Programming Guide
Trademarks
Contents
Programming Examples
Programming the Status Register System
Creating and Downloading Waveform Files
Creating and Downloading User-Data Files
Viii
Documentation Overview
Page
Getting Started with Remote Operation
Programming and Software/Hardware Layers
Interfaces
Software/Hardware Layers
LAN
IO Libraries and Programming Languages
Agilent IO Libraries Suite
Windows NT and Agilent IO Libraries M and Earlier
Visa Assistant
Selecting IO Libraries for Gpib
Visa Configuration Automatic
Visa Configuration Manual
Click on Gpib in the Available Interface Types text box
Selecting IO Libraries for LAN
Visa
Programming Languages
Perl
Using the Web Browser
Enabling the Signal Generator Web Server
Agilent MXG Web Server On
ESG/PSG/E8663B Web Server On
Getting Started with Remote Operation Using the Web Browser
Getting Started with Remote Operation Using the Web Browser
LAN Configuration System Defaults Agilent MXG
LAN Configuration Summary Values
Displaying the LAN Configuration Summary Agilent MXG
Web Password
Preferences
Select Update in Remote until On is highlighted
Setting the Help Mode ESG/PSG/E8663B
Getting Help Agilent MXG
Getting Help ESG/PSG/E8663B
Error Messages
Error Message File
Error Message Types
Using IO Interfaces
Using Gpib
Installing the Gpib Interface
Using Gpib
Set Up the Gpib Interface
Setting the Gpib Address on the Agilent MXG
If You Have Problems
Verify Gpib Functionality
Gpib Interface Terms
Interface Check Using NI-488.2 and C++
Before Using the Gpib Examples
Interface Check using HP Basic and Gpib
Gpib Programming Interface Examples
Using IO Interfaces Gpib Programming Interface Examples
Using LAN
Setting Up the LAN Interface
Configuring the VXI-11 for LAN Agilent MXG
Configuring the VXI-11 for LAN ESG/PSG/E8663B
Manual Configuration
Manually Configuring the Agilent MXG LAN
Manually Configuring the ESG/PSG/E8663B LAN
Dhcp Configuration
Auto DHCP/Auto-IP Configuration Agilent MXG
Configuring the Dhcp LAN Agilent MXG
Configuring the Dhcp LAN ESG/PSG/E8663B
Setting up Private LAN Verifying LAN Functionality
Using Interactive IO
Ping Responses
Using Visa Assistant
Click Edit Click the Edit Visa Config... button
Using
IO Config Form Windows NT
Configuring for
Show Devices Form Agilent IO Library version J.01.0100
Using Sockets LAN
Using Telnet LAN
Telnet example is provided in Unix Telnet Example on
Using Telnet On a PC With a Host/Port Setting Menu GUI
Using Telnet On Windows
Options and Parameters
Standard Unix Telnet Command Synopsis
Description
Unix Telnet Example
Using FTP
On the PC click Start Programs Command Prompt
FTP Screen
Using RS-232 ESG, PSG, and E8663B Only
Selecting IO Libraries for RS-232
Setting Up the RS-232 Interface
Setting the RS- 232 Interface Baud Rate ESG/PSG/E8663B
Setting the RS- 232 Echo Softkey
RS-232 Serial Interface Cable
Go to Settings Emulation and select VT100
Go to Settings Ascii Setup
Verifying RS-232 Functionality
If You Have Problems
Character Format Parameters
Before Using the Examples
Interface Check Using HP Basic
RS-232 Programming Interface Examples
Interface Check Using Visa and C
Queries Using HP Basic and RS-232
Queries for RS-232 Using Visa and C
Using USB Agilent MXG
Selecting I/O Libraries for USB
Front Panel USB Type-A
Setting Up the USB Interface
Rear Panel Interface Mini-B 5 pin
USB Interface Cable
Using IO Interfaces Using USB Agilent MXG
Programming Examples
