Application Guide
Bladeos 6.5.2 Application Guide
Contents
Part 2 Securing the Switch
Access Control Lists
Part 3 Switch Basics
Quality of Service
Part 4 Advanced Switching Features
FCoE and CEE
Part 5 IP Routing
Internet Group Management Protocol
Protocol Independent Multicast
Part 6 High Availability Fundamentals
Part 7 Network Management
Part 8 Monitoring
Bladeos 6.5.2 Application Guide
Who Should Use This Guide
Preface
What You’ll Find in This Guide
Part 2 Securing the Switch
Part 5 IP Routing
Additional References
Part 8 Monitoring
Typographic Conventions
Typographic Conventions
AaBbCc123
How to Get Help
Part 1 Getting Started
Part 1 Getting Started
Switch Administration
Administration Interfaces
Command Line Interface
Browser-Based Interface
RS G8124# configure terminal
Using the Switch Management Ports
Establishing a Connection
Enable
Exit
Using the Switch Data Ports
Configure the management IP interface/mask. Using IPv4
Configure the VLAN, and enable the interface
Configure the default gateway. If using IPv4
Using Telnet
RS G8124config# no access telnet enable
Using Secure Shell
Using SSH to Access the Switch
Using a Web Browser
G8124config# access http enable
G8124config# no access http enable
RS G8124config# access https enable
RS G8124config# access https save-certificate
BBI Summary
Using Simple Network Management Protocol
BOOTP/DHCP Client IP Address Services
Global Bootp Relay Agent Configuration
Domain-Specific Bootp Relay Agent Configuration
Switch Login Levels
User Access Levels
Setup vs. the Command Line
Bladeos 6.5.2 Application Guide
Initial Setup
Information Needed for Setup
Default Setup Options
Stopping and Restarting Setup Manually
Stopping Setup
Restarting Setup
When Setup is started, the system prompts
Setup Part 1 Basic System Configuration
Enter the hour of the current system time at the prompt
Enter the minute of the current time at the prompt
Setup Part 2 Port Configuration
Turn Spanning Tree Protocol on or off at the prompt
Enter new Vlan tag support d/e
Setup Part 3 VLANs
System prompts you to configure the next Vlan
To keep the current setting, press Enter
Setup Part 4 IP Configuration
IP Interfaces
System prompts you to configure another interface
System prompts you to configure another default gateway
Default Gateways
IP Routing
Setup Part 5 Final Steps
When prompted, decide whether to restart Setup or continue
Apply and save the configurations
Optional Setup for Telnet Support
# /cfg/sys/access/tnet
Bladeos 6.5.2 Application Guide
Part 2 Securing the Switch
Part 2 Securing the Switch
Securing Administration
Secure Shell and Secure Copy
To Enable or Disable the SSH Feature
Configuring SSH/SCP Features on the Switch
To Enable or Disable SCP Apply and Save
Configuring the SCP Administrator Password
Using SSH and SCP Client Commands
To Log In to the Switch
To Copy the Switch Configuration File to the SCP Host
To Apply and Save the Configuration
To Load a Switch Configuration File from the SCP Host
Scp ad4.cfg scpadmin@205.178.15.157putcfg
To Copy the Switch Image and Boot Files to the SCP Host
To Load Switch Configuration Files from the SCP Host
SSH and SCP Encryption of Management Messages
Encryption
Generating RSA Host and Server Keys for SSH Access
SSH/SCP Integration with Radius Authentication
SSH/SCP Integration with TACACS+ Authentication
Using SecurID with SSH
Using SecurID with SCP
SecurID Support
Considerations for Configuring End User Accounts
End User Access Control
Strong Passwords
User Access Control
Setting up User IDs
Defining a User’s Access Level
Validating a User’s Configuration
Listing Current Users
RS G8124# show access User
Logging into an End User Account
Authentication & Authorization Protocols
Radius Authentication and Authorization
How Radius Authentication Works
Configuring Radius on the Switch
Configure the Radius secret
RS G8124config# radius-server port UDP port number
Radius Authentication Features in Bladeos
RS G8124# show radius-server
Radius Attributes for Bladeos User Privileges
Switch User Accounts
BLADEOS-proprietary Attributes for Radius
TACACS+ Authentication
How TACACS+ Authentication Works
Default TACACS+ Authorization Levels
TACACS+ Authentication Features in Bladeos
Alternate TACACS+ Authorization Levels
Command Authorization and Logging
Accounting
Configure the TACACS+ secret and second secret
Configuring TACACS+ Authentication on the Switch
RS G8124config# tacacs-server port TCP port number
Ldap Authentication and Authorization
Configuring the Ldap Server
Configuring Ldap Authentication on the Switch
Configure the domain name
# ldap-server retransmit # ldap-server timeout
# ldap-server port
RS G8124config# access-control list Regular ACL number ?
