Rev 1910010529
Copyright & Trademarks
Contents
Gvrp
TC Protect 101
11.4.1
Ntdp
11.4.2
VII
Package Contents
Overview of This Guide
About this Guide
Intended Readers
Conventions
Path
Switch, which facilitates you to monitor the Igmp messages
Return to Contents
Main Features
Overview of the Switch
Introduction
Front Panel
Appearance Description
¾ LEDs Name Status Indication
Rear Panel
Login
Login to the Switch
Configuration
Return to Contents
¾ Port Status
System
System Info
System Summary
Rate
¾ Port Info
Port
Type
¾ Bandwidth Utilization
Device Description
¾ Device Description
System Time
¾ Time Config
¾ Time Info
System IP
User Table
User Manage
¾ User Info
User Config
User ID, Name, Access Level and status Operation
Config Restore
Password
Confirm Password Retype the password
Firmware Upgrade
Config Backup
¾ Config Backup
System Reset
System Reboot
Access Control
Access Security
MAC Address
¾ Access Control Config
¾ Session Config
IP Address&Mask
¾ Access User Number
SSL Config
¾ Key Download
SSH Config
¾ Global Config
¾ Certificate Download
Protocol
Idle Timeout
Max Connect
¾ Network Requirements
¾ Configuration Procedure
Key Type
Download
Application Example 2 for SSH
Page
Return to Contents
Port Select
Switching
Port Config
Port
Flow Control
Port Mirror
Description
Speed and Duplex
Egress
¾ Mirroring Port
¾ Mirrored Port
Ingress
¾ Port Security
Port Security
Max Learned MAC
Port Isolation
Learned Num
Forward Portlist Display the forwardlist
¾ Port Isolation Config
Forward Portlist Select the port that to be forwarded to
¾ Port Isolation List
LAG Table
LAG
Member
Aggregate Arithmetic
¾ LAG Table
Group Number
Static LAG
¾ LAG Config
LAG will delete this LAG
Lacp Config
Port Priority
¾ Lacp Config
Admin Key
System Priority
Traffic Summary
Traffic Monitor
¾ Auto Refresh
Traffic Statistics
MAC Address
Address and the port
Type Configuration Way Aging out
Relationship
Bound
¾ Address Table
¾ Search Option
¾ Create Static Address
MAC Address Displays the MAC address learned by the switch
Static Address
Displays the corresponding Vlan ID of the MAC address
¾ Static Address Table
Dynamic Address
¾ Dynamic Address Table
¾ Aging Config
Bind
Filtering Address
¾ Filtering Address Table
¾ Create Filtering Address
Vlan implementation
Vlan
¾ Link Types of ports
802.1Q Vlan
¾ Pvid
Vlan Config
Members Operation :
¾ Vlan Table
Vlan ID Select
Description :
¾ Vlan Members
¾ Vlan Config
Enter the ID number of Vlan
Is valid or not
Port Displays the port number
¾ Vlan Port Config
Vlan Description
Required. On the VLAN→802.1Q VLAN→Port Config page, set
Required. On the VLAN→802.1Q VLAN→VLAN Config
¾ Vlan of Port
MAC Vlan
Optional. On the VLAN→802.1Q VLAN→VLAN Config
¾ MAC Vlan Table
Port Enable
MAC Select
Protocol Vlan
Required. On the VLAN→MAC VLAN→Port Enable
¾ Protocol Vlan Table
Protocol Vlan
Protocol Template
¾ Create Protocol Vlan
¾ Protocol Template Table
¾ Create Protocol Template
Application Example for 802.1Q Vlan
Operation Description
