Citrix NetScaler
Citrix NetScaler Policy Configuration and Reference Guide
Copyright and Trademark Notice
Contents
Chapter
Converting Text to Hexadecimal Format
Contents
Citrix NetScaler Policy Configuration and Reference Guide
Contents Vii
Reducing Web Server Redirects
Accommodating Browser Dependent Content
Blocking Access by Robots
Blocking Access to Inline Images
About This Guide
Preface
Citrix NetScaler Policy Configuration and Reference Guide
Audience
New in This Release
Preface
Formatting Conventions
Formatting Conventions
Convention Meaning Boldface
Related Documentation
Getting Service and Support
To view the documentation
To provide feedback from the Knowledge Center home
Documentation Feedback
Advanced and Classic Policies
Introduction to Policies Expressions
Basic Components of an Advanced or a Classic Policy
Benefits of Using Advanced Policies
DNS
How Different NetScaler Features Use Policies
NetScaler Feature, Policy Type, and Policy Usage
Chapter Introduction to Policies and Expressions
AAA Traffic Classic
Authorization policies authorize users
Authorization
Associated cache server
Functions
Access Classic
Authorization policies, however, can be
About Actions and Profiles
Authorization. Uses Allow
Use of Actions and Profiles in Different NetScaler Features
Feature Use of an Action Use of a Profile
Pre-Authentication. Uses
Server
About Policy Bindings
About Evaluation Order of Policies
Order of Evaluation Based on Traffic Flow
Advanced and Classic Expressions
About Advanced Expressions
About Classic Expressions
Chapter
Before You Proceed
Citrix NetScaler Policy Configuration and Reference Guide
Configuring Advanced Policies
Advanced-Policy Parameters
Creating or Modifying an Advanced Policy
Argument Specifies
Following is an example of a Rewrite policy and action
Policy Configuration Examples
Feature-Specific Bindings for Advanced Policies
Feature-Specific Differences in Policy Bindings
Binding Advanced Policies
Address of the incoming
Policies Global default Responder function Policy label
NetScalers integrated
Provide rules for modifying
Bind Points and Order of Evaluation
Chapter Configuring Advanced Policies
Advanced Policy Evaluation Across Features
Entries in a Policy Bank
Format of Each Entry in a Policy Bank
Evaluation Order Within a Policy Bank
Optional
How Policy Evaluation Ends
Binding a Policy Globally
How Features Use Actions After Policy Evaluation
Example
Details pane, click Feature Name policy manager
Binding a Policy to a Virtual Server
Displaying Policy Bindings
Unbinding an Advanced Policy
Unbind responder global policyName
Creating a Policy Label
Creating Policy Labels
To create a policy label by using the configuration utility
Attribute Description
Configuring a Policy Label or Virtual Server Policy Bank
Binding a Policy to a Policy Label
Entries in a Policy Bank
Example
Configuring a Policy Label
Choices are Integrated Caching, Rewrite, or Responder
Configure Virtual Server dialog box click the Policies tab
Configuring a Policy Bank for a Virtual Server
Chapter Configuring Advanced Policies
At the NetScaler command prompt, for the Responder, type
Configuring and Binding Policies with the Policy Manager
Click Regenerate Priorities