Access Control Lists
RS G8124config# access-control list6 IPv6 ACL number ?
Well-Known Protocol Types
Summary of Packet Classifiers
Icmp Igmp Tcp Udp
Well-Known Application Ports
Well-Known TCP flag values
Assigning Individual ACLs to a Port
Summary of ACL Actions
ACL Order of Precedence
Metering
ACL Metering and Re-Marking
Re-Marking
RS G8124config# access-control list ACL number mirror port
RS G8124config# access-control vmap VMap number mirror port
RS G8124config# access-control list ACL number statistics
ACL Port Mirroring
ACL Configuration Examples
ACL Example
Add ACL 1 to port EXT1
Add ACL 2 to port EXT2
RS G8124config-if#access-control list6
Vlan Maps
Non-serverports
RS G8124config# access-control vmap Vmap ID ?
Serverportsnon-serverports
Using Storm Control Filters
Configuring Storm Control
RS G8124config-if#dest-lookup-threshold packet rate
Broadcast Storms
Part 3 Switch Basics
Part 3 Switch Basics
VLANs
VLANs and Port Vlan ID Numbers
VLANs Overview
Vlan Numbers
Pvid Numbers
Use the following command to set the port Pvid
RS G8124# show interface information
Vlan Tagging
Default Vlan settings
Port-based Vlan assignment
802.1Q tag assignment
Vlan Configuration Rules
Vlan Topologies and Design Considerations
Multiple VLANs with Tagging Adapters
Multiple VLANs with VLAN-Tagged Gigabit Adapters
Features of this Vlan are described below
Multiple VLANs Example
Enable tagging on uplink ports that support multiple VLANs
Vlan Configuration Example
Configure the VLANs and their member ports
Private VLANs
Private Vlan Ports
Configuration Guidelines
Configuration Example
Configure a secondary Vlan and map it to the primary Vlan
Verify the configuration
Bladeos 6.5.2 Application Guide
Ports and Trunking
Trunking Overview
Port Trunk Group
Before You Configure Static Trunks
Example below, three ports are trunked between two switches
Trunk Group Configuration Rules
Port Trunking Example
Follow these steps on the G8124 a. Define a trunk group
# show portchannel information
Configurable Trunk Hash Algorithm
Layer 2 destination MAC address
Layer 2 source and destination MAC address
Layer 3 IPv4/IPv6 source IP address
Actor vs. Partner Lacp configuration
Link Aggregation Control Protocol
Set the Lacp mode
Configuring Lacp
RS G8124 # show lacp information
Spanning Tree Protocols
Spanning Tree Protocol Modes
Depending on your preferred STG configurations
RS G8124config# spanning-tree mode disable
RS G8124config# spanning-tree mode pvstrstppvrstmst
Global STP Control
Port States
STP/PVST+ Mode
Ports, Trunk Groups, and VLANs
Bridge Protocol Data Units
RS G8124config# spanning-tree stp x bridge priority
Bridge Priority
Port Priority
Fast Uplink Convergence
Port Path Cost
Fast Uplink Configuration Guidelines
Configuring Fast Uplink Convergence
RS G8124config# spanning-tree uplinkfast
Port Fast Forwarding
Switch
Simple STP Configuration
Blocks Link Server
Restores Link Server
