202-10085-01, March
Statement of Conditions
Trademarks
EN 55 022 Declaration of Conformance
Bestätigung des Herstellers/Importeurs
Additional Copyrights
Certificate of the Manufacturer/Importer
Voluntary Control Council for Interference Vcci Statement
202-10085-01, March
MD5
Product and Publication Details
Contents
Chapter Connecting the FVS124G to the Internet
Chapter LAN Configuration
Chapter Router and Network Management
Chapter Troubleshooting
Appendix C Preparing Your Network
Appendix D Virtual Private Networking
Glossary-5
Manual Scope
Audience, Scope, Conventions, and Formats
Typographical Conventions
How to Use This Manual
Printing a Page in the Html View
How to Print this Manual
About This Manual
Chapter Introduction
Key Features of the VPN Firewall
Powerful, True Firewall with Content Filtering
Autosensing Ethernet Connections with Auto Uplink
Security
Extensive Protocol Support
Easy Installation and Management
Package Contents
FVS124G Front Panel
Router’s Front Panel
Object Activity Description
Router’s Rear Panel
FVS124G Rear Panel
Router’s IP Address, Login Name, and Password
FVS124G Bottom Label
Logging into the Router
Login screen on the Web browser
Default Factory Settings
Netgear Related Products
Factory Default Settings
Introduction
Virtual Private Networks VPNs
Overview of the Planning Process
Inbound Traffic
Port rolls over, the VPN tunnel collapses and address
Ports
Inbound Traffic
That the public and enabled
Always change at
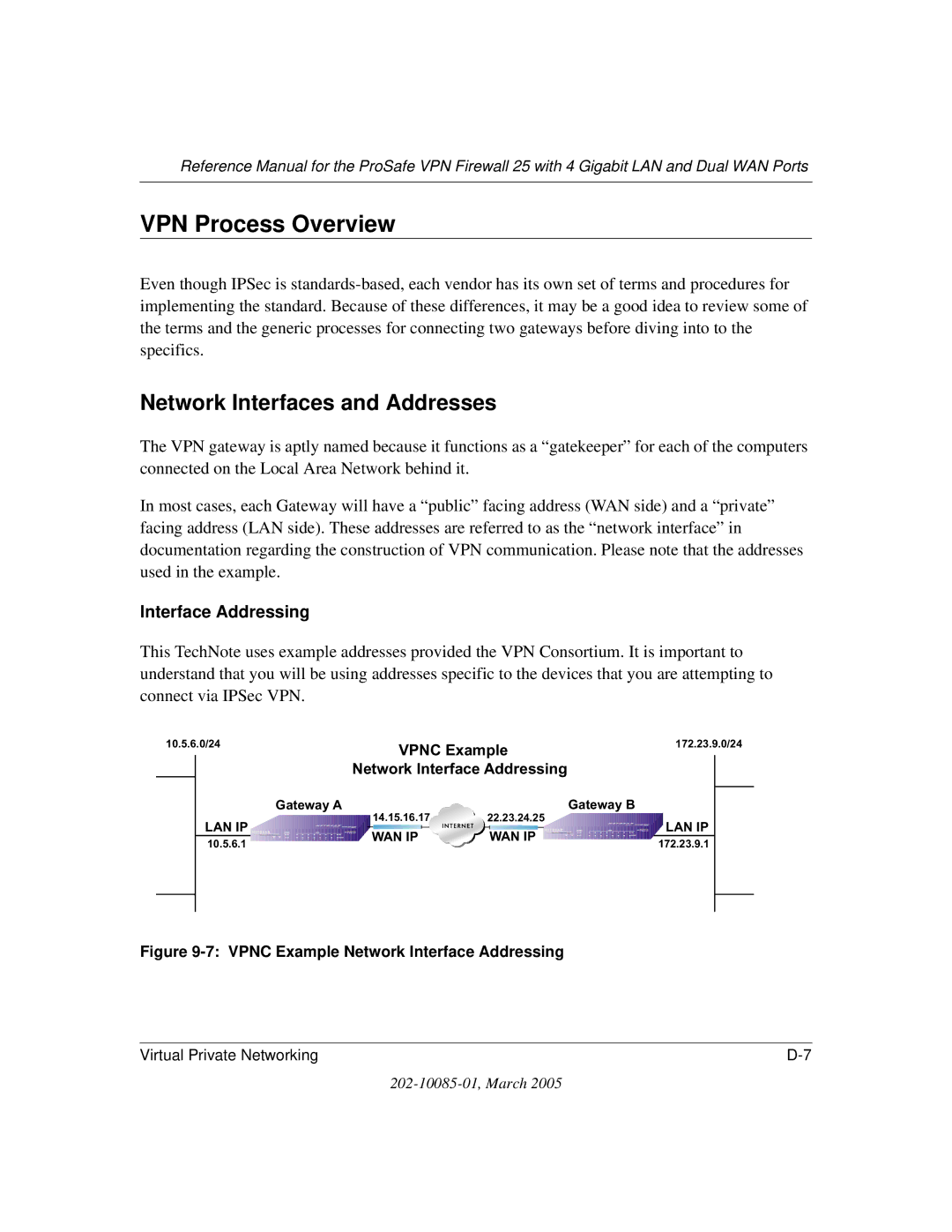
IP addressing requirements for VPNs in dual WAN port systems
Virtual Private Networks VPNs
VPN Road Warrior
Dual
Road Warrior Example Single WAN Port
Domain i.e., the IP
Road Warrior Example Dual WAN Ports, After Rollover
Domain
Gateway
13, either of the gateway WAN
For Improved Reliability
Gateway-to-Gateway Example Dual WAN Ports, After Rollover
VPN Telecommuter Client-to-Gateway Through a NAT Router
Gigabit LAN and Dual WAN Ports
Address to establish or re-establish a VPN Remote PC Or WAN2
What You Will Need to Do Before You Begin
Connecting the FVS124G to the Internet
Postulated WAN provisioning used in this document Internet
Customer premises Route diversity WAN port Physical facility
Cabling and Computer Hardware Requirements
Computer Network Configuration Requirements
Where Do I Get the Internet Configuration Parameters?
Internet Configuration Requirements
Record Your Internet Connection Information
Connect the firewall physically to your network required
Log in to the VPN Firewall Required
Physically Connect the VPN Firewall to Your Network Required
Configure the Internet Connections to Your ISPs Required
WAN1 screens WAN2 screens
WAN1 and WAN2 Basic Settings and Setup Wizard Screens
Connection Method Data Required
Internet connection methods
Connecting the FVS124G to the Internet
ISP Does Not Require Login
Manually Configuring Your Internet Connection
Traffic Meter screens
Programming the Traffic Meter if Desired
Parameter Description
Traffic meter
