Spinpoint
SpinPoint V40 Product Manual
Table of Contents
Smart
Ervo S Ystem EAD and W Rite O Perations
Irmware F Eatures
Timing
Programming Requirements
Protocol Overview
107
Maintenance Precautions
Service and Repair
General Information
Table of Figures
Page
Scope
User Definition
Manual Organization
Computer Message
Commands and Messages
Terminology and Conventions
Format C/S
Reference
Description
Key Features
Introduction
Standards and Regulations
Hardware Requirements
Specification Summary
Specifications
Physical Specifications
Logical Configurations
Performance Specifications
Power Requirements
28.71
Environmental Specifications
SV6003H SV6014H SV8004H
Reliability Specifications
Mtbf POH
Installation
Space Requirements
Orientation
Unpacking Instructions
Mounting
2Mounting Dimensions in Millimeters
Clearance
3Mounting-Screw Clearance
AT-Bus Interface Connector
Cable Connectors
DC Power Connector
Ventilation
SpinPoint V40 Product Manual
Jumper Block Configurations
Options for Jumper Block Configuration
Drive Installation
7DC Power Connector and AT-Bus Interface Cable Connections
System Startup Procedure
Parameter
System Setup
DC Spindle Motor Assembly
Head / Disk Assembly HDA
Base Casting Assembly
Disk Drive Operation
Exploded Mechanical View
Voice Coil Motor and Actuator Latch Assemblies
Disk Stack Assembly
Head Stack Assembly
Air Filtration System
AT Disk Controller
Digital Signal Process and Interface Controller
Drive Electronics
2SID2001 AT Controller Block Diagram
Host Interface Control Block
Buffer Control Block
Disk Control Block
SpinPoint V40 Product Manual
Disk ECC Control Block
Power Management
Read/Write IC
Frequency Synthesizer
Asymmetry Correction Circuitry ASC
Time Base Generator
Automatic Gain Control
Analog Anti-Aliasing Low Pass Filter
3Read/Write 88C5200
Read Channel
Servo System
Read and Write Operations
Read Caching
Firmware Features
Write Channel
Write Caching
Multi-burst ECC Correction
Defect Management
Automatic Defect Allocation
Smart
Blank
Physical Interface
Signal Conventions
Signal Summary
Signal Descriptions
Intrq Drive Interrupt
DMACK- DMA Acknowledge
Dmarq DMA Request
IOCS16- Drive 16-bit I/O
Iordy I/O Channel Ready
PDIAG- Passed Diagnostics
RESET- Drive Reset
SD3
SD8 SD6 SD9 SD5
SD4
SD2
Drive
Drive Host
DIR
Bit Conventions
Logical Interface
General
Environment
SpinPoint V40 Product Manual
Control Block Registers
Command Block Registers
2 I/O Register Address
N N N A a a
Drive Address Register 3F7h
Control Block Register Descriptions
Alternate Status Register 3F6h
Device Control Register 3F6h
Error Register 1F1h
Command Block Register Descriptions
Features Register 1F1h
Data Register 1F0h
Cylinder High Register 1F5h
Command Register 1F7h
Sector Count Register 1F2h
Cylinder Low Register 1F4h
Status Register 1F7h
BSY Drdy DWF DSC DRQ Corr IDX ERR
At Command Register Descriptions
Command Parameter Used
SpinPoint V40 Product Manual
Download Micro Code 92h
Check Power Mode 98h, E5h
Execute Device Diagnostics 90h