To remove unused policies by using the Policy Manager
Citrix NetScaler Policy Configuration and Reference Guide
Configuring Advanced Expressions Getting Started
Basic Elements of an Advanced Expression
Expression Characteristics
Prefixes
Http.res.header.myheader
Operations
Feature Types of Expression Prefix Used in the Feature
Features Content Switching
Single-Element Expressions
Basic Operations for Expressions
Basic Operations on Expression Prefixes
Operation Determines whether or not
Compound Advanced Expressions
Configuring Advanced Expressions Getting Started
Basic Types of Operations
String-Based Operations for Compound Advanced Expressions
Booleans in Compound Expressions
Parentheses in Compound Expressions
Compound Operations for Strings
Logical operations on strings
Arithmetic Operations for Compound Advanced Expressions
Compound Operations for Numbers
Result of applying the ~ operator is -11 a binary 1110011
Num % num
Expression on the right
Returns 12 binary
Following example assumes that numeric.expression1 returns
Binary 1100 and numeric.expression2 returns 10 binary
Whole expression evaluates to 8 binary
Right-side number argument number of bits
Integer Number value Following is an example
Number .ADD
Integer Value Following is an example
Number .SUB
Binary value of 10 is 1010, and the result of applying
Number .LE
Integer Integer argument Following is an example
Number .LT
Assumes that numeric.expression returns 12 binary
Result of applying the Bitneg operator is -11 a binary
1110011, 32 bits total with all ones to the left
Expression as an argument rather than an integer
Number.LSHIFT
Bitxor operator to the entire expression is 6 binary
Caret performs a similar function to BITXOR, but takes
Another expression as an argument rather than an integer
Parameters
Number.RSHIFT
Double .ADDi
Value represented by double
Value represented by double is greater than the argument
Double .GEi
Value represented by double is greater than or equal to
Double .GTi
Classic Expressions in Advanced Expressions
Configuring Advanced Expressions in a Policy
Following is an example of configuring a caching policy
HTTP.REQ.BODY1000.BETWEENthis,that
Click Advanced Expressions
Configuring Named Advanced Expressions
Chapter
Citrix NetScaler Policy Configuration and Reference Guide
Advanced Expressions Evaluating Text
About Operations on Text
About Text Expressions
Categories of Text Expressions
Compounding and Precedence in Text Expressions
Chapter Advanced Expressions Evaluating Text
Guidelines for Text Expressions
Prefix Description
Expression Prefixes for Text
Expression Prefixes for Text in Http Requests and Responses
Http Expression Prefixes that Return Text
Address. For information on expressions for IP
Returns the domain name part of the host name. For
Myhost.com8080, the domain is myhost.com
Returns incorrect results if the host name has an IP
URL
LISTT,.COUNT
LISTT,. IGNOREEMPTYELEMENTS.COUNT
HTTP.REQ.USER.EXTERNALGROUPS
HTTP.REQ.USER.GROUPS
HTTP.REQ.USER.INTERNALGROUPS
Returns a list of internal groups to which the user
For example, the following expression returns a
User belongs
Group
Integer argument
Default value of 80 or 443 for Https connections
Returns the Http version listed in the request