Configure the WAN Mode Required for Dual WAN
WAN Mode screen for auto-rollover
Rollover Setup
Load Balancing and Protocol Binding Setup
WAN Mode screen for load balancing and protocol binding
Connecting the FVS124G to the Internet
Configure Dynamic DNS If Needed
Dynamic DNS screens
Dynamic DNS service provider screens
Each DNS service provider requires its own parameters Figure
10 WAN Options Screens
Configure the WAN Options If Needed
Connecting the FVS124G to the Internet
Using the LAN IP Setup Options
Chapter LAN Configuration
LAN IP Setup menu
Configuring LAN TCP/IP Setup Parameters
LAN Configuration
Using the Firewall as a Dhcp server
Groups and Hosts Entry screen
Using Address Reservation
Multi Home LAN IPs
Configuring Static Routes
Static Routes Summary Table and Add screens
LAN Configuration
Using Rules to Block or Allow Specific Kinds of Traffic
Firewall Protection and Content Filtering Overview
Rules menu
Firewall Protection and Content Filtering
Services-Based Rules
Inbound Rules Port Forwarding
Add Inbound Service Rules screen
Services menu see Customized Services on
Inbound Services
Inbound Rule Example a Local Public Web Server
Inbound Rule Example One-to-One NAT Mapping
Rule example one-to-one NAT mapping
Rule example one-to-one NAT mapping on inbound services
Inbound Rule Example Exposed Host
Add Outbound Service Rules screen
Outbound Rules Service Blocking
Block or Allow Specific Traffic on
Outbound Services
QoS Priorities on
Outbound Rule Example Blocking Instant Messenger
10 Rules table with examples
Customized Services
11 Services and Add Custom Service screens
12 Setting and Overriding QoS priorities
Quality of Service QoS Priorities
Highest Default Lowest
Managing Groups and Hosts
13 Groups and Hosts screens
Groups and hosts
Using a Schedule to Block or Allow Specific Traffic
14 Schedule menu
Time Zone
Block Sites
15 Block Sites menu
Block Sites menu is shown in Figure
Filtering does not apply. See Managing Groups and Hosts on
Block Sites
16 Source MAC Filter screens
Source MAC Filtering
Source MAC address filter
Port Triggering
17 Port Triggering screens
Port Triggering
Getting E-Mail Notifications of Event Logs and Alerts
18 Logs and E-mail screens
Firewall Protection and Content Filtering
Syslog
Viewing Logs of Web Access or Attempted Web Access
19 Firewall Logs menu Log entry descriptions
Log action buttons
Administrator Information
Firewall Protection and Content Filtering
Dual WAN Port Systems
Rollover vs. Load Balancing Mode
Fully Qualified Domain Names
Rollover Mode Setup Screen
Functional operation of FVS124G WAN ports for rollover mode
FVS124G Functional Block Diagram FVS124G Firewall Rest
Load
Creating a VPN Connection Between FVX538 and FVS124G
Configuring the FVX538
WAN IP address of remote FVS124G
Click Next
IKE Policies
FVX538 VPN Policies screen
10 FVX538-to-FVS124G VPN screen
Configuring the FVS124G
12 WAN IP address of remote FVX538
11 VPN Wizard start
Creating a VPN Connection Netgear VPN Client to FVS124G