Identify Device ECh
Flush Cache E7h
Format Track 50h
Word Content Description
Xxxx
Capabilities
Command set supported
95-128 0000h Reserved 129-159 Vendor specific 160-255
Initialize Device Parameters 91h
Idle 97h,E3h
Idle Immediate 95h,E1h
Read Buffer E4h
Read Long 22hwith retry, 23h without retry
Read Multiple Command C4h
Read Native Max Address F8h
Read Sectors 20hwith retry, 21hwithout retry
Seek 7xh
Read Verify Sectors 40hwith retry, 41hwithout retry
Recalibrate 1xh
Set Features EFh
Mode
Normal outputs
Inputs
LBA
BSY Drdy DRQ ERR
Description
Set Multiple Mode C6h
Sleep 99h, E6h
Smart B0h
Smart disable operation D9h
Standby 96h,E2h
Smart execute off-line immediate D4h
Smart enable/disable attribute autosave D2h
Smart enable operations D8h
Smart read data D0h
Byte Descriptions
Value Definition
Off-line data collection capability
Smart return status DAh
Smart capability
Smart read log sector D5h
Smart save attribution value D3h
Write Buffer E8h
Standby 96h, E2h
Standby Immediate 94h, E0h
Write DMA CAh
Write Multiple Command C5h
Write Sectors 30hwith retry, 31hwithout retry
SpinPoint V40 Product Manual
Programming Requirements
Reset Response
Error Posting
Command Error Register Status Register
BBK
Standby mode
Power Conditions
Sleep mode
Idle mode
Normal mode
PIO Data in Commands
Protocol Overview
PIO Read Aborted Command
PIO Data Out Commands
PIO Read Command
BSY=0 DRDY=1 BSY=1
PIO Write Command
PIO Write Aborted Command
BSY=0 DRQ=1 BSY=1 DRQ=0
Non-Data Commands
DMA Data Transfer Commands
BSY=1 BSY=0
Aborted DMA Command Initialize DMA Reset DMA Status
BSY=0 BSY=1
Timing
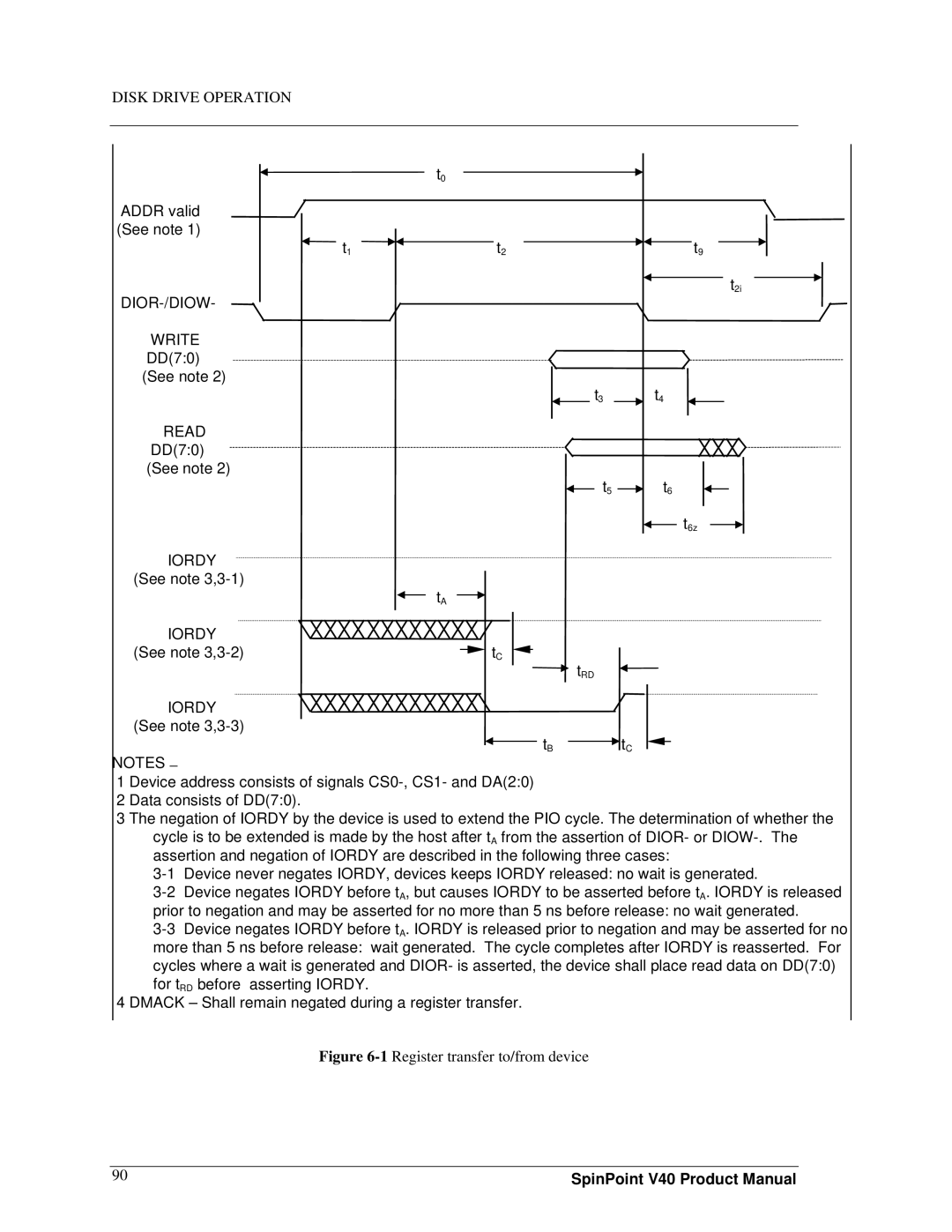
Register transfers
DIOR-/DIOW Write
PIO timing parameters Mode
PIO data transfers
Addr valid See note T1 t2
DIOR-/DIOW
Multiword DMA data transfer
DIOR-/DIOW
Multiword DMA timing parameters Mode
Ultra DMA data transfer
Initiating an Ultra DMA data in burst
Ultra DMA data burst timing requirements
19Ultra DMA data burst timing requirements
Sustained Ultra DMA data in burst
5Sustained Ultra DMA data in burst
Host pausing an Ultra DMA data in burst
6Host pausing an Ultra DMA data in burst
Device terminating an Ultra DMA data in burst
7Device terminating an Ultra DMA data in burst 100
Host terminating an Ultra DMA data in burst
8Host terminating an Ultra DMA data in burst
Initiating an Ultra DMA data out burst
9Initiating an Ultra DMA data out burst 102
Sustained Ultra DMA data out burst
10Sustained Ultra DMA data out burst
Device pausing an Ultra DMA data out burst
11Device pausing an Ultra DMA data out burst 104
Host terminating an Ultra DMA data out burst
12Host terminating an Ultra DMA data out burst
Device terminating an Ultra DMA data out burst
13Device terminating an Ultra DMA data out burst 106
General Information
Maintenance Precautions
Service And Repair

![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() (See note 2)
(See note 2)![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() (See note
(See note