subconscious panel differentiation. With a separate module used for every form of communication, a Director’s station may have separate panels for PL, ISO, point-to point, and IFB control. A minimal link exists between the control stations and sub-systems. The link is provided by an un-switched microphone connection on the control station. Therefore, in the heat of a production, the director knows which panel does what, and may quickly access IFB to a specified talent.
In contrast, a digital four-wire control station emulates each form of communication from different keys on one panel. Because panel differentiation is gone from the digital station, a concern for operator confusion arises. To solve the problem, the forms of communication can be easily be grouped into specific areas of the station panel or expansion panels.
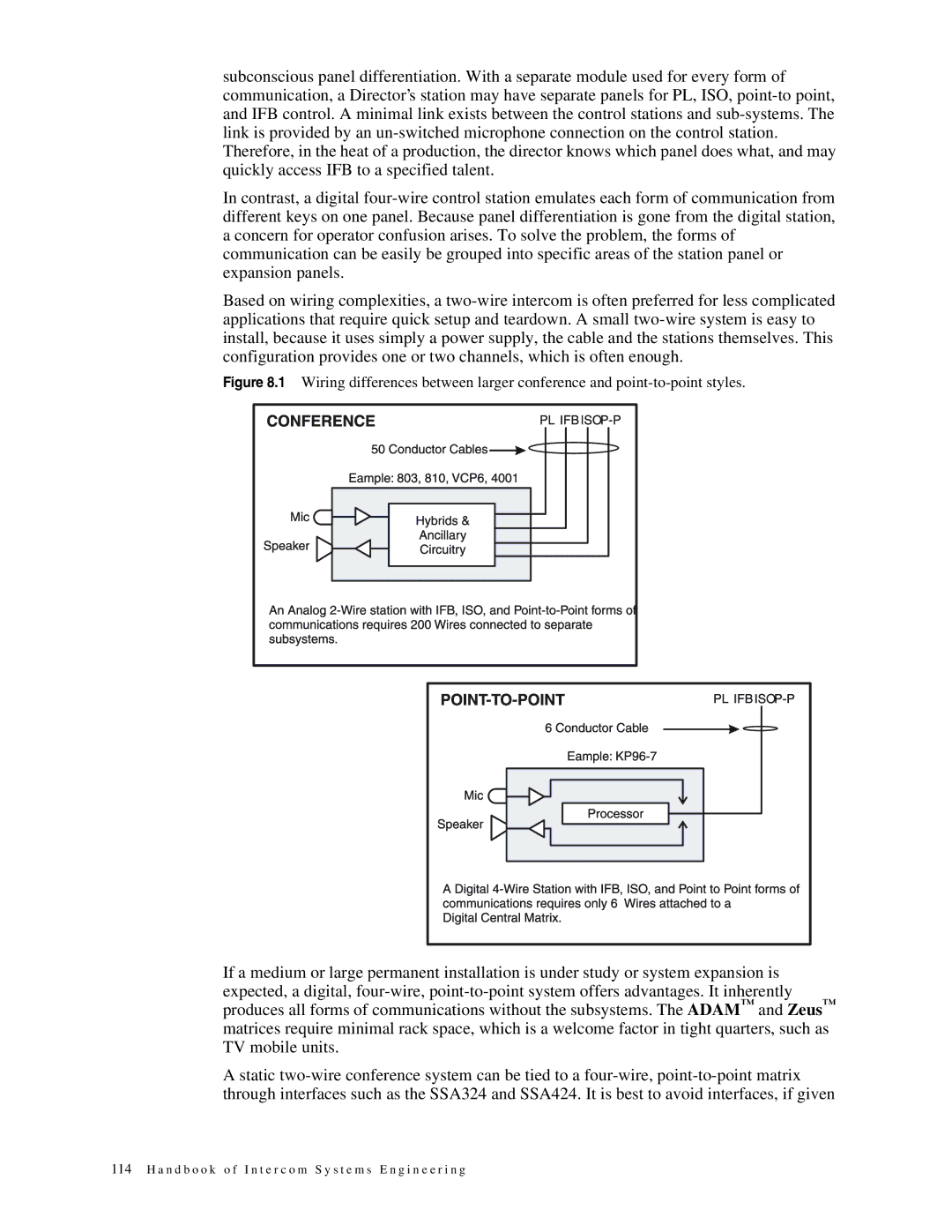
Based on wiring complexities, a two-wire intercom is often preferred for less complicated applications that require quick setup and teardown. A small two-wire system is easy to install, because it uses simply a power supply, the cable and the stations themselves. This configuration provides one or two channels, which is often enough.
Figure 8.1 Wiring differences between larger conference and point-to-point styles.
If a medium or large permanent installation is under study or system expansion is expected, a digital, four-wire, point-to-point system offers advantages. It inherently produces all forms of communications without the subsystems. The ADAM™ and Zeus™ matrices require minimal rack space, which is a welcome factor in tight quarters, such as TV mobile units.
Astatic two-wire conference system can be tied to a four-wire, point-to-point matrix through interfaces such as the SSA324 and SSA424. It is best to avoid interfaces, if given