Advanced Features
Advanced Features
![]() NAT – NAT (Network Address Translation) is the technology which allows a number of LAN PCs to share one (1) Internet IP address.
NAT – NAT (Network Address Translation) is the technology which allows a number of LAN PCs to share one (1) Internet IP address.
![]() Remote Access Configuration – This feature allows you to manage the
Remote Access Configuration – This feature allows you to manage the
![]() External Filters Configuration – These settings determine whether or not the
External Filters Configuration – These settings determine whether or not the
![]() Interface Binding – Use these to ensure that certain traffic is sent by a particular WAN port, and thereby a particular ISP account. These settings are only useful if using both WAN ports.
Interface Binding – Use these to ensure that certain traffic is sent by a particular WAN port, and thereby a particular ISP account. These settings are only useful if using both WAN ports. ![]() Protocol & Port Binding – This allows you binding WAN 1 or WAN 2 ports by selecting TCP/UDP protocol
Protocol & Port Binding – This allows you binding WAN 1 or WAN 2 ports by selecting TCP/UDP protocol
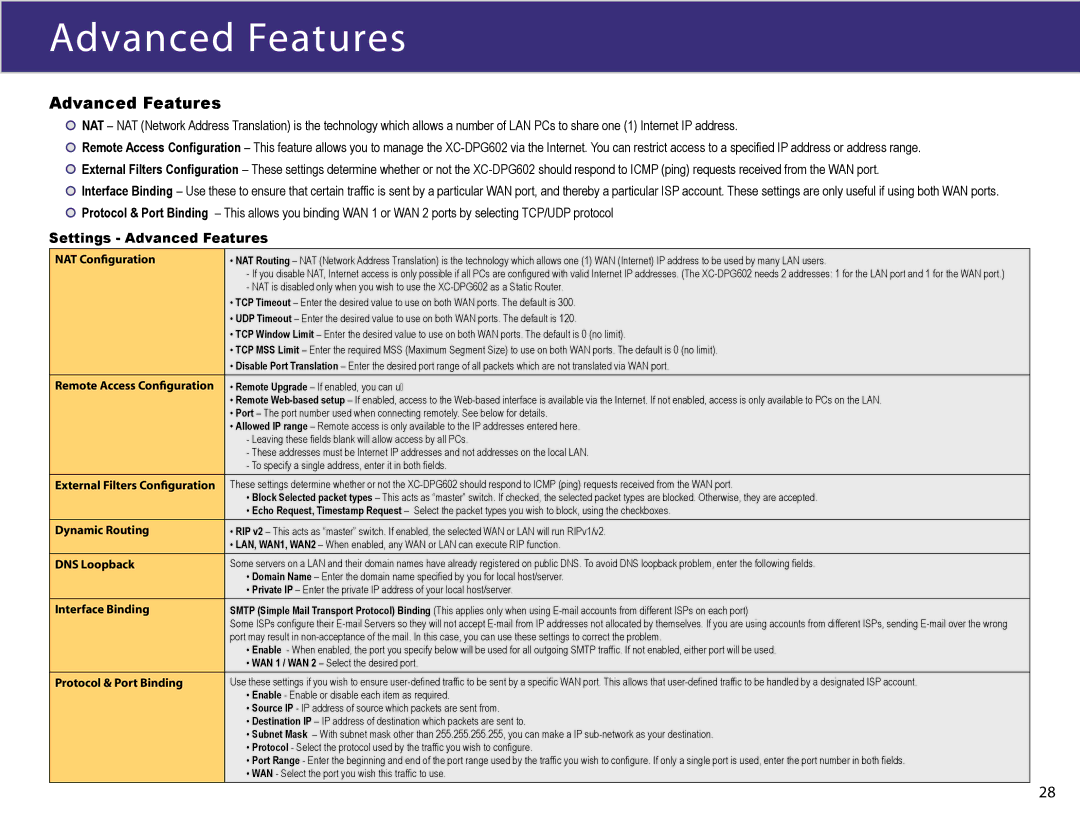
Settings - Advanced Features
NAT Configuration | • NAT Routing – NAT (Network Address Translation) is the technology which allows one (1) WAN (Internet) IP address to be used by many LAN users. |
| - If you disable NAT, Internet access is only possible if all PCs are configured with valid Internet IP addresses. (The |
| - NAT is disabled only when you wish to use the |
| • TCP Timeout – Enter the desired value to use on both WAN ports. The default is 300. |
| • UDP Timeout – Enter the desired value to use on both WAN ports. The default is 120. |
| • TCP Window Limit – Enter the desired value to use on both WAN ports. The default is 0 (no limit). |
| • TCP MSS Limit – Enter the required MSS (Maximum Segment Size) to use on both WAN ports. The default is 0 (no limit). |
| • Disable Port Translation – Enter the desired port range of all packets which are not translated via WAN port. |
Remote Access Configuration | • Remote Upgrade – If enabled, you can u� |
| • Remote |
| • Port – The port number used when connecting remotely. See below for details. |
| • Allowed IP range – Remote access is only available to the IP addresses entered here. |
| - Leaving these fields blank will allow access by all PCs. |
| - These addresses must be Internet IP addresses and not addresses on the local LAN. |
| - To specify a single address, enter it in both fields. |
External Filters Configuration | These settings determine whether or not the |
| • Block Selected packet types – This acts as “master” switch. If checked, the selected packet types are blocked. Otherwise, they are accepted. |
| • Echo Request, Timestamp Request – Select the packet types you wish to block, using the checkboxes. |
Dynamic Routing | • RIP v2 – This acts as “master” switch. If enabled, the selected WAN or LAN will run RIPv1/v2. |
| • LAN, WAN1, WAN2 – When enabled, any WAN or LAN can execute RIP function. |
DNS Loopback | Some servers on a LAN and their domain names have already registered on public DNS. To avoid DNS loopback problem, enter the following fields. |
| • Domain Name – Enter the domain name specified by you for local host/server. |
| • Private IP – Enter the private IP address of your local host/server. |
Interface Binding | SMTP (Simple Mail Transport Protocol) Binding (This applies only when using |
| Some ISPs configure their |
| port may result in |
| • Enable - When enabled, the port you specify below will be used for all outgoing SMTP traffic. If not enabled, either port will be used. |
| • WAN 1 / WAN 2 – Select the desired port. |
Protocol & Port Binding | Use these settings if you wish to ensure |
| • Enable - Enable or disable each item as required. |
| • Source IP - IP address of source which packets are sent from. |
| • Destination IP – IP address of destination which packets are sent to. |
| • Subnet Mask – With subnet mask other than 255.255.255.255, you can make a IP |
| • Protocol - Select the protocol used by the traffic you wish to configure. |
| • Port Range - Enter the beginning and end of the port range used by the traffic you wish to configure. If only a single port is used, enter the port number in both fields. |
| • WAN - Select the port you wish this traffic to use. |
28