Using the Programming Interface Examples
Programming Examples Development Environment
Running C++ Programs
++ Examples
Running C# Examples
Running Basic Examples
Visual Basic 6.0 Programming Examples
Running Perl Examples
Running Java Examples
Running Matlab Examples
Visual Basic Examples
Installing the Gpib Interface Card
Installing the Gpib Interface Card on
Gpib Function Statements Command Messages
Abort Function
Remote Function
Local Lockout Function
Local Function
Clear Function
Output Function
Enter Function
Programming Examples
Interface Check for Gpib Using Visa and C
Local Lockout Using HP Basic and Gpib
Pause
Local Lockout Using NI-488.2 and C++
Queries Using HP Basic and Gpib
Integer B
Queries Using NI-488.2 and Visual C++
Programming Examples Gpib Programming Interface Examples
Queries for Gpib Using Visa and C
Page
Generating a CW Signal Using Visa and C
Programming Examples Gpib Programming Interface Examples
Programming Examples Gpib Programming Interface Examples
Page
Generating an Internal FM Signal Using Visa and C
Programming Examples Gpib Programming Interface Examples
Generating a Step-Swept Signal Using Visa and C++
Generating a Swept Signal Using Visa and Visual C++
Programming Examples Gpib Programming Interface Examples
Programming Examples Gpib Programming Interface Examples
Programming Examples Gpib Programming Interface Examples
Saving and Recalling States Using Visa and C
SAV,*RCL
Program NAMEvisaex9.cpp
Gpib
Programming Examples Gpib Programming Interface Examples
Programming Examples Gpib Programming Interface Examples
Reading the Service Request Interrupt SRQ Using Visa and C
Programming Examples Gpib Programming Interface Examples
Programming Examples Gpib Programming Interface Examples
Programming Examples Gpib Programming Interface Examples
Using 8757D Pass-Thru Commands PSG with Option 007 Only
Equipment Setup
Gpib Address Assignments
Example Pass-Thru Program
Sweep Sweep Type 8757D System Sweep Time to Manual
Insert line 115, that recalls state 1, RC1
Using VXI-11 with Gpib Programs
LAN Programming Interface Examples
VXI-11 Programming
VXI-11 Programming Using Sicl and C++
VXI-11 Programming Using Visa and C++
104
Sockets LAN Programming and C
Sockets on Unix
Sockets on Windows
Queries for Lan Using Sockets
Programming Using main1 Function
108
Programming Examples LAN Programming Interface Examples
110
Programming Examples LAN Programming Interface Examples
112
Programming Examples LAN Programming Interface Examples
114
Programming Examples LAN Programming Interface Examples
116
Programming Examples LAN Programming Interface Examples
118
Sensfreqcent CALC1MARK1X?
120
Programming Examples LAN Programming Interface Examples
Winsock
Programming Examples LAN Programming Interface Examples
124
Char *charBuf = char * mallocINPUTBUFSIZE
Synopsis
Programming Examples LAN Programming Interface Examples
Sockets LAN Programming Using Java
Generating a CW Signal Using Java
Programming Examples LAN Programming Interface Examples
Sockets LAN Programming Using Perl
Setting the Power Level and Sending Queries Using Perl
RS-232 Programming Interface Examples ESG/PSG/E8663B Only
END
Page
None
Rs232ex2.cpp
136
Programming the Status Register System
Overview
Overall Status Byte Register Systems
N5181A/82A/83A Overall Status Byte Register System 1
N5181A/82A/83A Overall Status Byte Register System 2
E8663B Overall Status Byte Register System 1