RS G8124config-if#spanning-tree stp 1 path-cost
Using Multiple Instances of Spanning Tree Group
Per-VLAN Spanning Tree Groups
STP/PVST+ Defaults and Guidelines
Creating a Vlan
Adding and Removing Ports from STGs
Switch-Centric Configuration
RS G8124config# spanning-tree stp 2 vlan 2,3
Configuring Multiple STGs
RS G8124config# spanning-tree stp 2 vlan
RS G8124config# spanning-tree stp 2 vlan
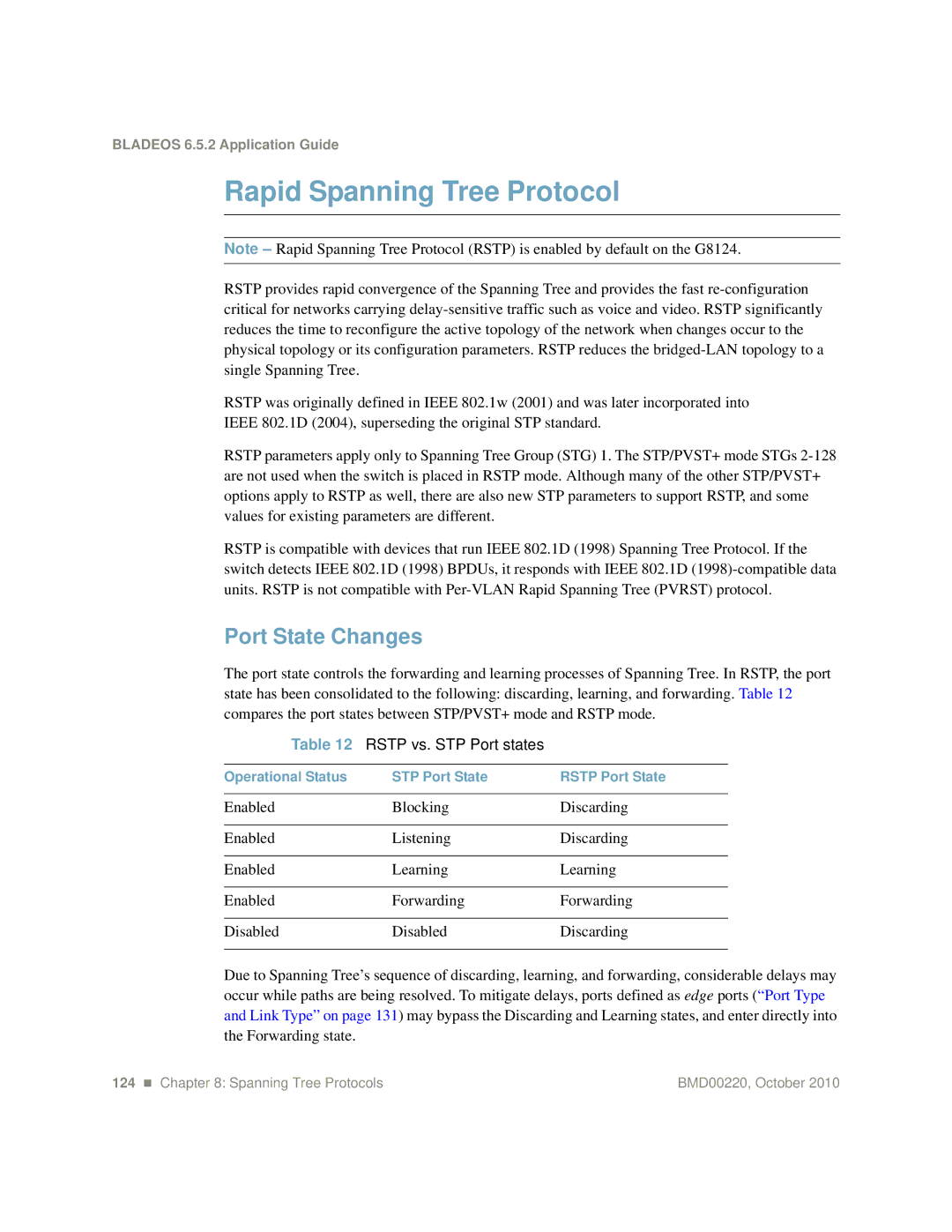
Port State Changes
Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol
Rstp vs. STP Port states
Rstp Configuration Guidelines
Rstp Configuration Example
Configure STP Group 1 parameters
RS G8124config# spanning-tree mode rstp
RS G8124config# spanning-tree mode pvrst
Configuring Pvrst
Per-VLAN Rapid Spanning Tree Groups
Mstp Region
Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol
Common Internal Spanning Tree
Mstp Configuration Example
Mstp Configuration Guidelines
Assign VLANs to Spanning Tree Groups
Passing Vlan Blocking Vlan
Configure Mstp Spanning Tree mode, region name, and version
RS G8124config-if# no spanning-tree link-type type
Port Type and Link Type
Edge Port
Link Type
Bladeos 6.5.2 Application Guide
Quality of Service
QoS Overview
Shows the basic QoS model used by the switch
QoS Model
Using ACL Filters
Summary of ACL Actions
ACL Metering and Re-Marking
Using Dscp Values to Provide QoS
Differentiated Services Concepts
Highest
Per Hop Behavior
Lowest
Default QoS Service Levels
QoS Levels
Critical
Network Control
Dscp Re-Marking and Mapping
RS G8124config# qos dscp re-marking
RS G8124# show qos dscp
Enable Dscp re-marking on a port
Dscp Re-Marking Configuration Example
RS G8124config-if#qos dscp dscp-remarking
Using 802.1p Priority to Provide QoS
Layer 2 802.1q/802.1p Vlan tagged packet
Queuing and Scheduling
Bladeos 6.5.2 Application Guide
Part 4 Advanced Switching Features
Part 4 Advanced Switching Features
Deployment Profiles
Available Profiles
Deployment Mode Comparison
Automatic Configuration Changes
Selecting Profiles
Bladeos 6.5.2 Application Guide
Virtualization
Virtualization
Virtual NICs
Virtualizing the NIC for Multiple Virtual Pipes on Each Link
Enabling the vNIC Feature
Defining Server Ports
VNIC IDs on the Switch
VNIC IDs
VNIC Interface Names on the Server
VNIC ID Correlation
VNIC Bandwidth Metering
VNIC Groups
Outer and Inner Vlan Tags
Bladeos 6.5.2 Application Guide
Disables associated server ports
To Backup
VNIC Teaming Failover
Upon Port 1 link failure, the switch To Backup
For failover on affected VNICs only
VNIC Configuration Example
Consider the following example configuration
Enable the vNIC feature on the switch
Configure the external trunk to be used with vNIC group
Define the server ports
Add ports, trunks, and virtual pipes to their vNIC groups
RS G8124config# vnic port 1 index
RS G8124config# vnic port 2 index
RS G8124config# vnic port 3 index
VNICs for iSCSI on Emulex Eraptor
VMready
VE Capacity
VM Group Types
