Low Average Active Power | Figure 4. Current Versus Cycle Time (Write) |
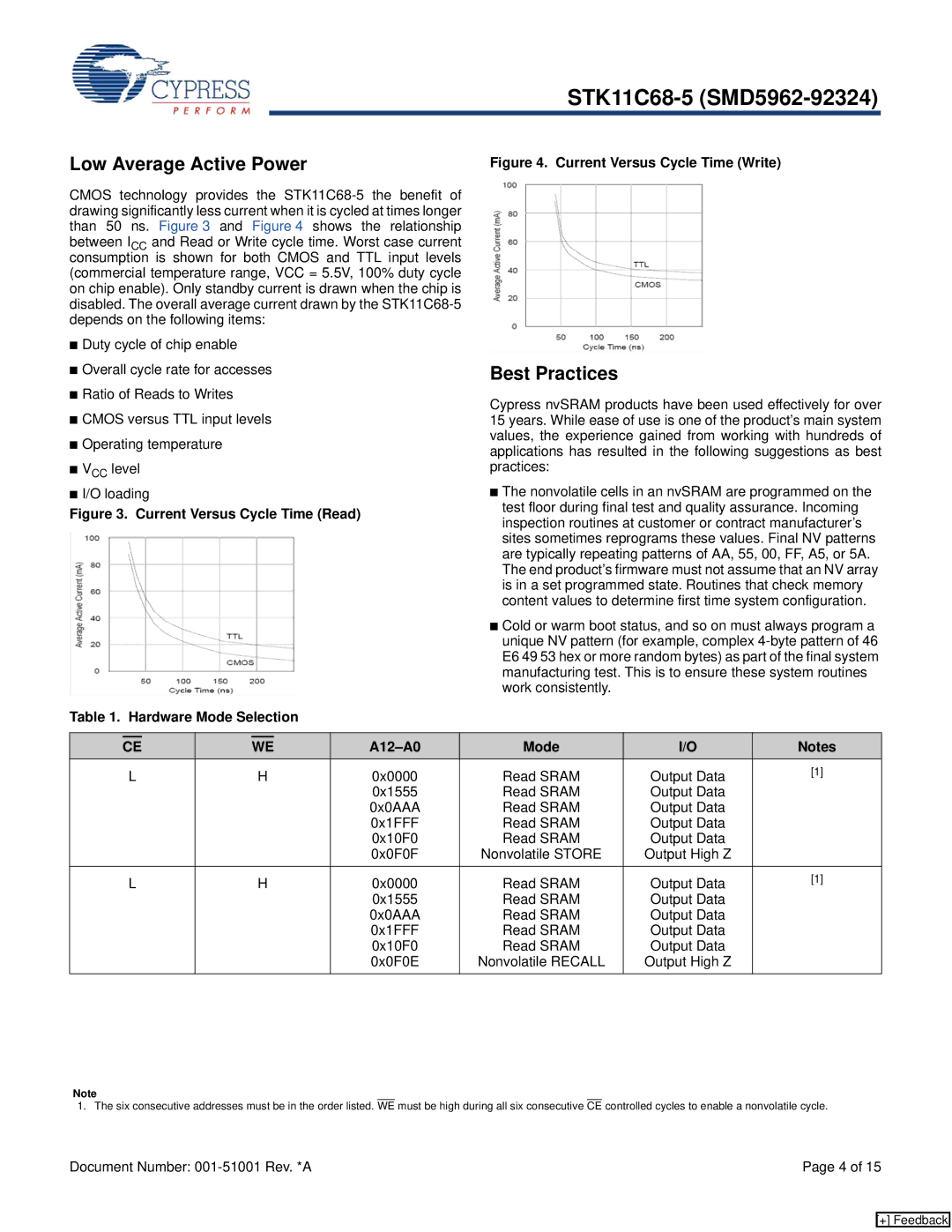
CMOS technology provides the
■Duty cycle of chip enable
■Overall cycle rate for accesses
■Ratio of Reads to Writes
■CMOS versus TTL input levels
■Operating temperature
■VCC level
■I/O loading
Figure 3. Current Versus Cycle Time (Read)
Best Practices
Cypress nvSRAM products have been used effectively for over 15 years. While ease of use is one of the product’s main system values, the experience gained from working with hundreds of applications has resulted in the following suggestions as best practices:
■The nonvolatile cells in an nvSRAM are programmed on the test floor during final test and quality assurance. Incoming inspection routines at customer or contract manufacturer’s sites sometimes reprograms these values. Final NV patterns are typically repeating patterns of AA, 55, 00, FF, A5, or 5A. The end product’s firmware must not assume that an NV array is in a set programmed state. Routines that check memory content values to determine first time system configuration.
■Cold or warm boot status, and so on must always program a unique NV pattern (for example, complex
Table 1. Hardware Mode Selection
| CE |
|
| WE |
|
| Mode | I/O | Notes |
| L |
|
| H |
| 0x0000 | Read SRAM | Output Data | [1] |
|
|
|
|
|
| 0x1555 | Read SRAM | Output Data |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 0x0AAA | Read SRAM | Output Data |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 0x1FFF | Read SRAM | Output Data |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 0x10F0 | Read SRAM | Output Data |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 0x0F0F | Nonvolatile STORE | Output High Z |
|
| L |
|
| H |
| 0x0000 | Read SRAM | Output Data | [1] |
|
|
|
|
|
| 0x1555 | Read SRAM | Output Data |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 0x0AAA | Read SRAM | Output Data |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 0x1FFF | Read SRAM | Output Data |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 0x10F0 | Read SRAM | Output Data |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 0x0F0E | Nonvolatile RECALL | Output High Z |
|
Note
1. The six consecutive addresses must be in the order listed. WE must be high during all six consecutive CE controlled cycles to enable a nonvolatile cycle.
Document Number: | Page 4 of 15 |
[+] Feedback