |
| interfere with the | |
| unlicensed band | unlicensed |
| unlicensed | |
| 2.4GHz | band 2.4GHz |
| band 2.4GHz | |
|
|
|
|
| |
Compatibility | Compatible | Compatible | Incompatible | Compatible with | |
| |||||
| with 802.11b | 802.11g | |||
| with 802.11g | with 802.11b | |||
| or 802.11g | or 802.11b | |||
|
|
| |||
|
|
|
|
| |
Coverage* | Depends on | Depends on | Interference | Up to 800% | |
| |||||
| interference— | interference— | wider coverage | ||
| range is typically | ||||
| typically | typically 100– | than standard | ||
| ft. indoors | 200 ft. indoors | 802.11g* | ||
|
| ||||
|
|
|
|
| |
Advantage |
| Common— | Less |
| |
| interference— | Leading edge— | |||
|
| ||||
| widespread | ||||
| great for | best coverage | |||
| technology | use for Internet | |||
| multimedia | and throughput | |||
|
| sharing | |||
|
| application |
| ||
|
|
|
|
*Distance and connection speeds will vary depending on your networking environment.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
section
73