Configuring a Local VM Group
Local VM Groups
RS G8124config# no virt vmgroup VM group number ?
Distributed VM Groups
RS G8124config# virt vmprofile edit profile name ?
VM Profiles
Initializing a Distributed VM Group
RS G8124config# no virt vmgroup VM group number profile
Assigning Members
Synchronizing the Configuration
Removing Member VEs
Virtualization Management Servers
Assigning a vCenter
RS G8124config# no virt vmware vcspec
VCenter Scans
Deleting the vCenter
G8124# virt vmware scan
Exporting Profiles
VMware Operational Commands
Virt vmware ?
Pre-Provisioning VEs
Vlan Maps
For a VM group, use the global configuration mode
RS G8124config# virt vmpolicy vmbwidth VM MACindexUUID
VM Policy Bandwidth Control Commands
VM Policy Bandwidth Control
Bandwidth Policies vs. Bandwidth Shaping
Local VE Information
VMready Information Displays
RS G8124# show virt vm
G8124# show virt vm
VCenter Hypervisor Hosts
RS G8124# show virt vmware hosts
VCenter VE Details
VCenter VEs
RS G8124# show virt vmware vms
Enable the VMready feature
VMready Configuration Example
Specify the VMware vCenter IPv4 address
Define the VM group
Bladeos 6.5.2 Application Guide
FCoE and CEE
Fibre Channel over Ethernet on
Enhanced Transmission Selection on
Fibre Channel over Ethernet
FCoE Topology
Bladeos 6.5.2 Application Guide
FCoE Requirements
Turning CEE On or Off
Converged Enhanced Ethernet
Effects on Link Layer Discovery Protocol
CEE Effects on 802.1p Defaults
Effects on 802.1p Quality of Service
Default ETS Bandwidth Allocation
Effects on Flow Control
FCoE Initialization Protocol Snooping
Global FIP Snooping Settings
FIP Snooping for Specific Ports
FCoE Connection Timeout
RS G8124config# fcoe fips port ports fcf-mode autoonoff
RS G8124config# no fcoe fips timeout-acl
Port FCF and ENode Detection
FCoE ACL Rules
FCoE VLANs
Viewing FIP Snooping Information
Operational Commands
For example
FIP Snooping Configuration
RS G8124config# fcoe fips port 2 enable
RS G8124config# fcoe fips port 2 fcf-mode on
RS G8124config# fcoe fips port 3 fcf-mode off
Priority-Based Flow Control
Global Configuration
PFC Configuration Example
Port-Based PFC Configuration
Enable PFC for the FCoE traffic
Enable PFC for the business-critical LAN application
G8124config# Cee global Pfc Priority Enable
G8124config# Cee global Pfc Priority Description FCoE
Enhanced Transmission Selection
802.1p Priority Values
Pgid
Priority Groups
Pgid
Assigning Priority Values to a Priority Group
Allocated Bandwidth for Pgid 0 Through
Unlimited Bandwidth for Pgid
Configuring ETS
ETS Configuration
RS G8124config# cee global ets bandwidth 2
RS G8124config# cee global ets priority-group 2 description
RS G8124config# cee global ets priority-group 3 priorities
RS G8124config# cee global ets bandwidth 3
Dcbx Settings
Data Center Bridging Capability Exchange
Peer Configuration Negotiation
Enabling and Disabling Dcbx
Willing flag is set or reset using the following command
