4-3 DESCRIPTION of GENERATOR OPERATION
4-3-1 PRIMARY EXCITING ACTION (RGV12100)
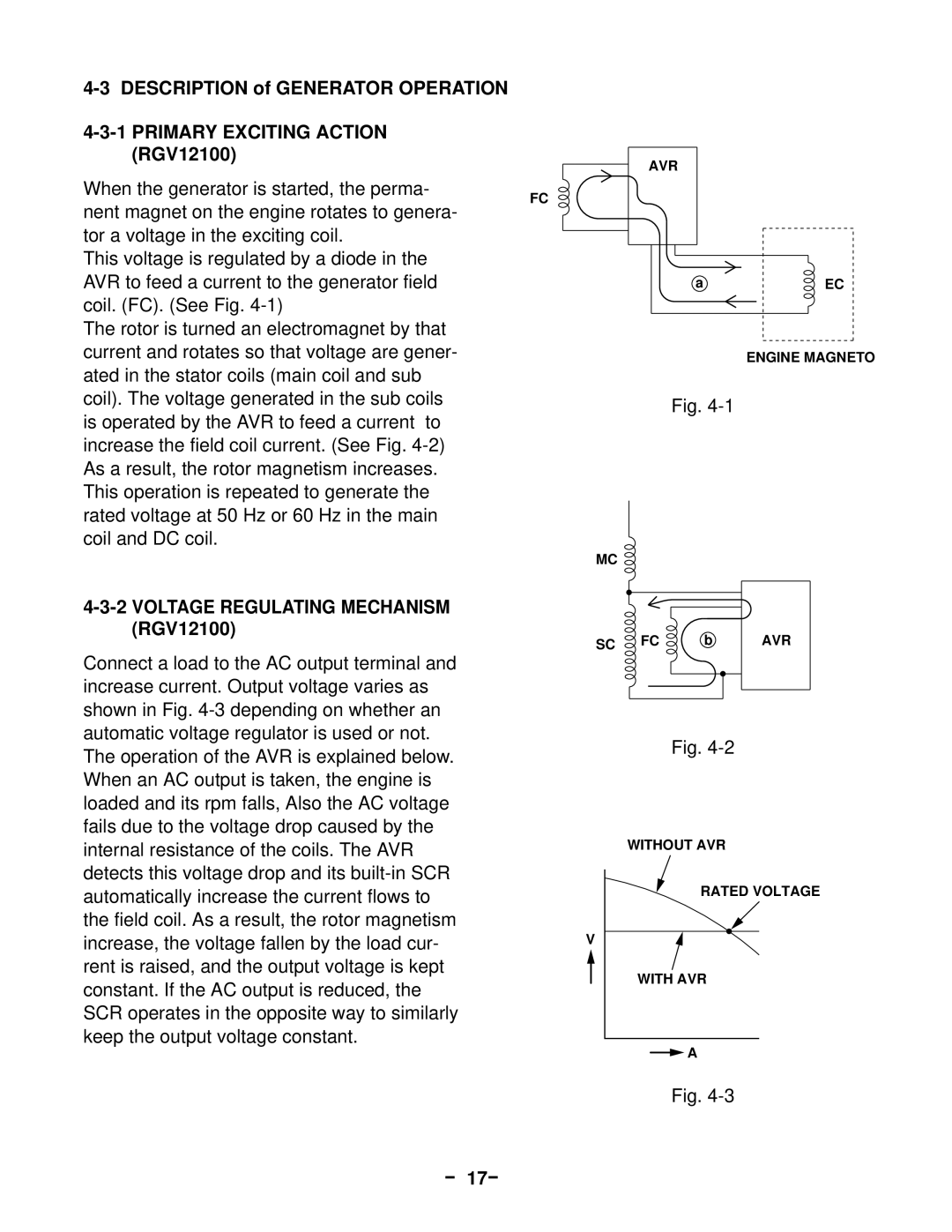
When the generator is started, the perma-
FC
nent magnet on the engine rotates to genera- tor a voltage in the exciting coil.
This voltage is regulated by a diode in the AVR to feed a current to the generator field coil. (FC). (See Fig.
The rotor is turned an electromagnet by that current and rotates so that voltage are gener- ated in the stator coils (main coil and sub coil). The voltage generated in the sub coils is operated by the AVR to feed a current to increase the field coil current. (See Fig.
MC
4-3-2 VOLTAGE REGULATING MECHANISM (RGV12100)
SC
AVR
aEC
ENGINE MAGNETO
Fig.
FC b AVR
Connect a load to the AC output terminal and increase current. Output voltage varies as shown in Fig.
Fig.
WITHOUT AVR
RATED VOLTAGE
V![]()
WITH AVR
![]() A
A
Fig.