Required. On VLAN→802.1Q VLAN→Port Config page, configure
Required. On VLAN→802.1Q VLAN→VLAN Config page, create a
Application Example for MAC Vlan
¾ Network Diagram ¾ Configuration Procedure
Application Example for Protocol Vlan
Required. On VLAN→Protocol VLAN→Protocol Template
Protocol type Value
On VLAN→Protocol VLAN→Protocol Vlan page, create protocol
Vlan Mapping
VPN Config
¾ VPN Up-link Ports
¾ Vlan Mapping Table
¾ Vlan Mapping Config
Required. On the VLAN→VLAN VPN→VLAN Mapping
Required. On the VLAN→VLAN VPN→VPN Config
Optional. On the VLAN→VLAN VPN→VPN Config
Required. On the VLAN→VLAN VPN→Port Enable
¾ Garp
Gvrp
¾ Gvrp
Select Port Status Registration Mode
¾ Port Config
Private Vlan
Configuration Procedure
¾ The Elements of a Private Vlan
¾ Features of Private Vlan
¾ Private Vlan Implementation
Pvid
¾ Packet forwarding in Private Vlan
Pvlan
Secondary Vlan
¾ Create Private Vlan
¾ Private Vlan Table
Primary Vlan
Required. On the VLAN→Private VLAN→PVLAN
Port Select the desired port for configuration Port Type
Required. On the VLAN→Private VLAN→Port Configure
¾ Private Vlan Port Table
Application Example for Private Vlan
Required. On the VLAN→802.1Q VLAN→VLAN Config page, click
¾ STP Elements
Spanning Tree
¾ Bpdu Comparing Principle in STP mode
¾ STP Timers
Step Operation
¾ STP Generation
¾ Rstp Elements
Tips:
¾ Mstp Elements
¾ Port Roles
¾ Port States
STP Config
STP Config
Max Age
Forward Delay
Version
Hello Time
STP Summary
STP Summary
Port Config
Edge Port
Priority
ExtPath
IntPath
Port Status
Region Config
Mstp Instance
Port Role
¾ Region Config
Instance Config
Clear
Instance Port Config
¾ Instance Table
Instance
Path Cost
Instance ID
Port Protect
STP Security
¾ Bpdu Protect
¾ TC Protect
¾ Bpdu Filter
Bpdu Protect
Loop Protect
Root Protect
TC Protect
11 TC Protect
TC Protect
On Spanning Tree→MSTP Instance→Instance
On Spanning Tree→STP Config→STP Config
On Spanning Tree→STP Config→Port Config
Application Example for STP Function
Bridge of Instance
Configure Switch D
¾ Suggestion for Configuration
¾ Multicast Overview
Multicast
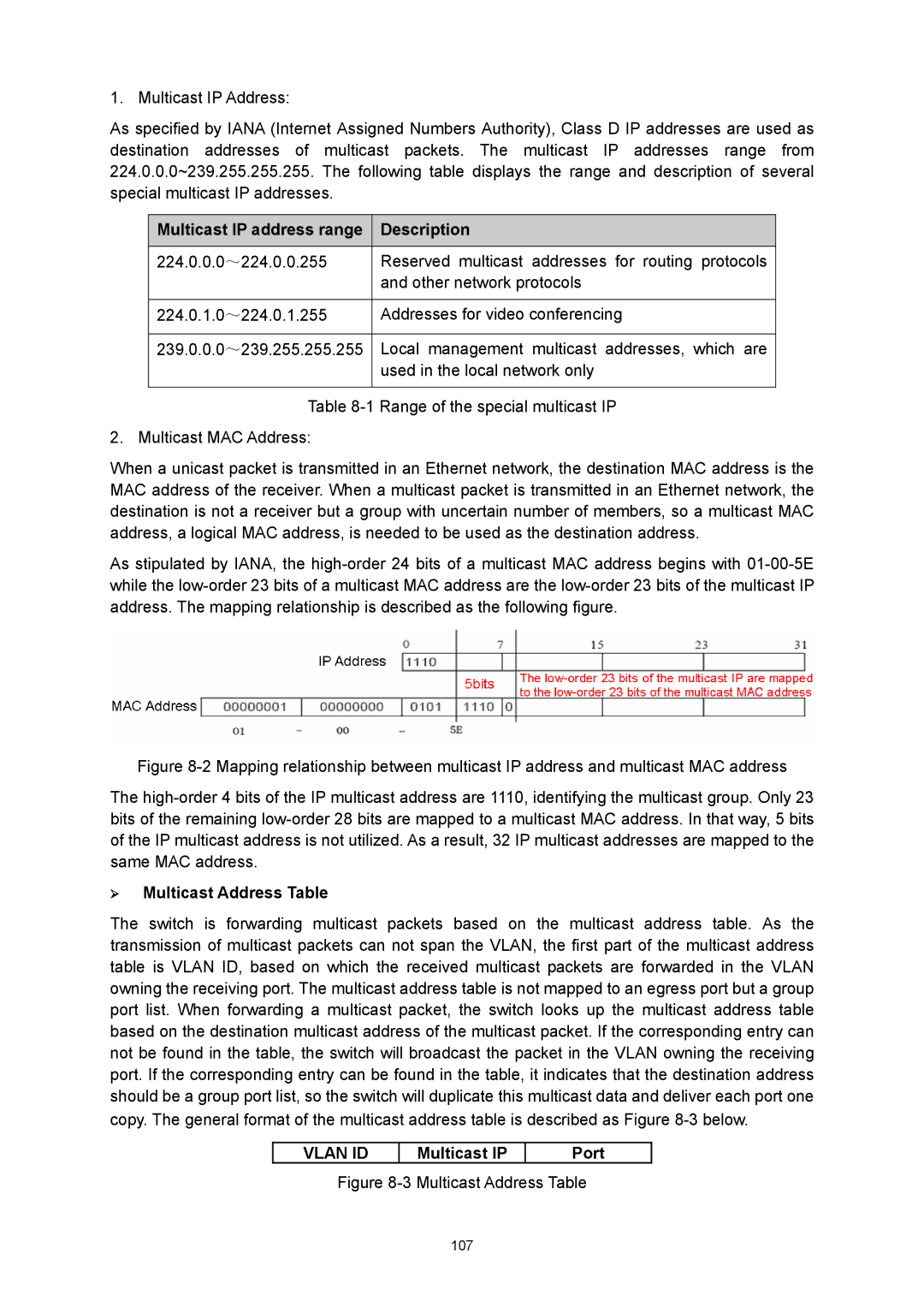
¾ Multicast Address
Multicast IP Port
¾ Multicast Address Table
¾ Igmp Messages
Igmp Snooping
¾ Igmp Snooping
¾ Igmp Snooping Process
¾ Igmp Snooping Fundamentals
Snooping Config
Description Displays Igmp Snooping status Member
¾ Igmp Snooping Status
Fast Leave
Igmp Snooping
Static Router Port
Router Port Time
Member Port Time
Leave Time
Router Port
Snooping→Snooping Config and Port Config
Multicast→IGMP Snooping→VLAN Config
Multicast Vlan
¾ Multicast Vlan
Multicast→IGMP Snooping→Multicast Vlan
On the Multicast→IGMP Snooping→Snooping Config
Application Example for Multicast Vlan
Vlan
Multicast IP
¾ Configuration Procedure Step Operation Description
Snooping→Port Config
Snooping→Snooping Config
Static Multicast IP
Multicast IP Table
¾ Static Multicast IP Table
¾ Create Static Multicast
IP-Range
Multicast Filter
Port Filter
¾ Port Filter Config
Multicast→Multicast Filter→IP-Range