PFC
Enable desired Dcbx configuration negotiation on FCoE ports
Configuring Dcbx
Enable desired Dcbx advertisements on other CEE ports
Disable Dcbx for each non-CEE port as appropriate
RS G8124config# no cee port 5-24 dcbx enable
Bladeos 6.5.2 Application Guide
Part 5 IP Routing
Part 5 IP Routing
IP Routing Benefits
Basic IP Routing
Routing Between IP Subnets
For example, consider the following topology migration
Router Legacy Network
Switch-Based Routing Topology
Example of Subnet Routing
Subnet Routing Example IP Address Assignments
Using VLANs to Segregate Broadcast Domains
Subnet Routing Example IP Interface Assignments
Subnet Routing Example Optional Vlan Ports
Add ports to Vlan
Enable IP routing
Ospf Integration
Ecmp Static Routes
Ecmp Route Hashing
RS G8124config# show ip route static
Configuring Ecmp Static Routes
Select an Ecmp hashing method optional
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol
Dhcp Relay Agent
Bladeos 6.5.2 Application Guide
Internet Protocol Version
RFC RFC 4293 RFC 3411, 3412, 3413
IPv6 Limitations
Example IPv6 address
IPv6 Address Format
Address can be compressed as follows
Unicast Address
IPv6 Address Types
Multicast
IPv6 Address Autoconfiguration
Anycast
IPv6 Interfaces
Second IPv6 address can be a unicast or anycast address
Neighbor Discovery
Neighbor Discovery Overview
Host vs. Router
G8124 supports up to 1156 IPv6 routes
Supported Applications
HTTP/HTTPS servers support both IPv4 and IPv6 connections
RS G8124config# ip dns ipv6 request-version ipv4ipv6
SSH
Configuration Guidelines
IPv6 Configuration Examples
This section provides steps to configure IPv6 on the switch
Configure the IPv6 default gateway
IPv6 Example
RS G8124config-ip-if# show layer3
Bladeos 6.5.2 Application Guide
Distance Vector Protocol
Routing Information Protocol
Stability
RIPv1
Routing Updates
RIPv2
RIPv2 in RIPv1 Compatibility Mode
RIP Features
Triggered Updates
Poison
Authentication
Default
Metric
RIP Configuration Example
Turn on RIP globally and enable RIP for each interface
Add VLANs for routing interfaces
Add IP interfaces with IPv4 addresses to VLANs
# show ip route
# show ip rip
Internet Group Management Protocol
Igmp Snooping
FastLeave
Igmp Groups
IGMPv3 Snooping
RS G8124config# no ip igmp snoop igmpv3
Igmp Snooping Configuration Example
Enable IGMPv3 Snooping optional
Enable the Igmp feature
View dynamic Igmp information
RS G8124config# ip igmp mrouter 5 1
Configure a Static Multicast Router
Static Multicast Router
Configure the querier election type and define the address
Enable Igmp Querier on the Vlan
Igmp Querier
Configuring the Action
Configuring the Range
Igmp Filtering
Configure Igmp Filtering
Enable Igmp Filtering on the switch
Define an Igmp filter with IPv4 information
Assign the Igmp filter to a port
Bladeos 6.5.2 Application Guide
Border Gateway Protocol
Internal Routing Versus External Routing
IBGP and eBGP
What is a Route Map?
