Quick Installation Guide
Rosemount 8712 / 8700 Series
00825-0100-4664, Rev BB January 2013
STEP 6: WIRING
Conduit Ports and Connections
This wiring section covers the connection between the transmitter and sensor, the 4-20 mA loop, and supplying power to the transmitter. Follow the conduit information, cable requirements, and disconnect requirements in the sections below.
Conduit Ports and Connections
Both the sensor and transmitter junction boxes have ports for 1/2-inch NPT conduit connections with optional CM20 or PG 13.5 connections available. These connections should be made in accordance with national, local, and plant electrical codes. Unused ports should be sealed with metal plugs. Proper electrical installation is necessary to prevent errors due to electrical noise and interference. Separate conduits are not necessary for the coil drive and signal cables, but a dedicated conduit line between each transmitter and sensor is required. Shielded cable must be used for best results in electrically noisy environments. When preparing all wire connections, remove only the insulation required to fit the wire completely under the terminal connection. Removal of excessive insulation may result in an unwanted electrical short to the transmitter housing or other wire connections. For flanged sensors installed into an application requiring IP68 protection, sealed cable glands, conduit, and conduit plugs that meet IP68 ratings are required.
Conduit Requirements
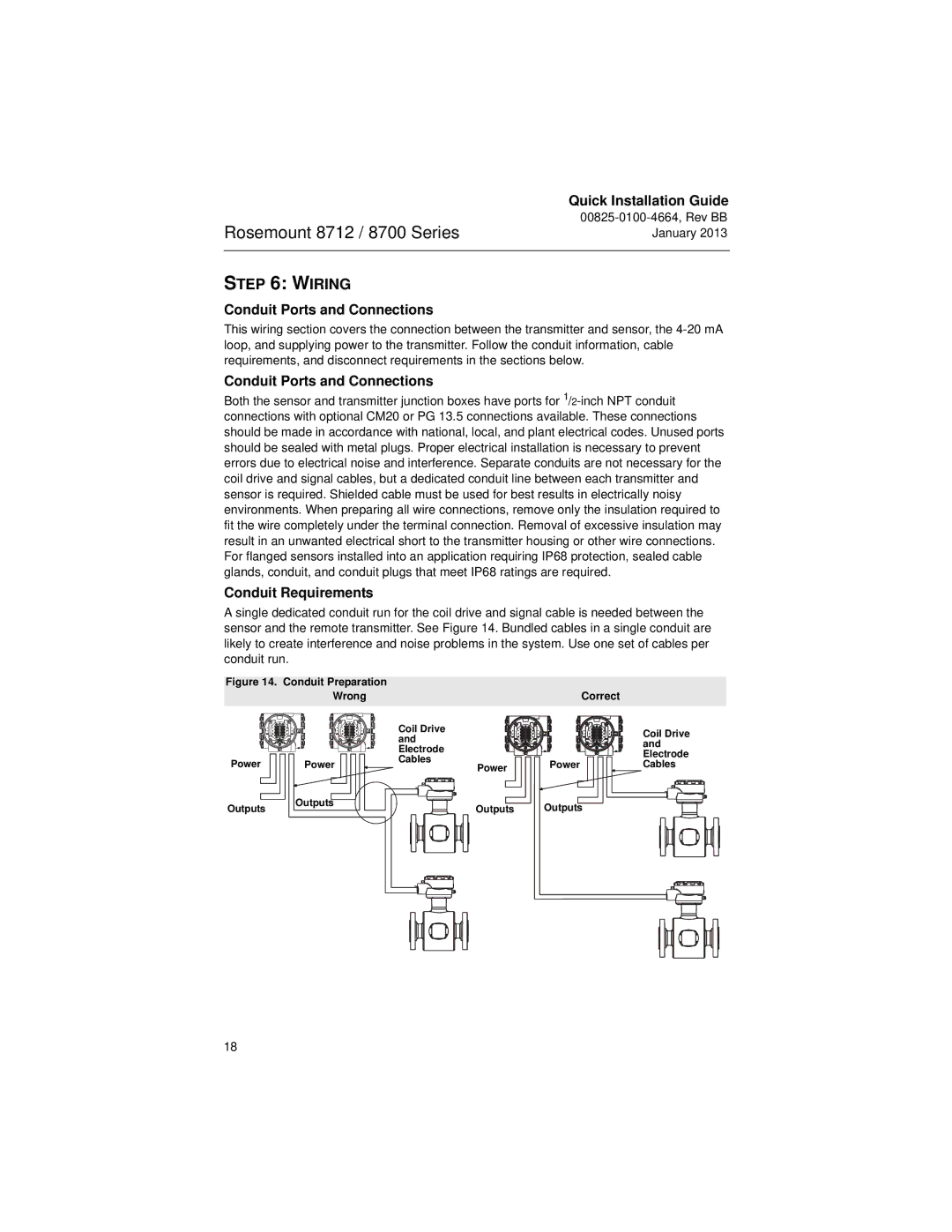
A single dedicated conduit run for the coil drive and signal cable is needed between the sensor and the remote transmitter. See Figure 14. Bundled cables in a single conduit are likely to create interference and noise problems in the system. Use one set of cables per conduit run.
Figure 14. Conduit Preparation | |
Wrong | Correct |
Power
Outputs
Coil Drive and Electrode Cables
Power
Outputs
Coil Drive and Electrode Cables