Packet Statistics
Multicast→Multicast Filter→Port Filter
¾ Igmp Statistics
QoS
¾ Priority Mode
¾ QoS
802.1Q frame
¾ Schedule Mode
SP-Mode
Displays the LAG number which the port belongs to
¾ Port Priority Config
DiffServ
Port Priority
¾ Schedule Mode Config
Schedule Mode
3 802.1P Priority
¾ 802.1P Priority Config
¾ Priority Level
Dscp Priority
Priority levels are labeled as TC0, TC1, TC2 and TC3
¾ Dscp Priority Config
It ranges from 0 to
Priority Level
Bandwidth Control
¾ Rate Limit Config
Rate Limit
Ingress Rate bps
Storm Control
Egress Ratebps
Multicast Rate
¾ Storm Control Config
Broadcast Rate
Bps
Voice Vlan
¾ Port Voice Vlan Mode
Number OUI Address Vendor
Packet Type Processing Mode
¾ Security Mode of Voice Vlan
12 Global Configuration
Global Config
13 Port Config
Port Mode
OUI Config
Required. On QoS→Voice VLAN→Global Config
Required. On VLAN→802.1Q VLAN→Port Config
Optional. On QoS→Voice VLAN→OUI Config page, you
Required. On QoS→Voice VLAN→Port Config
Index
ACL
Time-Range
Time-Range Summary
Time-Range Create
¾ Holiday Table
ACL Config
Holiday Config
¾ Create Holiday
¾ Create ACL
ACL Summary
ACL Create
¾ Rule Table
EtherType
MAC ACL
¾ Create MAC ACL
Rule ID
Mask
Standard-IP ACL
¾ Create Standard-IP ACL
Fragment
¾ Create Extend-IP ACL
Extend-IP ACL
Policy Summary
Policy Config
Desired policy, please click the Delete button
Policy Create
Action Create
Select Policy
¾ Create Action
11 Action Create
¾ Policy Bind Table
Policy Binding
Binding Table
Port Binding
Direction Displays the binding direction
Vlan Binding
Enter the ID of the Vlan you want to bind
¾ VLAN-Bind Table
Application Example for ACL
On ACL→ACL Config→ACL Create page, create ACL
On ACL→ACL Config→Standard-IP ACL page, select ACL
IP-MAC Binding
Network Security
Manual Binding
¾ Manual Binding Table
¾ Manual Binding Option
Enter the Vlan ID
Protect Type Select the Protect Type for the entry
ARP Scanning
Scan
Dhcp Snooping
Start IP Address
End IP Address
¾ Dhcp Working Principle
Network diagram for DHCP-snooping implementation
¾ Option
¾ Dhcp Cheating Attack
Dhcp Cheating Attack Implementation Procedure
163
Customization Circuit ID Remote ID
¾ Option 82 Config
¾ Port Config Port Select
Decline Threshold Decline Flow Control
¾ Imitating Gateway
ARP Inspection
¾ Cheating Gateway
¾ Cheating Terminal Hosts
10 ARP Attack Cheating Gateway
¾ Man-In-The-Middle Attack
¾ ARP Flooding Attack
¾ ARP Detect
ARP Detect
¾ Trusted Port
Required. On the Network Security→IP-MAC
ARP Defend
Network Security→ARP
Speed
ARP Statistics
¾ ARP Defend
Defend
¾ Illegal ARP Packet
IP Source Guard
DoS Defend
¾ IP Source Guard Config
DoS Attack Type Description
DoS Detect
DoS Defend
Attack Type
11.5
Detect Time
Detect
¾ 802.1X Authentication Procedure
¾ The Mechanism of an 802.1X Authentication System
178
179
¾ Guest Vlan
¾ 802.1X Timer
Guest Vlan ID
Authentication Method
802.1X
Guest Vlan
Server Timeout
Supplicant Timeout
Retry Times
Authorized
Control Mode
Radius Server
Control Type