E8663B Overall Status Byte Register System 2
E4428C/38C Overall Status Byte Register System 1
E4428C/38C Overall Status Byte Register System 2
E8257D/67D Overall Status Byte Register System 1
E8257D/67D Overall Status Byte Register System 2
Example Enable a Register
Status Register Bit Values
Example Query a Register
Monitoring When a Condition Bit Changes
Accessing Status Register Information
Deciding How to Monitor
Determining What to Monitor
Using the Service Request SRQ Method
Generating a Service Request
Status Register Scpi Commands
152
Effects of STATusPRESet
Registera Value after STATusPRESet
Status Byte Group
Service Request Enable Register
Status Byte Register
Status Byte Register Bits
Status Groups
Standard Event Status Group
Standard Event Status Enable Register
Standard Event Status Register
Standard Event Status Register Bits
Standard Operation Status Group
Standard Operation Condition Register
Standard Operation Condition Register Bits
Standard Operation Event Enable Register
Standard Operation Transition Filters negative and positive
Standard Operation Event Register
Baseband Operation Status Group
Baseband Operation Condition Register
Baseband Operation Transition Filters negative and positive
Baseband Operation Condition Register Bits
Baseband Operation Event Enable Register
Baseband Operation Event Register
Data Questionable Status Group
Data Questionable Condition Register
Data Questionable Condition Register Bits
Data Questionable Event Enable Register
Data Questionable Transition Filters negative and positive
Data Questionable Event Register
Data Questionable Power Status Group
Data Questionable Power Condition Register
Data Questionable Power Event Register
Data Questionable Power Condition Register Bits
Data Questionable Power Event Enable Register
Data Questionable Frequency Status Group
Data Questionable Frequency Condition Register
Data Questionable Frequency Event Register
Data Questionable Frequency Condition Register Bits
Data Questionable Frequency Event Enable Register
Data Questionable Modulation Status Group
Data Questionable Modulation Condition Register
Data Questionable Modulation Event Register
10 Data Questionable Modulation Condition Register Bits
Data Questionable Modulation Event Enable Register
Data Questionable Calibration Status Group
Data Questionable Calibration Condition Register
Data Questionable Calibration Event Register
11 Data Questionable Calibration Condition Register Bits
Data Questionable Calibration Event Enable Register
Data Questionable Bert Status Group
Data Questionable Bert Condition Register
12 Data Questionable Bert Condition Register Bits
Data Questionable Bert Event Enable Register
Data Questionable Bert Event Register
Creating and Downloading Waveform Files
Overview of Downloading and Extracting Waveform Files
Understanding Waveform Data
Waveform Data Requirements
Bits and Bytes
LSB and MSB Bit Order
Little Endian and Big Endian Byte Order
Little Endian Order
Byte Swapping
DAC Input Values
Using E443xB ESG DAC Input Values
Scaling DAC Values
DAC over-range
’s Complement Data Format
Q Interleaving
Interleaved Hex Data
Waveform Structure
File Header
Marker File
File
Binary 0000
Waveform Phase Continuity
Phase Discontinuity, Distortion, and Spectral Regrowth
Waveform
Avoiding Phase Discontinuities
Sampled Sinewave with No Discontinuity
Waveform Memory
Signal Generators and Non-Volatile Memory Types