Testing the Connection
14 VPN Wizard
Configuring the VPN Client
15 New Client Connection screen
16 New connection named
Give the New Connection a name, such as toFVS
17 Remote client info
18 My Identity screen
19 Pre-shared key
Left frame, click on Security Policy
20 Client Security Policy screen
21 Client Authorization screen
22 Client Key Exchange screen
23 Client Connection Monitor screen
Virtual Private Networking
Bandwidth Capacity
Performance Management
Service Blocking
VPN Firewall Features That Reduce Traffic
Services
Source MAC Filtering
VPN Firewall Features That Increase Traffic
Block Sites
Port Forwarding
VPN tunnels
Port Triggering
VPN Tunnels
Using QoS to Shift the Traffic Mix
Tools for Traffic Management
Changing the Passwords and Login Timeout
Administrator and Guest Access Authorization
Remote Management screen
Enabling Remote Management Access
Https//134.177.0.1238080
Command Line Interface
Traffic Limits Reached
Event Alerts
WAN Port Rollover
Traffic Limit Reached alert
Login Failures and Attacks
Logs and email screen
Firewall Status
Monitoring
Viewing VPN Firewall Status and Time Information
Router Status screen
Router Status
Time Information
Time information is found on the Schedules screen
Time information on the Schedule screen
WAN Port Connection Status
WAN Ports
Internet Traffic Information
Dynamic DNS Status
Known PCs and Devices
LAN Ports and Attached Devices
Known PCs and Devices table
10 Network Database screen
Port Triggering Status
Dhcp Log
Port Triggering Status data
Firewall
You can view the log of the firewall activities
13 Logs and email screen
14 Firewall Log screen invoked from Logs and Email screen
Invoke the Firewall Log screen from Logs and Email screen
You can view the status of the VPN tunnels
VPN Tunnels
16 Snmp Configuration screens
Diagnostics
17 Diagnostics screen
Diagnostics
Configuration File Management
Options are described in the following sections
Be careful how you use these
Upgrading the Firewall Software
Restoring and Backing Up the Configuration
Be careful how you use this
Erasing the Configuration Factory Defaults Reset
Router and Network Management
Basic Functioning
Power LED Not On
LAN or Internet Port LEDs Not On
LEDs Never Turn Off
Troubleshooting the Web Configuration Interface
Troubleshooting the ISP Connection
Testing the LAN Path to Your Firewall
Troubleshooting a TCP/IP Network Using a Ping Utility
Click on OK You should see a message like this one
If the path is working, you see this message
If the path is not working, you see this message
Testing the Path from Your PC to a Remote Device
Problems with Date and Time
Restoring the Default Configuration and Password
Troubleshooting
Voltage and amperage 12 VDC, 1.2A
Dimensions 15 x 7.5 x 4.75 Weight
Data and Routing Protocols
10BASE-T or 100BASE-Tx
Interface Specifications
10BASE-T or 100BASE-Tx, RJ-45
Related Publications Basic Router Concepts
Appendix B Network, Routing, Firewall, and Basics
IP Addresses and the Internet
What is a Router?