Required. On the Network Security→802.1X→Port
On the Network Security→802.1X→Global Config
802.1X Client Software
Required. On the Network Security→802.1X→Radius
¾ Snmp Versions
Snmp
¾ Snmp Overview
¾ Snmp Management Frame
¾ MIB Introduction
¾ Snmp Configuration Outline
¾ Local Engine
Snmp Config
¾ Remote Engine
View Name
Snmp View
MIB Object ID
View Type
Snmp Group
¾ Group Config
¾ Group Table
Snmp User
Privacy Password
Auth Mode
Auth Password
Privacy Mode
Access
¾ Community Config
Snmp Community
¾ Community Table
Required. On the SNMP→SNMP Config→Global
Required. On the SNMP→SNMP Config→SNMP
MIB View
Notification
On the SNMP→SNMP Config→SNMP
Retry
Timeout
UDP Port
User
¾ Rmon Group
Rmon
Rmon Group Function
History Control
Event Config
¾ History Control Table
¾ Event Table
Alarm Config
Rising Event
Variable
Sample Type
Rising Threshold
200
¾ Cluster Role
Cluster
Neighbor Info
13.1 NDP
¾ Introduction to Cluster
¾ Neighbor
NDP Summary
¾ Neighbor Info
NDP
¾ Port Status Displays the port number of the switch
Detail :
NDP Config
Aging Time
Displays NDP status of the current port
Port Displays the port number of the switch
Ntdp
Device Table
Ntdp Summary
Ntdp Summary
Ntdp Interval Time
Ntdp Config
Ntdp Hops
Cluster
Enable
Cluster Summary
¾ Member Info
¾ Global Config Cluster
¾ Cluster Config
¾ Global Cluster
11 Cluster Summary for Member Switch
Switch
¾ Current Role
Cluster Config
¾ Role Change
14 Cluster Configuration for Commander Switch
16 Cluster Configuration for Individual Switch
Member Config
Member MAC
Cluster Topology
¾ Create Member
Device Name
¾ Graphic Show
18 Collect Topology
Application Example for Cluster Function
On Cluster→NTDP→NTDP Config page, enable
On Cluster→NDP→NDP Config page, enable NDP
220
System Monitor
Maintenance
CPU Monitor
Memory Monitor
14.2 Log
Module
Content
Log Table
Time
Log Buffer
¾ Local Log Config
Local Log
Remote Log
¾ Log Host
Backup Log
Host IP
¾ Cable Test
¾ Backup Log
Device Diagnose
Cable Test
Length
Error
Switch is available
Loopback
Test
¾ Ping Config
Network Diagnose
Ping
Tracert
¾ Tracert Config
Hardware Installation
System Maintenance via FTP
Configure the Hyper Terminal
232
5Port Settings
Download Firmware via bootrom menu
TP-LINK upgrade You can only use the port 1 to upgrade
TP-LINK ifconfig ip 172.31.70.22 mask 255.255.255.0 gateway
TP-LINK start Start User Access Login
Appendix a Specifications
Configure TCP/IP component
Appendix B Configuring the PCs
238
Now
Appendix C 802.1X Client Software
Installation Guide
241
242
Figure C-7 InstallShield Wizard Complete
Uninstall Software
Figure C-10 Uninstall Complete
Configuration
245
Figure C-15 Connection Status
FAQ
Appendix D Glossary
Ieee 802.1Q
Multicast Switching
Group Attribute Registration Protocol Garp
Ieee 802.1D
Link Aggregation Control Protocol Lacp
Port Authentication
Remote Authentication Dial-in User Service Radius
Link Aggregation
Telnet
Simple Network Management Protocol Snmp
Simple Network Time Protocol Sntp
Spanning Tree Algorithm STA