Forming BGP Peer Routers
Distributing Network Filters in Access Lists and Route Maps
Incoming and Outgoing Route Maps
RS G8124config# ip match-address 1 enable
Configuration Overview
Precedence
Exit Router BGP mode
Enable the route map
Turn BGP on
Aggregating Routes
Redistributing Routes
Local Preference Attribute
BGP Attributes
Metric Multi-Exit Discriminator Attribute
Selecting Route Paths in BGP
BGP Failover Configuration
BGP Failover Configuration Example
Configure BGP peer router 1 and 2 with IPv4 addresses
# ip routing
# router bgp
Default Redistribution and Route Aggregation Example
# ip router-id
Configure redistribution for Peer
Bladeos 6.5.2 Application Guide
Ospf
OSPFv2 Overview
Types of Ospf Areas
Ospf Area Types
Types of Ospf Routing Devices
Ospf Domain and an Autonomous System
Neighbors and Adjacencies
Link-State Database
Shortest Path First Tree
Internal Versus External Routing
Configurable Parameters
OSPFv2 Implementation in Bladeos
Area index set to an arbitrary value
Defining Areas
Area Area-id
Using the Area ID to Assign the Ospf Area Number
Interface Cost
Electing the Designated Router and Backup
Summarizing Routes
Default Routes
Injecting Default Routes
Router ID
Virtual Links
Neighbor-router router ID
Authentication
Ospf Authentication
Configuring Plain Text Ospf Passwords
Enable Ospf authentication for Area 2 on switch
Configure MD5 key ID for Area 0 on switches 1, 2,
Assign MD5 key ID to Ospf interfaces on switches 1, 2,
Enable Ospf MD5 authentication for Area 2 on switch
Assign MD5 key ID to Ospf virtual link on switches 2
Ospf Features Not Supported in This Release
Host Routes for Load Balancing
OSPFv2 Configuration Examples
Enable Ospf
Example 1 Simple Ospf Domain
Attach the network interface to the backbone
Define the stub area
Attach the network interface to the stub area
RS G8124config# ip router-id
Configuring Ospf for a Virtual Link on Switch #1
Example 2 Virtual Links
Define the backbone
Attach the network interface to the transit area
Configuring Ospf for a Virtual Link on Switch #2
Define the transit area
Other Virtual Link Options
Example 3 Summarizing Routes
Summarizing Routes
RS G8124config-router-ospf#area-range 1 address 36.128.192.0
Verifying Ospf Configuration
RS G8124config-router-ospf#area-range 2 address 36.128.200.0
OSPFv3 Implementation in Bladeos
OSPFv3 Differences from OSPFv2
Iscli
# /cfg/l3/ospf3
# /info/l3/ospf3
# /stats/l3/ospf3
OSPFv3 Configuration Example
Blade Switch
RS G8124config-ip-if#ipv6 address
RS G8124config-ip-if#ip address
Enable OSPFv3
RS G8124config-router-ospf3#area-range 1 address 360000000
RS G8124config-router-ospf#area-range 2 address 360000000
Protocol Independent Multicast
PIM Overview
Supported PIM Modes and Features
Basic PIM Settings
Globally Enabling or Disabling the PIM Feature
Defining a PIM Network Component
Defining an IP Interface for PIM Use
PIM Neighbor Filters
Additional Sparse Mode Settings
Specifying the Rendezvous Point
Specifying a Bootstrap Router
Influencing the Designated Router Selection
Using PIM with Other Features
Using the CLI
PIM with ACLs or VMAPs
PIM with Igmp
PIM Configuration Examples
Set the Bootstrap Router BSR preference
RS G8124config-ip-if#ip address 10.10.1.1
RS G8124config-ip-if#ip pim cbsr-preference
RS G8124config# ip pim static-rp enable
Example 2 PIM-SM with Static RP
Example 3 PIM-DM
255.255.0.0
Configure a PIM component and set the PIM mode
Bladeos 6.5.2 Application Guide
Part 6 High Availability Fundamentals
High Availability Fundamentals
Basic Redundancy
Trunking for Link Redundancy
Internet
For more information on trunking, see Ports and Trunking on
Forward Delay
FDB Update
Hot Links
Preemption
Configuring Hot Links
Use the following commands to configure Hot Links
Active MultiPath Protocol
AMP Topology
Health Checks
FDB Flush
Define the AMP group links, and enable the AMP group
Configuring an Aggregator Switch
Turn AMP on, and define the aggregator
Configuring an Access Switch
# active-multipath enable
Verifying AMP Operation
Turn AMP on
Bladeos 6.5.2 Application Guide
Layer 2 Failover
Monitoring Trunk Links
Setting the Failover Limit
Basic Layer 2 Failover