Returns a portion of the Http response body.
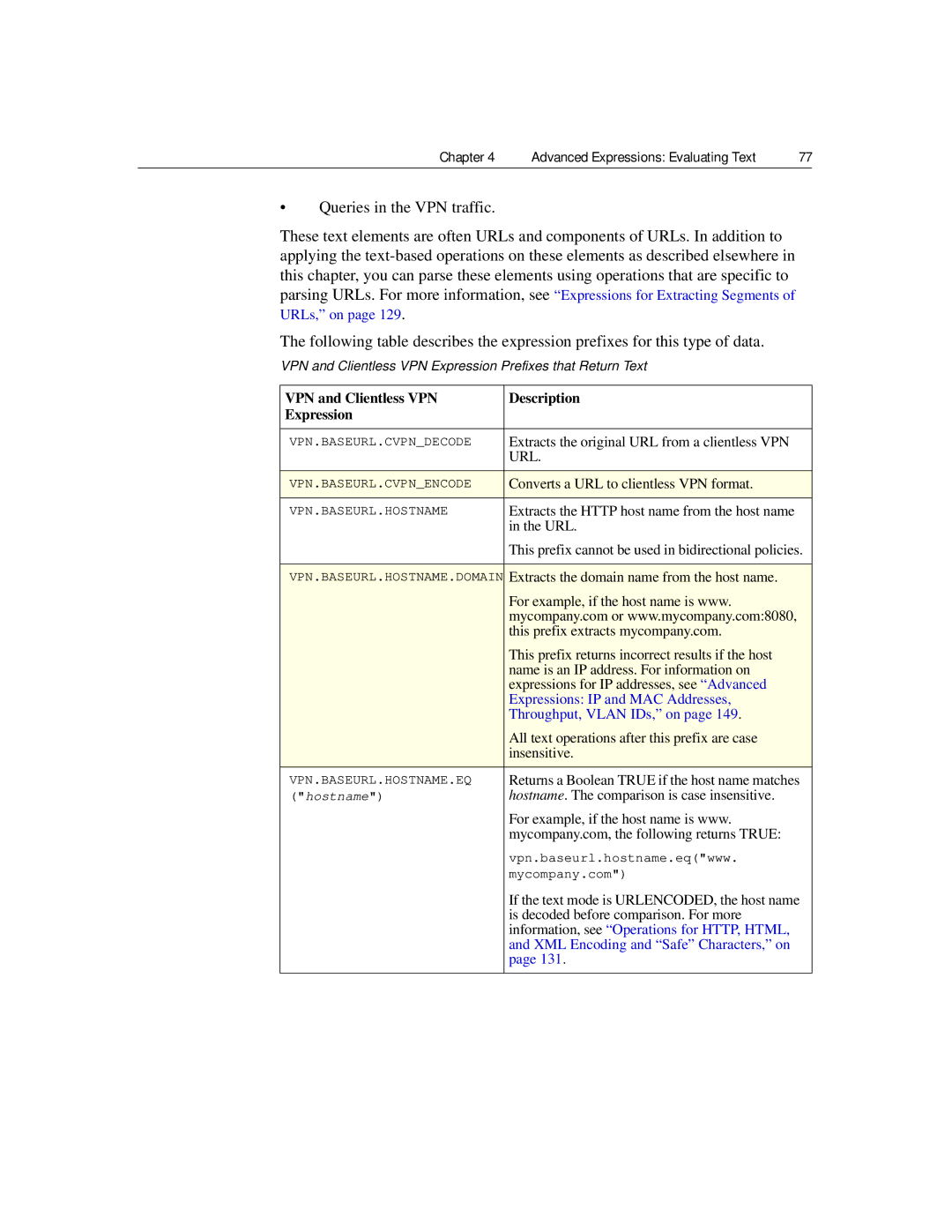
Expression Prefixes for VPNs and Clientless
VPN and Clientless VPN Description Expression
VPN and Clientless VPN Expression Prefixes that Return Text
Extracts a slash- / separated list from the path
By default, is not considered an empty element
When evaluating this header
Evaluates the server portion of the host name
This method ignores the empty elements in a
Extracts a name-value list, using the =
Evaluates the protocol in the URL
Delimiters from the query string in a URL
Hostname
Evaluating this header
Ignores empty elements in a list. For example, if
List delimiter is a comma , the following list
Has an empty element following a=10
As another example, consider the following http
Ignores empty elements in a name-value list. For
Example, the following list contains an empty
Element after a=10
Evaluates the server part of the host name
Results in Boolean True if the host name
Is case insensitive
Following expression returns True
Consider the following header
This method ignores the empty elements in a list
For example, if the delimiter in a list is ,
Entry a=10
Evaluating the same header
Example, the following list uses a semicolon
Preceding example, the element following
=11 is not considered an empty element
Returns a Boolean True value if the target contains
Operations on Text
Basic Operations on Text
Basic Operations on Text
Basic Text Operation Description
Operations for Calculating the Length of a String
Operations for Controlling Case Sensitivity
Operations on Case Sensitivity of Text
Case Operation Description
Complex Operations on Text
Operations on the Length of a String
Operations on Strings Based on a Character Count
Object of 0 length
Operations on a Portion of a String
Basic Operations on a Portion of a String
Character Count Operation Description
Matches ending string
Returns a Boolean True value if the length of the text
Object is greater than or equal to the sum starting string
Matches starting string, and if the suffix of the target
Operation Description
Converting Text to a Hash Value
Raises an Undef if text is not in B64-encoded format
Operator Description
Base64 encoding algorithm
Applying the Base64 decoding algorithm. The operation
Converting Text to Hexadecimal Format
Citrix NetScaler Policy Configuration and Reference Guide
Advanced Expressions Working with Dates, Times, and Numbers
Format of Dates and Times in an Expression
Expressions for the NetScaler System Time
Dates and Times in a Rewrite Action
NetScaler Time Description Operation
Expressions that Return NetScaler System Dates and Times
Advanced Expressions Working with Dates, Times, and Numbers
False depending on the current timezone
Scheduled reboot, and returns an integer
Is equal to the time argument
Sys.time.leGMT 2006 True in this example
Time2
Expressions for SSL Certificate Dates
True
SSL Certificate Operation Description
This example are in parentheses
For example, if the current time is GMT 2005 May
10h 15m 30s, and it is the first Sunday of the month
You can specify the following evaluation results for
Equal to the time argument
Closest boot time is in the past, the integer is
Extracts the last hour that the certificate is valid
