| Functional Details |
When reading synchronously, all counters are set to zero at the start of an acquisition. When reading asynchronously, counters may be cleared on each read, count up continually, or count until the
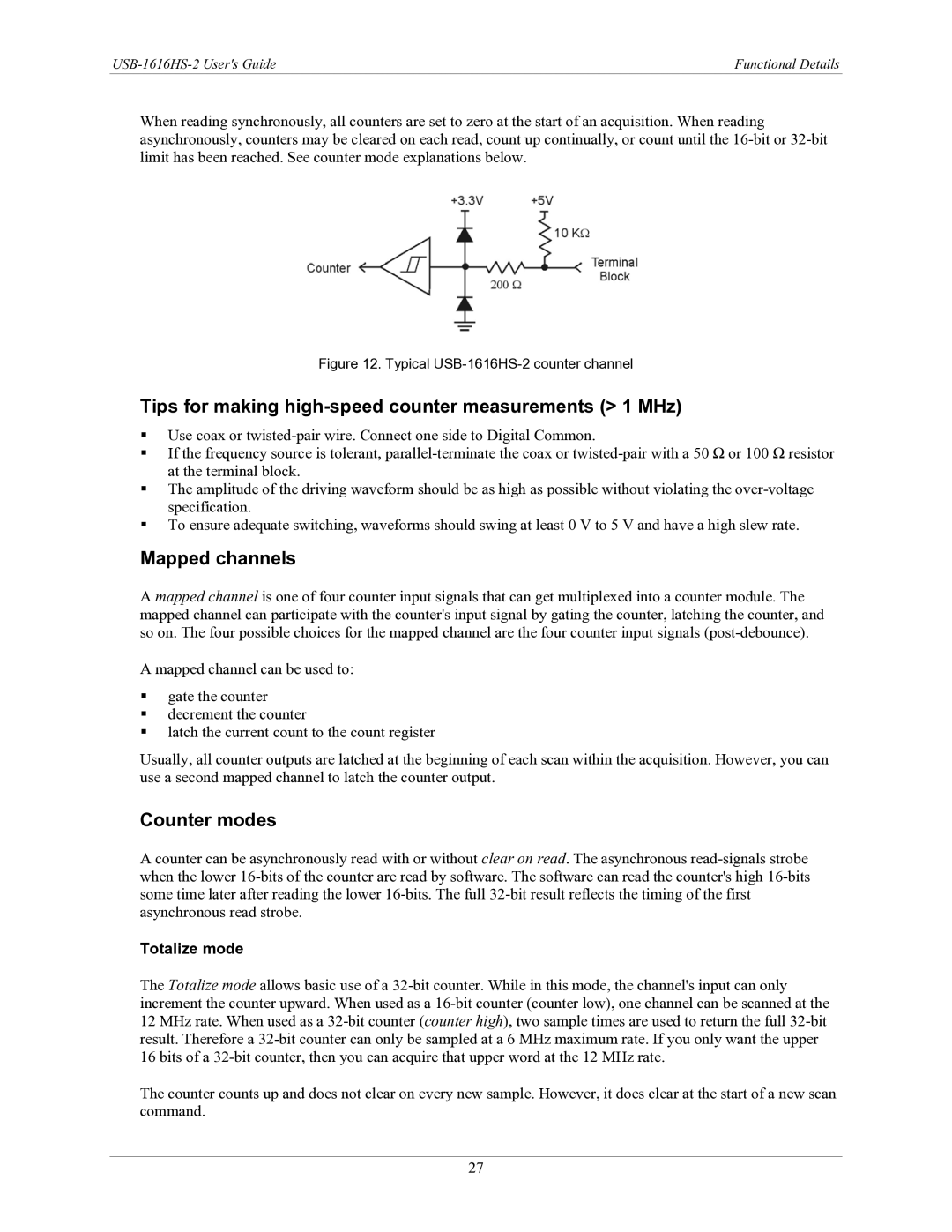
Figure 12. Typical USB-1616HS-2 counter channel
Tips for making high-speed counter measurements (> 1 MHz)
Use coax or
If the frequency source is tolerant,
The amplitude of the driving waveform should be as high as possible without violating the
To ensure adequate switching, waveforms should swing at least 0 V to 5 V and have a high slew rate.
Mapped channels
A mapped channel is one of four counter input signals that can get multiplexed into a counter module. The mapped channel can participate with the counter's input signal by gating the counter, latching the counter, and so on. The four possible choices for the mapped channel are the four counter input signals
A mapped channel can be used to:
gate the counter
decrement the counter
latch the current count to the count register
Usually, all counter outputs are latched at the beginning of each scan within the acquisition. However, you can use a second mapped channel to latch the counter output.
Counter modes
A counter can be asynchronously read with or without clear on read. The asynchronous
Totalize mode
The Totalize mode allows basic use of a
The counter counts up and does not clear on every new sample. However, it does clear at the start of a new scan command.
27