EL-738
Page
Contents
Introduction
Operational Notes
Key Notations in This Manual
Using the .and
Keys
Resetting the calculator
Resetting the Calculator In Case of Difficulty
Preparing to Use the Calculator
Calculator layout
Calculator and Display Layout
Key operation keys
Display layout
2ndF
SET UP Menu
Selecting the display notation and number of decimal places
000
3333333
0003
Selecting the angular unit see
Operating Modes
Selecting a mode
Operations available in each mode
Selecting the date format see
9000
14000
343
Basic Calculations
⋅ ⋅
Delete key
Cursor keys
Editing and Correcting an Entry
Memory clear key
Playback function
500
Errors
Memory use in each mode for memory calculations
192
Last answer memory ANS
Temporary memories A-H, X-Z
Independent memory M
TVM variables
Memory calculations
Statistical variables
Example Key operation
General Information
Financial calculations
Variables used in financial calculations
Variables shared among calculations
TVM variables N, I/Y, PV, PMT, FV
Basic variable operations
Listed financial variables
ENT and Comp symbols
Category Display symbols Descriptions
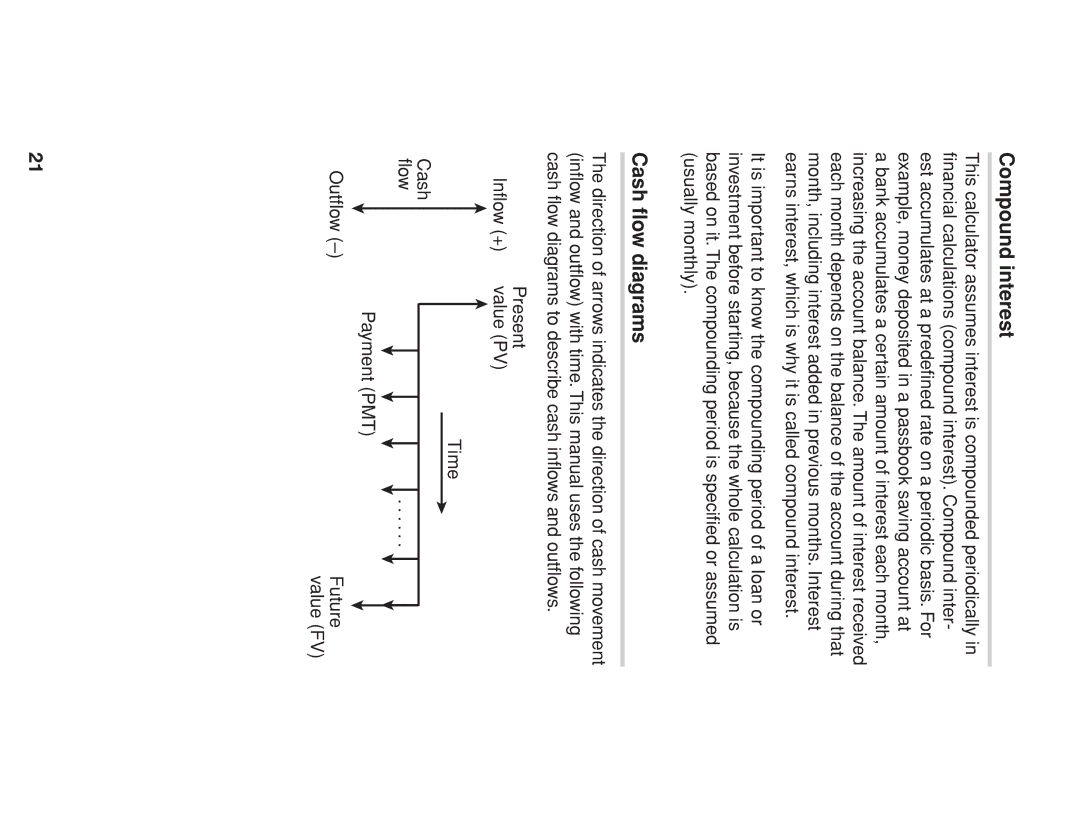
Cash flow diagrams
Compound interest
TVM Time Value of Money Solver
Setting the payment period payment due
Variable Corresponding Description Default Variable key
Variables used in the TVM solver
Basic examples for the TVM solver
Calculating basic loan interest
5600000
1200
24000
44000
125586
400
8000
Calculating basic loan payments
FV=
3600
20000
Calculating future value
1000000
100
2000
376889
Annuity due BGN
Specifying payments due
Ordinary annuity END
Ordinary annuity
360
1800
30000000
1624570
14500
2400
29950
299500
627995
3400
150000
Calculating down payment and amount to borrow
550
30000
90000
14655892
Amortization Calculations
Variable Description Default value
Variables used in amortization
61656
8895148
600
104852
203428
1700
48275524
384457
4800
1724476
Single cash flows
Discounted Cash Flow Analysis
Entering cash flow data
Repeated cash flows
300
000*2
200
Confirming and editing data
Deleting data
2500000
Editing data
Inserting data
Variables used in discounted cash flow analysis
3000000
600000
NPV and IRR
To obtain NPV
Procedure Key operation Display Bring up the initial dis
Play in Normal mode
To obtain IRR
2314
Calculating the present value of variable cash flows
662752
Bond Calculations
Setting the day-count method
Variables used in bond calculations
To obtain bond price Price PV
To obtain yield to maturity Yield I/Y
15-2023
650
10000
720
728
9250
Entering dates
Variables used in depreciation calculations
Setting the depreciation method
Depreciation Calculations
Key operation Description
Page
5000000
3000
Calculating straight-line depreciation
To change APR to EFF
1956
Conversion between APR and EFF
To change EFF to APR
Day and Date Calculations
Variables used in day and date calculations
Calculating number of days
10-2009
22800
Answer 228 days
Percent Change/Compound Interest Cal- culations
Procedure Key operation Display Move to the last date
Calculate
5467
7500000
11600000
800000
Cost/Sell/Margin/Markup Calculations
980000
113
Variables used in cost/sell/margin/markup calcula- tions
88842
45560
9500
Determining selling price
Variables used in breakeven calculations
Breakeven Calculations
Calculating the breakeven point
12000
1500000
7580
33937
Constant Calculations
Chain Calculations
5000
087
071
4500
Random dice
Random Functions
Random numbers
Random coin
Modify Function
532
Random integer
For a two-variable data set x value y value J
Entering statistical data
For a single-variable data set
Key operation Sub-mode Display
Entering statistical data
1000 2000
Linear regression calculations
Statistical Calculations and Variables
Single-variable statistical calculations
Quadratic regression calculation
Variables Content
17857
53000
Single-variable statistical calculation
Linear regression calculation
Quadratic regression calculation
Amortization calculations
Financial Calculation Formulas
TVM solver
Discounted cash flow analysis
Bond calculations
Conversion between APR and EFF
Depreciation calculations
Day and date calculations
Cost/Sell/Margin/Markup calculations
Statistical Calcula- tion Formulas
Breakeven calculations
Syntax error Error
Errors and Calculation Ranges
Error codes and error types
Calculation error Error
Display error Error
Equation too long Error
No solution Error
Input value error Error
Calculation ranges of functions
Function Calculation range
Integer
Battery Replacement
When to replace the battery
Automatic power-off function
Replacement procedure
Priority Levels in Calculations
For more information about business/ financial calculators
Specifications
Key operation and calculation priority
Index
Formulas, 72-75 FV, 18, 22, 72 GRAD, 8, 9, 61
Memo