Returns a Boolean True if the time precedes or is
To give the weekday in the time value
System time and the specified time and returns an
If it is in the future, the integer is positive
Extracts the last weekday that the certificate is valid
LOCAL, and time2 must be bigger than time1
Returns a Boolean True if the time value is between
Time1, time2 arguments. Both the time1, time2
Arguments must be fully specified
Returns a Boolean True if the time occurs after
Returns a Boolean True if the time is greater than
After or equal to the time argument
Results are in parentheses
NetScaler system time and the specified time as an
Extracts the last minute that the certificate is valid
Returns the current month as an integer from
Returns the number of seconds between the current
Element of time from time2, it is assumed to have
Extracts the last second that the certificate is valid
Returns the current second as an integer from 0 to
6 Saturday
Prefixes That Evaluate Http Date Headers
Expressions for Http Request and Response Dates
111
Citrix NetScaler Policy Configuration and Reference Guide
Advanced Expressions Parsing HTTP, TCP, and UDP Data
About Evaluating the Payload Body
About Evaluating Http and TCP Payload
115
Expressions for Http Headers
Prefixes That Extract Http Headers
Prefixes for Http Headers
Http Header Prefix Description
Advanced Expressions Parsing HTTP, TCP, and UDP Data
For example, the following is a cookie with
Returns the value of Path field of the cookie
As a slash- / separated list. Multiple
First instance is returned
ABC PATH=/a/b/c PORT= 80
Returns the value of Port field of the cookie
Operate as a comma-separated list
From Set-Cookie Customer =
DOMAIN=.xyz.com
Returns the value of the Domain field
First cookie with the specified name. For
Example, the following expression returns a
From the cookie Set-Cookie Customer
Named cookie as a , separated list. For
Header type exists
Operations for Http Headers
Operations That Evaluate Http Headers
Returns the value of Version field of the nth
Does not concatenate the different values
Any instance of the header value
Following is an example of request with two headers
Following returns a Boolean True
Following extracts the string def from the last
STR string
Instance to the first
Following is an example of a request
Instance number argument cannot exceed
Or a response. This operation returns the header that
Occurs instance number of places before the final
Used in bidirectional policies
Cannot exceed
Prefixes for Cache-Control Headers
Operations for Cache-Control Headers
Prefixes That Extract Cache-Control Headers
127
Operations That Evaluate Cache-Control Headers
Http Header Operation Description
Has the value No-Transform
Has the value Min-Fresh
Has the value Max-Stale
Has the value Must-Revalidate
Expressions for Extracting Segments of URLs
URL Prefix Description
Expressions for Numeric Http Payload Data Other Than Dates
Prefixes That Extract URLs
Prefixes That Evaluate Http Request or Response Length
Returns the response status code
Operations That Evaluate Html and XML Encoding
Html or XML Operation Description
Read-only operation
Where xx is a hex-based representation
Specifies how to treat the plus character +.
