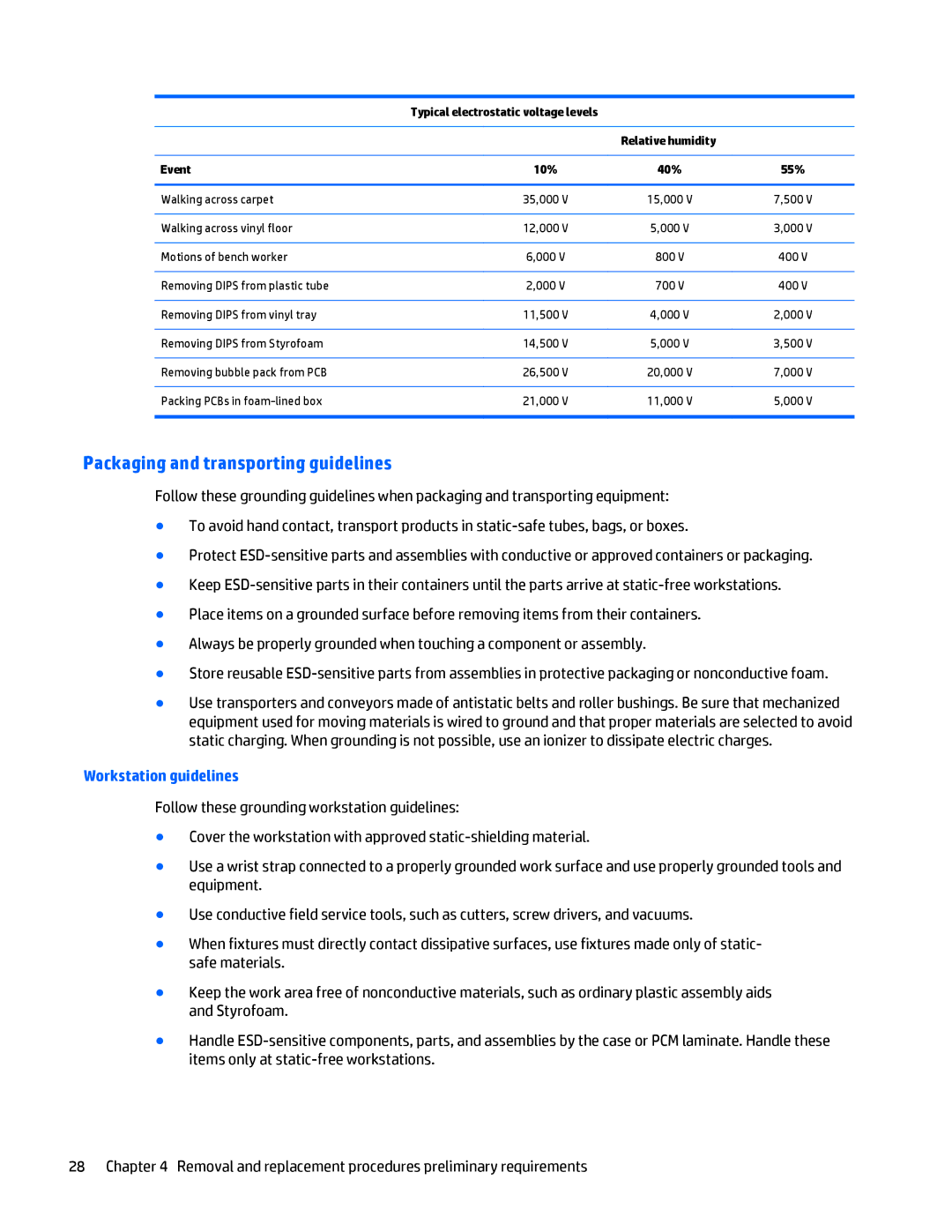
Typical electrostatic voltage levels
|
| Relative humidity |
|
|
|
|
|
Event | 10% | 40% | 55% |
|
|
|
|
Walking across carpet | 35,000 V | 15,000 V | 7,500 V |
|
|
|
|
Walking across vinyl floor | 12,000 V | 5,000 V | 3,000 V |
|
|
|
|
Motions of bench worker | 6,000 V | 800 V | 400 V |
|
|
|
|
Removing DIPS from plastic tube | 2,000 V | 700 V | 400 V |
|
|
|
|
Removing DIPS from vinyl tray | 11,500 V | 4,000 V | 2,000 V |
|
|
|
|
Removing DIPS from Styrofoam | 14,500 V | 5,000 V | 3,500 V |
|
|
|
|
Removing bubble pack from PCB | 26,500 V | 20,000 V | 7,000 V |
|
|
|
|
Packing PCBs in | 21,000 V | 11,000 V | 5,000 V |
|
|
|
|
Packaging and transporting guidelines
Follow these grounding guidelines when packaging and transporting equipment:
●To avoid hand contact, transport products in
●Protect
●Keep
●Place items on a grounded surface before removing items from their containers.
●Always be properly grounded when touching a component or assembly.
●Store reusable
●Use transporters and conveyors made of antistatic belts and roller bushings. Be sure that mechanized equipment used for moving materials is wired to ground and that proper materials are selected to avoid static charging. When grounding is not possible, use an ionizer to dissipate electric charges.
Workstation guidelines
Follow these grounding workstation guidelines:
●Cover the workstation with approved
●Use a wrist strap connected to a properly grounded work surface and use properly grounded tools and equipment.
●Use conductive field service tools, such as cutters, screw drivers, and vacuums.
●When fixtures must directly contact dissipative surfaces, use fixtures made only of static- safe materials.
●Keep the work area free of nonconductive materials, such as ordinary plastic assembly aids and Styrofoam.
●Handle
28 Chapter 4 Removal and replacement procedures preliminary requirements