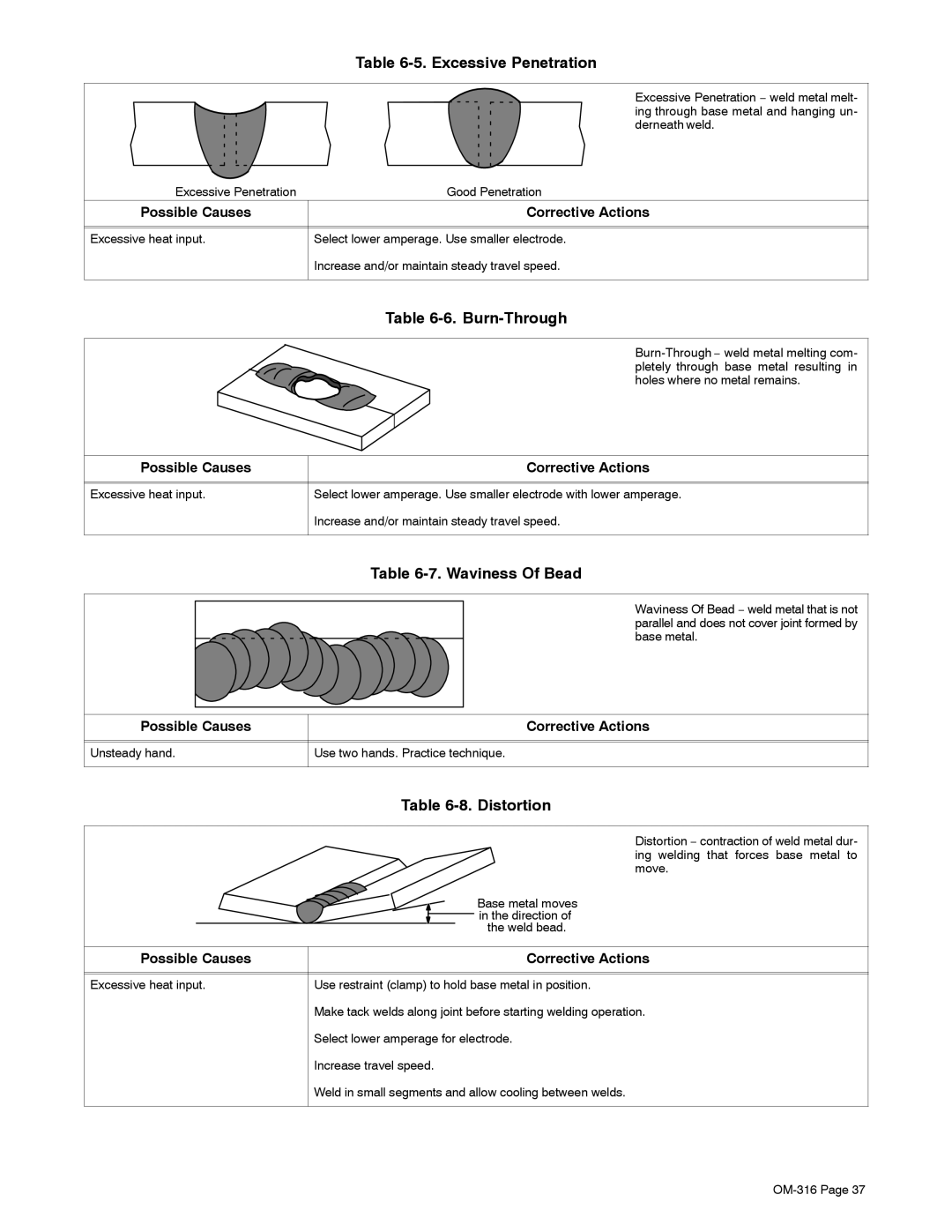
| Table |
| Excessive Penetration − weld metal melt- |
| ing through base metal and hanging un- |
| derneath weld. |
Excessive Penetration | Good Penetration |
Possible Causes | Corrective Actions |
Excessive heat input. | Select lower amperage. Use smaller electrode. |
| Increase and/or maintain steady travel speed. |
| Table |
| |
| pletely through base metal resulting in |
| holes where no metal remains. |
Possible Causes | Corrective Actions |
|
|
|
|
Excessive heat input. | Select lower amperage. Use smaller electrode with lower amperage. |
| Increase and/or maintain steady travel speed. |
|
|
Table 6-7. Waviness Of Bead
Waviness Of Bead − weld metal that is not parallel and does not cover joint formed by base metal.
Possible Causes | Corrective Actions |
|
|
|
|
Unsteady hand. | Use two hands. Practice technique. |
|
|
Table 6-8. Distortion
Distortion − contraction of weld metal dur- ing welding that forces base metal to move.
|
|
| Base metal moves |
|
|
| in the direction of |
|
|
| |
|
|
| the weld bead. |
|
|
|
|
Possible Causes |
|
| Corrective Actions |
|
| ||
|
| ||
Excessive heat input. | Use restraint (clamp) to hold base metal in position. | ||
| Make tack welds along joint before starting welding operation. | ||
| Select lower amperage for electrode. | ||
| Increase travel speed. | ||
| Weld in small segments and allow cooling between welds. | ||
|
|
|
|