Converts unsafe URL characters to %xx values
Where WW and XX represent two distinct
With the character Y where XXX represents
Where the colon is the Ascii equivalent
Decoded to http//, where the colon is
Prefixes that Extract TCP and UDP Data
Expressions for TCP, UDP, and Vlan Data
GET Operation Description
NS. This is a name server record that includes a
Enables locating the domain name that is
MX mail exchanger. This DNS record describes
Domain and the priority for each server
XPath and Json Expression Prefixes that Return Text
XPath and Json Expressions
Json file and returns a Boolean True if
Or a string. Node-sets are converted to
XPath string conversion routine
File Book creator person Namename , titletitle
File and returns the corresponding string
For example, consider the following Json
That are enclosed by /Book a node-set
First 1000 bytes of the body of the Json
Bytes of the body
Text.XPATHWITH
MARKUPxp%/Book/creator%
Citrix NetScaler Policy Configuration and Reference Guide
About SSL and Certificate Expressions
Advanced Expressions Parsing SSL Certificates
SSL cryptographic cipher is exportable
Prefixes for Text-Based SSL and Certificate Data
Returns the SSL client certificate in the current
SSL transaction
Expressions for SSL Certificates
Prefixes for Numeric Data in SSL Certificates
Advanced Expressions Parsing SSL Certificates
Returns the Distinguished Name DN
Issuer in the certificate as a name-value list. An
Based on the preceding Issuer definition
Returns a Boolean True if the client has an SSL
= is the delimiter for the name and the value
Returns the Issuer Distinguished Name
An Authority Key Identifier extension
Certificate as a name-value list. An equals sign
False
IGNOREEMPTYELEMENTS.COUNT
CLIENT.SSL.CLIENTCERT.ISSUER
Citrix NetScaler Policy Configuration and Reference Guide
Expressions for IP Addresses and IP Subnets
Operations on IPV4 Addresses
Prefixes for IPV4 Addresses and IP Subnets
Operations for IPV4 Addresses
Prefixes That Evaluate IP and MAC Addresses
Qual1.qual2.qual3.qual4.qual5.qual6
About IPv6 Expressions
Returns the IPv6 address in the source field of the IP
Expression Prefixes for IPv6 Addresses
IPv6 Expression Prefixes that Return Text
IP header
Operations That Evaluate IPv6 Addresses
Operations for IPV6 Prefixes
IPv6 Operation Description
Prefixes That Evaluate MAC Addresses
Expressions for MAC Addresses
Prefixes for MAC Addresses
Operations for MAC Addresses
Prefixes That Evaluate Numeric Client and Server Data
Expressions for Numeric Client and Server Data
155
Citrix NetScaler Policy Configuration and Reference Guide
Matching Text With Strings in a Set
To patternsetname
Operators That Use a Pattern Set
Matching Operators Description
Patternsetname
Setname
Name
Configuring a Pattern Set
161
At a NetScaler command prompt, type
Add policy patset myPatSet
163
Matching Text With a Pattern
Operations for Regular Expressions
Basic Characteristics of Regular Expressions
165
Expression does not match any text in the target
Selects text that precedes the string that matches
Regular expression argument. If the regular
From text/plain
Settextmodeignorecase
Regular Expression Operation Description
From the last to the first
Insensitive, multi-line match, where the dot
Text following the string that matches
Header value. The header instances are matched
First
Transforming Text and Numbers into Different Data Types
Following example selects NS-CACHE-9.0
Typecasting Operations
Delimiter
If the current text mode is Ignorecase and you specify
Are ignored
As the delimiter, an uppercase P is not treated as a
For example, the following policy matches Http requests
Hostname path? query, and the text mode is set to
Urlencoded by default
Treats a numeric string like an IP address
Following Http response header
Following policy extracts a numeric portion of a query
String, adds 4 to the number, and inserts an Http header
For example, this policy would extract 4444 from
HTTP.REQ.COOKIE.TYPECASTHTTPHEADER
HTTP.REQ.SETCOOKIE