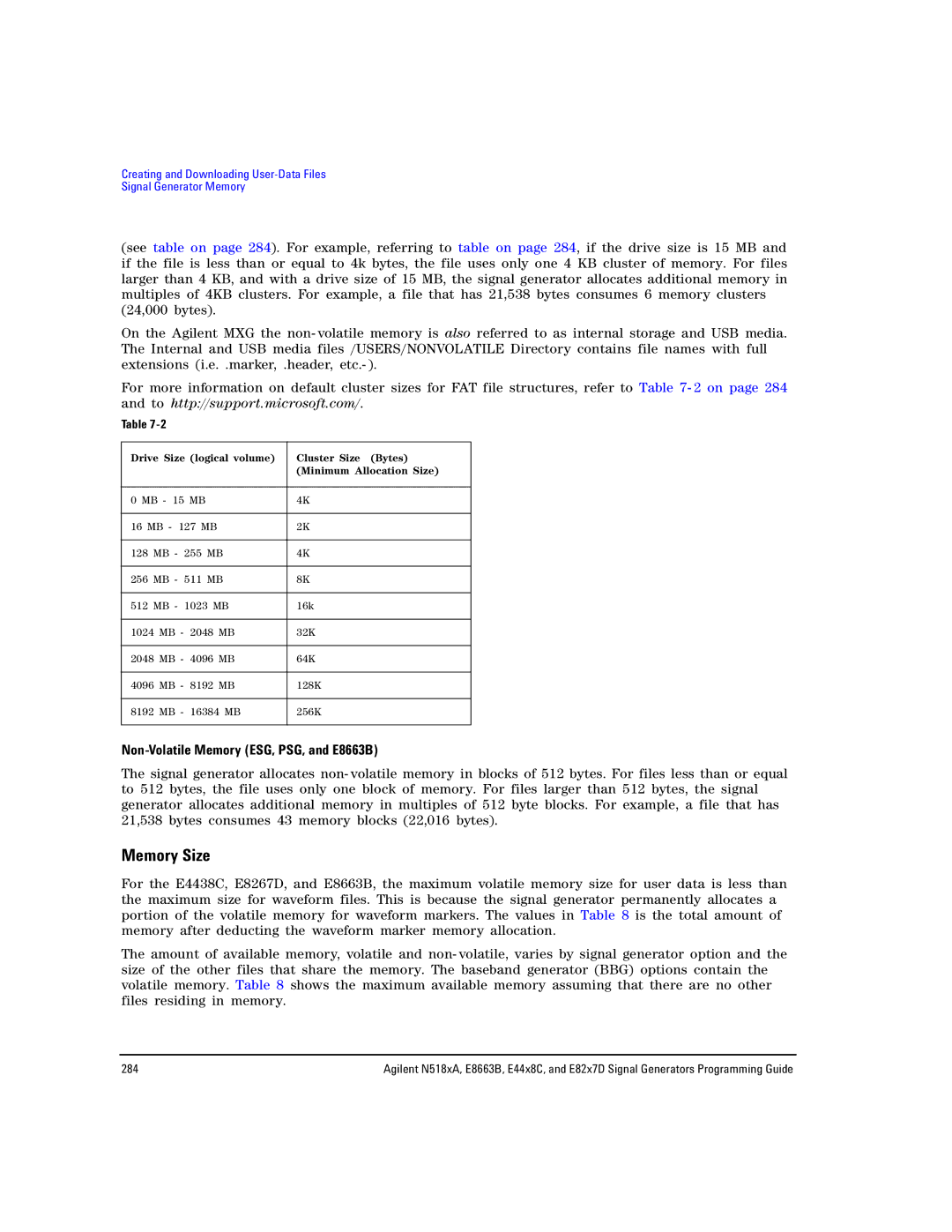
Memory Allocation
Volatile Memory
Non-Volatile Memory Agilent MXG
Drive Size logical volume
Memory Size
Non-Volatile Memory ESG/PSG
Volatile and Non-Volatile Memory N5182A
Fixed File System Overhead
Commands for Downloading and Extracting Waveform Data
Waveform Data Encryption
E4438C and E8267D Non-Volatile Nvwfm Memory
Scpi Command Line Structure
File Transfer Methods
Encrypted I/Q Files and the Securewave Directory
Mmemdata
Download Method Command Syntax Options Memory Type
Downloading Unencrypted Files for Extraction
10 Extracting Unencrypted I/Q Data
Memorya
11 Downloading Encrypted Files for Extraction
12 Extracting Encrypted Waveform Data
FTP Procedures
Using Microsoft’s Internet Explorer
Using the Command Window PC or Unix
13 Put Command Examples
To put a file, type
Using the Signal Generator’s Internal Web Server
14 Get Command Examples
Creating Waveform Data
Code Algorithm
Create I and Q data
214
Save the I/Q data to a text file to review
Line Code Description-Saving the I/Q Data to a Text File
216
1 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 1 0 1 1 0 1 0 1
Downloading Waveform Data
Line Code-Interleaving I and Q data for Big Endian Order
Using Simulation Software
Open a connection session with the signal generator
Download the I/Q data
Secondary address io = agtnewconnectiongpib,0,19
Using Advanced Programming Languages
Line Code Description-Download the I/Q data
Line CodeDescription-Download the I/Q Data
Numsamples by four. This is shown in the following example
Loading, Playing, and Verifying a Downloaded Waveform
Loading a File from Non-Volatile Memory
Play the waveform Send the following Scpi commands
Playing the Waveform
Verifying the Waveform
Building and Playing Waveform Sequences
Using the Download Utilities
Downloading E443xB Signal Generator Files
E443xB Data Format
Storage Locations for E443xB ARB files
Volatile Memory Storage Locations
Non-Volatile Memory Storage Locations
1100110110111001
Scpi Commands
Programming Examples
++ Programming Examples
Creating and Downloading Waveform Files Programming Examples
234
Creating and Downloading Waveform Files Programming Examples
Creating and Storing I/Q Data-Little Endian Order
Creating and Downloading Waveform Files Programming Examples
238
Creating and Downloading Waveform Files Programming Examples
240
Creating and Downloading Waveform Files Programming Examples
Importing and Downloading I/Q Data-Big Endian Order
Creating and Downloading Waveform Files Programming Examples
244
Importing and Downloading Using VISA-Big Endian Order
246
Creating and Downloading Waveform Files Programming Examples
248
Creating and Downloading Waveform Files Programming Examples
250
Creating and Downloading Waveform Files Programming Examples
252
Creating and Downloading Waveform Files Programming Examples
254
Matlab Programming Examples
Creating and Storing I/Q Data
256
Creating and Downloading Waveform Files Programming Examples
Creating and Downloading a Pulse
Creating and Downloading Waveform Files Programming Examples
Simulated Plot of In-Phase Signal
Creating and Downloading Waveform Files Programming Examples
Visual Basic Programming Examples
Creating I/Q Data-Little Endian Order
MSB
264
Downloading I/Q Data
266
HP Basic Programming Examples
Program Comments
Sets the number of points in the waveform
Assign @PSG to 719FORMAT on
290
272
Sets up loop to calculate waveform points
