4- 1. ANTENNA
The Performance of the transceiver depends upon the type of antenna to be used. To ensure the maximum perfor- mance of the
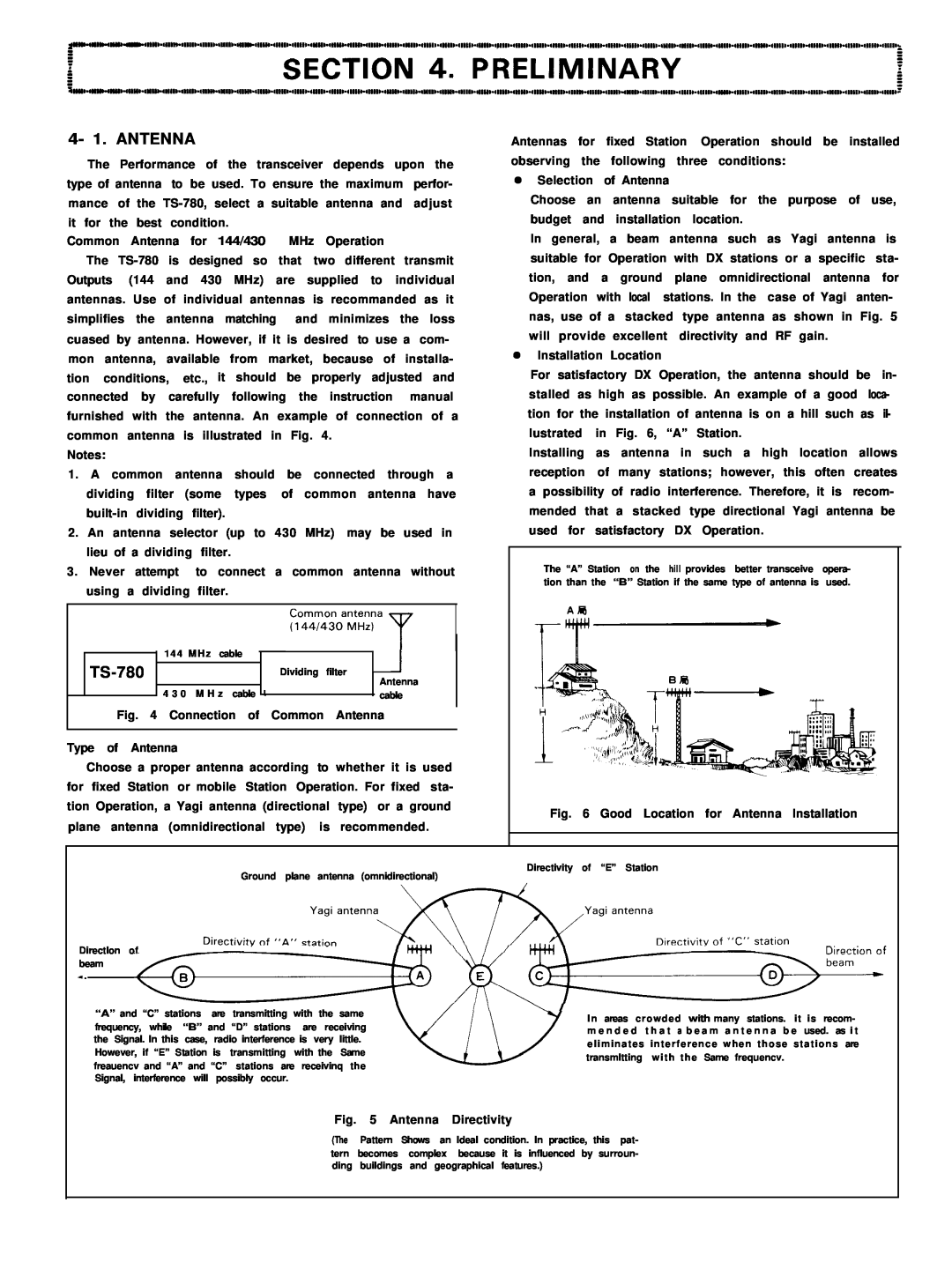
Common Antenna for 144/430 MHz Operation
The
Notes:
1.A common antenna should be connected through a dividing filter (some types of common antenna have
2.An antenna selector (up to 430 MHz) may be used in lieu of a dividing filter.
3.Never attempt to connect a common antenna without using a dividing filter.
|
| 144 MHz cable |
|
|
| Dividing filter | Antenna |
|
|
|
|
| |||
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
| 4 3 0 M H z cable |
| L |
| cable | |
|
|
|
| ||||
Fig. 4 Connection of Common Antenna | I |
|
Type of Antenna
Choose a proper antenna according to whether it is used for fixed Station or mobile Station Operation. For fixed sta- tion Operation, a Yagi antenna (directional type) or a ground plane antenna (omnidirectional type) is recommended.
Antennas for fixed Station Operation should be installed observing the following three conditions:
•Selection of Antenna
Choose an antenna suitable for the purpose of use, budget and installation location.
In general, a beam antenna such as Yagi antenna is suitable for Operation with DX stations or a specific sta- tion, and a ground plane omnidirectional antenna for Operation with local stations. In the case of Yagi anten- nas, use of a stacked type antenna as shown in Fig. 5 will provide excellent directivity and RF gain.
•Installation Location
For satisfactory DX Operation, the antenna should be in- stalled as high as possible. An example of a good loca- tion for the installation of antenna is on a hill such as il- lustrated in Fig. 6, “A” Station.
Installing as antenna in such a high location allows reception of many stations; however, this often creates a possibility of radio interference. Therefore, it is recom- mended that a stacked type directional Yagi antenna be used for satisfactory DX Operation.
The “A” Station on the hill provides better transceive opera- tion than the “B” Station if the same type of antenna is used.
Fig. 6 Good Location for Antenna Installation
Directivity of “E” Station
Ground plane antenna (omnidirectional)
Directlon of *beam.
“A” and “C” stations are transmitting with the same frequency, while “B” and “D” stations are receiving the Signal. In this case, radio interference is very little.
However, if “E” Station is transmitting with the Same freauencv and “A” and “C” stations are receivinq the Signal, interference will possibly occur.
In areas crowded with many stations. it is recom- m e n d e d t h a t a b e a m a n t e n n a b e used. as i t eliminates interference when those stations are transmltting with the Same frequencv.
Fig. 5 Antenna Directivity
(The Pattern Shows an Ideal condition. In practice, this pat- tern becomes complex because it is influenced by surroun- ding buildings and geographical features.)