HTTP.REQ.COOKIE.TYPECASTHTTPHEADERT
MyHeader to InHeader
Converts the designated text to a multi-line Http header
That you specify in a name argument
For example, the following expression converts
Betweengmt 2004, GMT 2006 True
EQLocal 2005 May True or FALSE, depending on
Time value argument t
Eqgmt 2005 True
Eqgmt 2005 Dec False
Gtgmt 8h True
Gtgmt 2004 True
Gtgmt 2005 Jan True
GTLocal 2005 May True or FALSE, depending on
Legmt 8h False
Legmt 2006 True
Legmt 2005 Dec True
LELocal 2005 May True or FALSE, depending on
Value as an integer that ranges from 1 January to
Most recent reboot or the number of seconds to the next
Time is in the future scheduled reboot time, the integer is
Value as an integer that ranges from 0 to
Time1 and time2
Transforms the double-precision number represented by
Extracts the year from the current system time and returns
Double to an integer
About Policies that Monitor the Traffic Rate
Advanced Policies Controlling Rate of Traffic
Expressions for Controlling the Traffic Rate
Configuring Policies That Control the Traffic Rate
Chapter
About Http Callout Policies
About Calling Out to an External Application
187
Following is an example of a response
Elements in an Http Callout Policy
Configuring an Http Callout Policy
Parameter Specifies
URL stem expression urlStemExpr
Attribute-based Http Method httpMethod
Server mutually
Expression that derives the value. Examples
Must manually validate the request
Example, if you configure a return type of text, the result
Expression to 8191 characters
NetScaler does not check the validity of this request. You
191
Examples
To modify a callout policy using the NetScaler command line
193
To delete a callout policy using the NetScaler command line
To view a callout policy using the NetScaler command line
Invoking an Http Callout Policy
If the return type is NUM, the following expression is valid
195
Citrix NetScaler Policy Configuration and Reference Guide
Where Classic Policies Are Used
Configuring Classic Policies Expressions
Http
Auditing of user access
Configuring Classic Policies and Expressions
Click Policies
Viewing Classic Policies
201
Configuring a Classic Policy
To create a classic policy using the NetScaler command line
At the command line, type
203
Configuring a Classic Expression
REQ.IP.SOURCEIP == 200.0.0.0 -netmask
205
Flow Type.protocol.qualifier.operator.value.header Name
207
Binding a Classic Policy
Configure Virtual Server dialog box, click the Policies tab
209
Creating Named Classic Expressions
Citrix NetScaler Policy Configuration and Reference Guide
Advanced Expressions
Expressions Reference
Expression Prefix Descriptions
Citrix NetScaler Policy Configuration and Reference Guide
Appendix a Expressions Reference
Operates on the Vlan through which the current
Expression Prefixes for Text in Http
Ignores spaces in the data. See the table Http
Appendix a Expressions Reference 217
Obtains the Expires field of the cookie as a date
Appendix a Expressions Reference 219
SERVER.INTERFACE.ID.EQLA/1
Appendix a Expressions Reference 221
Ignores spaces in the data. For an example, see
VPNs, on
Appendix a Expressions Reference 223
Operators
Classic Expressions
Expression Element Definition
Appendix a Expressions Reference 225
General Expressions
REQ.SSL.CLIENT.CERT
REQ.SSL.CLIENT.CERT.ISSUER
REQ.HTTP.URLQUERYLEN
REQ.SSL
Appendix a Expressions Reference 227
Expression Element
Client Security Expressions
Actual Expression Definition
Appendix a Expressions Reference 229
Network-Based Expressions
Expression Definition
Date
Date/Time Expressions
File System Expressions
Time
Appendix a Expressions Reference 231
Built-In Named Expressions General
Always returns a value of False
Appendix a Expressions Reference 233
Nsmsexcel Nsmsie Nsmsppt Nsmsword
Nsfarclient
Nstrue Nsurlpathbin
Built-InNamed Expressions Personal Firewall
Built-InNamed Expressions Anti-Virus
Appendix a Expressions Reference 235
Expression Definition Norton Internet Security
Built-InNamed Expressions Client Security