274
300
Troubleshooting Waveform Files
Symptom Possible Cause
Configuring the Pulse/RF Blank Agilent MXG
Configuring the Pulse/RF Blank ESG/PSG
278
Creating and Downloading User-Data Files
Pram
Signal Generator Memory
282
Agilent MXG Only Internal
Non-Volatile Memory ESG, PSG, and E8663B
Maximum Signal Generator Memory
Checking Available Memory
User-Data File Memory Location
User File Data Bit/Binary Downloads E4438C and E8267D
E4438C ESG
User File Bit Order LSB and MSB
Bit File Type Data
As Seen in the Signal Generator’s Bit File Editor
LSB
Binary File Type Data
Unframed Binary Data
User File Size
Framed Binary Data
Determining Memory Usage for Custom and Tdma User File Data
Maximum User File Size
Calculating Volatile Memory Pram Usage for Unframed Data
Calculating Volatile Memory Pram Usage for Framed Data
Number of Frames Bytes per Frame
Command Format
Downloading User Files
Command Format in a Program Routine
Memdata
Line Code Description-Download User File Data
Command for Bit File Downloads
Bit File Type Scpi Commands
Commands for Binary File Downloads
Command Syntax Example
Binary File Type Commands
Selecting a Downloaded User File as the Data Source
File Name Syntax
Modulating and Activating the Carrier
Modifying User File Data
Modifying a Binary File with a Hex Editor
FTP Procedures
Modifying a Bit File with a Hex Editor
Understanding Framed Transmission For Real-Time Tdma
GSM Multiframe Transmission
Mapping User File Data to a Single Timeslot
Real-Time Custom High Data Rates
Symbol Wide FIR Filter
Pattern RAM Pram Data Downloads E4438C and E8267D
Understanding Pram Files
Pram Data Byte
EVENT1
Viewing the Pram Waveform
Pram Byte Patterns and Bit Positions
Maximum Pram User File Size Payload Bits Only
Pram File Size
Determining the File Size
Maximum File Size After Downloading
Scpi Command for a List Format Download
Minimum File Size
Scpi Command for a Block Data Download
Command Syntax
Command Syntax in a Program Routine
MEMoryDATAPRAMFILEBLOCk myfile,#324012%S!4&07#8g*Y9@7
Line Code Description-Download Pram File Data
Selecting a Downloaded Pram File as the Data Source
Extracting a Pram File
Volatile Memory to Non- Volatile Memory
Extracting a Pram File
10 Downloading a File for Extraction
Modifying Pram Files
11 Downloading a File for No Extraction
FIR Filter Coefficient Downloads N5182A, E4438C and E8267D
Data Requirements
Data Limitations
Selecting a Downloaded User FIR Filter as the Active Filter
Sample Command Line
Downloading FIR Filter Coefficient Data
FIR Filter Data for Tdma Format
FIR Filter Data for Custom Modulation
FIR Filter Data for Cdma and W-CDMA Modulation
Modulating and Activating the Carrier
Save and Recall Scpi Commands
Save and Recall Instrument State Files
Save and Recall Programming Example Using Visa and C#
# and Microsoft .NET Framework
Page
328
Page
330
Page
332
Page
334
Page
User Flatness Correction Downloads Using C++ and Visa
FlatCal Console Application
Page
338
Page
User File Download Problems
12 Use-File Download Trouble Symptoms and Causes
Data Requirements
13 Pram Download Symptoms and Causes
Pram Download Problems
Using Externally Generated, Real-Time Data for Large Files
Multiple-of-8-Bits Requirement
14 Pram Data Byte
User FIR Filter Coefficient File Download Problems
15 User FIR File Download Trouble Symptoms and Causes
344
Index
Visa
Index
USB
Index
LAN
Sicl
Tdma
Scpi
354
Gpib
98 5 ME 5 NT 6 XP