Routing Information Protocol
Is normally written as
Three Main Address Classes
Equals
Netmask
Combined with
Example of Subnetting a Class B Address
Subnet Addressing
Netmask Formats
Netmask Notation Translation Table for One Octet
Private IP Addresses
Single IP Address Operation Using NAT
Single IP Address Operation Using NAT
Related Documents
MAC Addresses and Address Resolution Protocol
Domain Name Server
IP Configuration by Dhcp
Internet Security and Firewalls
Denial of Service Attack
What is a Firewall?
Ethernet Cabling
Stateful Packet Inspection
Category 5 Cable Quality
Table B-1 UTP Ethernet cable wiring, straight-through
Figure B-1illustrates straight-through twisted pair cable
Inside Twisted Pair Cables
Uplink Switches, Crossover Cables, and MDI/MDIX Switching
Network, Routing, Firewall, and Basics
Network, Routing, Firewall, and Basics
Preparing Your Computers for TCP/IP Networking
Appendix C Preparing Your Network
Install or Verify Windows Networking Components
Configuring Windows 95, 98, and Me for TCP/IP Networking
Preparing Your Network
Locate your Network Neighborhood icon
Enabling Dhcp to Automatically Configure TCP/IP Settings
Primary Network Logon is set to Windows logon
Click OK to continue Restart the PC
Selecting Windows’ Internet Access Method
Verifying TCP/IP Properties
Configuring Windows NT4, 2000 or XP for IP Networking
Locate your Network Neighborhood icon
Dhcp Configuration of TCP/IP in Windows XP
Preparing Your Network
Dhcp Configuration of TCP/IP in Windows
Preparing Your Network
Obtain an IP address automatically is selected
Dhcp Configuration of TCP/IP in Windows NT4
Preparing Your Network
TCP/IP Properties dialog box now displays
Verifying TCP/IP Properties for Windows XP, 2000, and NT4
Default gateway is Type exit
Configuring the Macintosh for TCP/IP Networking
MacOS 8.6 or
MacOS
Verifying TCP/IP Properties for Macintosh Computers
Verifying the Readiness of Your Internet Account
Are Login Protocols Used?
What Is Your Configuration Information?
Select the Gateway tab
Preparing Your Network
Restarting the Network
Preparing Your Network
Appendix D Virtual Private Networking
What is a VPN?
IPSec Security Features
What Is IPSec and How Does It Work?
IPSec Components
IPSec contains the following elements
Encapsulating Security Payload ESP
IKE Security Association
Authentication Header AH
Mode
Original packet and packet with IPSec ESP in Tunnel mode
Key Management
Understand the Process Before You Begin
Vpnc Example Network Interface Addressing
VPN Process Overview
Interfaces and Addresses
Firewalls
Setting Up a VPN Tunnel Between Gateways
WAN Internet/Public and LAN Internal/Private Addressing
Subnet Addressing
IPSec Security Association IKE VPN Tunnel Negotiation Steps
Exchange
Vpnc IKE Security Parameters
Vpnc IKE Phase I Parameters
Additional Reading
Testing and Troubleshooting
Vpnc IKE Phase II Parameters
Virtual Private Networking
Numeric
List of Glossary Terms
Adsl
Packet sent to all devices on a network
DSL
See Internet Control Message Protocol
Internet service provider
Megabits per second
Set of rules for communication between devices on a network
See Quality of Service
See Wide Area Network
Wins
Glossary