Any version of Norton Internet Security
Examples of Advanced Expressions
Summary Examples of Advanced Expressions and Policies
Expression Type Sample Expressions
Extension
Content-Type header
Look for a particular file type in an
Http request based on the file
Purpose Example
Examples of Advanced Expressions and Policies
Modify a URL to redirect
To https// in all URLs
This policy uses
Responder functionality
Check the client IP
Limit the number
Through unchanged
Request and insert an
Remove old headers from
NS-Client header
Header action so that
Request, insert an
NS-Client header,
Then modify the insert
Citrix NetScaler Policy Configuration and Reference Guide
Redirecting an External URL to an Internal URL
Tutorial Examples of Advanced Policies for Rewrite
Bind the policy globally
247
Redirecting a Query
Redirecting Http to Https
Appendix C
Removing Unwanted Headers
Masking the Server Header
Reducing Web Server Redirects
249
Add rewrite policy polmask-server true actmask-server
Tutorial Examples of Classic Policies
Citrix NetScaler Policy Configuration and Reference Guide
Appendix D Tutorial Examples of Classic Policies 253
REQ.HTTP.HEADER URL Contains string
Appendix D Tutorial Examples of Classic Policies 255
Application Firewall Policy to Protect Scripted Web Pages
DNS Policy to Drop Packets from Specific IPs
Add dns policy polddosdrop
SSL Policy to Require Valid Client Certificates
Citrix NetScaler Policy Configuration and Reference Guide
Migration of Apache modrewrite Rules to Advanced Policies
Converting Host Name Variations to Canonical Host Names
Apache modrewrite solution for converting a URL
NetScaler solution for converting a URL
Converting URL Variations into Canonical URLs
Appendix E
Apache modrewrite solution for moving the document root
NetScaler solution for moving the document root
Moving a Document Root
Working with Structured Home Directories
Moving Home Directories to a New Web Server
Redirecting Invalid URLs to Other Web Servers
Apache modrewrite solution for structured home directories
NetScaler solution for structured home directories
NetScaler solution for redirection if a URL is wrong method
Rewriting a URL Based on Time
NetScaler solution for rewriting a URL based on the time
Redirecting to New File Name User-Visible URL
Redirecting to a New File Name Invisible to the User
265
Apache modrewrite solution for browser-specific settings
Accommodating Browser Dependent Content
267
Blocking Access by Robots
NetScaler solution for blocking access to an inline image
Blocking Access to Inline Images
Creating Extensionless Links
NetScaler policy for adding a .php extension to all requests
269
Redirecting a Working URI to a New Format
Apache modrewrite solution
Ensuring That a Secure Server Is Used for Selected Pages
NetScaler solution
NetScaler solution using regular expressions
NetScaler solution using pattern sets
Bind patset pat1 page4 Bind patset pat1 page5
Number.TYPECASTIPADDRESSAT
New Advanced Expression Operators in This Release
Operators for Extracting and Evaluating Numeric Data
New Operators for Extracting and Evaluating Numeric Data
New Operators for Evaluating Text
Operators for Extracting and Evaluating Text
Operators Operation
Operators for Client and ipv6 Expression Prefixes
Operators for Extracting and Evaluating Http Data
Operators for the Client and ipv6 Expression Prefixes
New Operators for Extracting and Evaluating Http data
Operators for Evaluating Groups to Which a User Belongs
XPath and Json Operators for Evaluating XML and Json Data
Operators for Evaluating Groups to Which a User Belongs
XPath and Json Operators for Evaluating XML and Json Text
Index
Introduction to 224 migration to advanced
RES.VLANID
Index 279
CLIENT.ETHER.DSTMAC
HTTP.RES.SETCOOKIE2.COOKIEname, i
Index
Omain 82 VPN.CLIENTLESSHOSTURL.HOSTNAME.E
Authkeyid
Citrix NetScaler Policy Configuration and Reference Guide
Index
Useinvocationresult
VPN 65 Character 57 ? character
Citrix NetScaler Policy Configuration and Reference Guide