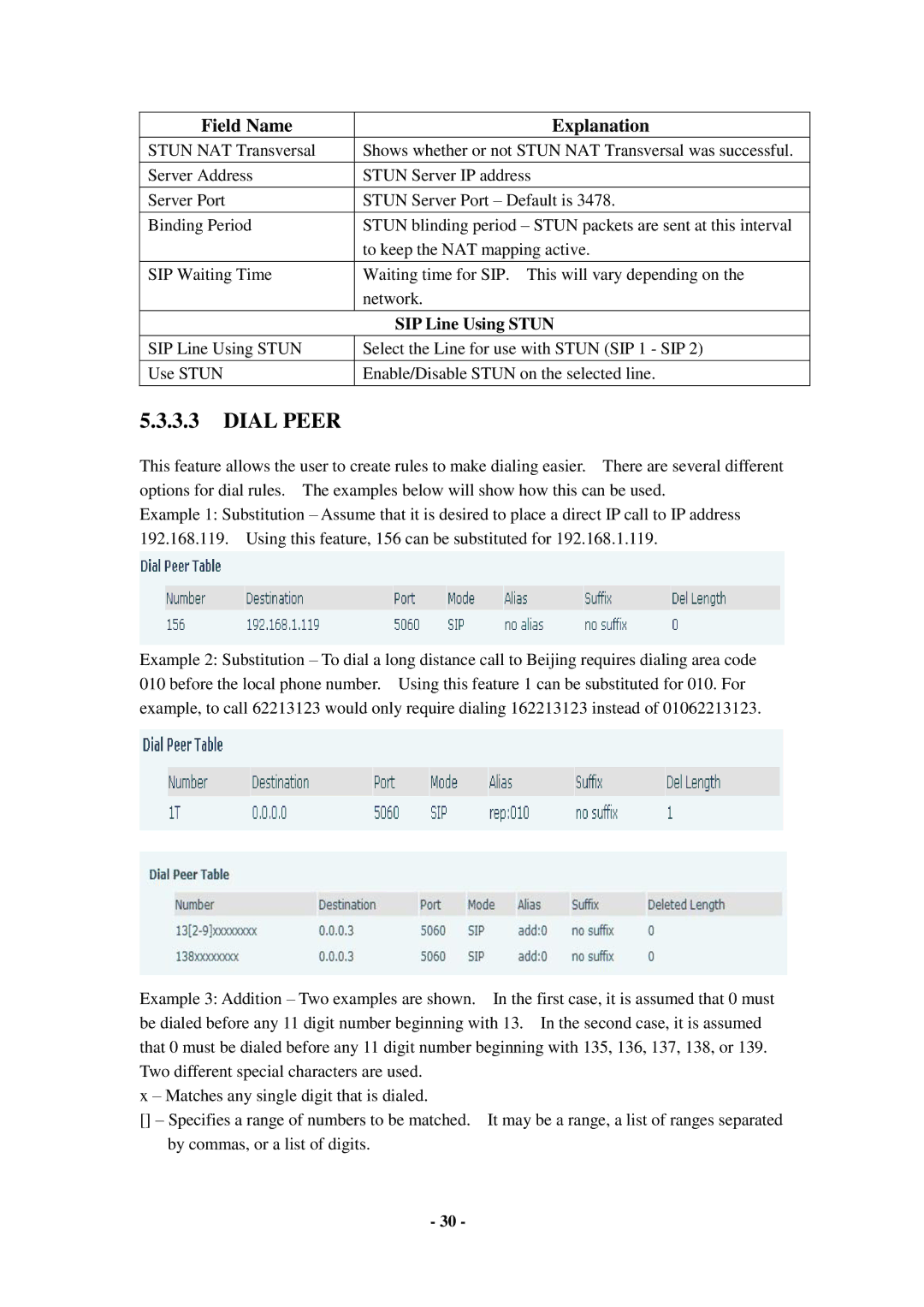
Field Name | Explanation |
STUN NAT Transversal | Shows whether or not STUN NAT Transversal was successful. |
|
|
Server Address | STUN Server IP address |
|
|
Server Port | STUN Server Port – Default is 3478. |
|
|
Binding Period | STUN blinding period – STUN packets are sent at this interval |
| to keep the NAT mapping active. |
|
|
SIP Waiting Time | Waiting time for SIP. This will vary depending on the |
| network. |
|
|
| SIP Line Using STUN |
|
|
SIP Line Using STUN | Select the Line for use with STUN (SIP 1 - SIP 2) |
|
|
Use STUN | Enable/Disable STUN on the selected line. |
|
|
5.3.3.3DIAL PEER
This feature allows the user to create rules to make dialing easier. There are several different options for dial rules. The examples below will show how this can be used.
Example 1: Substitution – Assume that it is desired to place a direct IP call to IP address 192.168.119. Using this feature, 156 can be substituted for 192.168.1.119.
Example 2: Substitution – To dial a long distance call to Beijing requires dialing area code 010 before the local phone number. Using this feature 1 can be substituted for 010. For example, to call 62213123 would only require dialing 162213123 instead of 01062213123.
Example 3: Addition – Two examples are shown. In the first case, it is assumed that 0 must be dialed before any 11 digit number beginning with 13. In the second case, it is assumed that 0 must be dialed before any 11 digit number beginning with 135, 136, 137, 138, or 139. Two different special characters are used.
x – Matches any single digit that is dialed.
[] – Specifies a range of numbers to be matched. It may be a range, a list of ranges separated by commas, or a list of digits.
- 30 -