Monitor Port State
Manually Monitoring Port Links
Control Port State
L2 Failover with Other Features
Spanning Tree Protocol
Configuring Layer 2 Failover
Configure general Failover parameters
# failover trigger 1 mmon monitor member
# failover trigger 1 mmon control member
Bladeos 6.5.2 Application Guide
Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol
Vrrp Overview
Vrrp Components
Virtual Router
Virtual Router MAC Address
Vrrp Operation
Master and Backup Virtual Router
Virtual Interface Router
Failover Methods
Selecting the Master Vrrp Router
Active-Active Redundancy
Virtual Router Group
Bladeos Extensions to Vrrp
Vrrp Tracking Parameters
Configuring the Switch for Tracking
RS G8124config-vrrp#virtual-router 1 virtual-router-id
Virtual Router Deployment Considerations
Assigning Vrrp Virtual Router ID
High Availability Configurations
Active-Active High-Availability Configuration
Configure client and server interfaces
Task 1 Configure G8124
Turn on Vrrp and configure two Virtual Interface Routers
Configure ports
Turn off Spanning Tree Protocol globally
Task 2 Configure G8124
Virtual-router 2 priority
Part 7 Network Management
Part 7 Network Management
Link Layer Discovery Protocol
Lldp Overview
Enabling or Disabling Lldp
Global Lldp Setting
Transmit and Receive Control
Lldp Transmit Features
RS G8124config# lldp refresh-interval interval
RS G8124config# lldp transmission-delay interval
Scheduled Interval
RS G8124config# lldp holdtime-multiplier multiplier
RS G8124config# lldp trap-notification-interval interval
Time-to-Live for Transmitted Information
Trap Notifications
Changing the Lldp Transmit State
Types of Information Transmitted
Lldp Optional Information Types
Lldp Receive Features
RS G8124config# show lldp remote-device index number
Types of Information Received
Viewing Remote Device Information
Time-to-Live for Received Information
Lldp Example Configuration
Bladeos 6.5.2 Application Guide
Simple Network Management Protocol
Snmp Version
Default Configuration
RS G8124config# snmp-server user 1-16authentication-protocol
User Configuration Example
Configuring Snmp Trap Hosts
Configure a user with no authentication and password
Configure an entry in the notify table
SNMPv1 Trap Host
SNMPv2 Trap Host Configuration
SNMPv3 Trap Host Configuration
Enter current admin password
Enter new authentication password
Re-enter new authentication password
Snmp MIBs
Bladeos Snmp agent supports the following standard MIBs
BLADEOS-Supported Enterprise Snmp Traps
An altSwStgBlockingState trap is sent when port
Signifies that the Backup interface is active
Signifies that the Backup interface is not active
Signifies that there was a STG topology change
Switch Images and Configuration Files
MIBs for Switch Image and Configuration Files
Loading a New Switch Image
Loading a Saved Switch Configuration
Saving the Switch Configuration
Saving a Switch Dump
Set the name of dump file
Initiate the transfer. To save a dump file, enter
Part 8 Monitoring
Part 8 Monitoring
Remote Monitoring
Rmon Overview
Example Configuration
Enable Rmon on a port
RS G8124config-if# show interface port 1 rmon-counters
Rmon Group 1-Statistics
History MIB Object ID
Rmon Group 2-History
Last digit x represents the number of the port to monitor
Configure the Rmon History parameters for a port
Configuring Rmon History
View Rmon history for the port
Rmon Group 3-Alarms
Alarm MIB objects
Configuring Rmon Alarms
Configure the Rmon Alarm parameters to track Icmp messages
Rmon Group 9-Events
SFlow Statistical Counters
SFLOW
SFlow Network Sampling
SFlow Example Configuration
RS G8124config# sflow Server
G8124config# Sflow
G8124config# Sflow Enable
Port Mirroring
Mirroring Ports
Configuring Port Mirroring
Enable port mirroring
View the current configuration
RS G8124config# port-mirroring enable
Part 9 Appendices
Part 9 Appendices
Glossary
Two or more virtual routers
Whom to share
224.0.0.18
Network. For a more detailed description, refer to RFC
Index
Default password
214
209
199
355
142
76, 249 to
310
Dense Mode 304, 306
138
303 to
Examples 311 to
154
25, 35, 278
Uplink ports 154 User account
332
Tagging 45, 89 to