Radeon X1600 Series
Disclaimer
Important Safety Instructions
Page
Table of Contents
Using TV Display and Capture Features
Using TV Out
CrossFire FAQ Reference
Glossary
Viii
Ring Bus Memory Controller
Radeon X1600 Series Features
Features
Ultra-Threaded Shader Engine
Advanced Image Quality Features
Avivo Video and Display Platform
CrossFire
System Requirements
External Connections
Before You Begin
Uninstall Previous Graphics Card Drivers
To uninstall previous drivers
Record Your Serial and Part Numbers
Turn off your system and remove the old graphics card
Installing Hardware
Basic Graphics Card Installation
Graphics Card Bus Types
Installing the Radeon graphics card
Advanced Installation AGP
Graphic Card Installation
Installing the Radeon graphics card
Advanced Installation PCIe
Graphics Card Installation
Connecting Devices
Connector Types
Using Multiple Displays
Connecting Your Monitors
Page
Display Configurations
Display Connectors Comments Configuration Used
Display Configurations
Installing Drivers and Software in Windows
Software Installation Prerequisites
To install ATI drivers and software
Monitor Configuration
To set up a multi-monitor display
Reinstalling Drivers
To configure your primary display
To manually reinstall drivers
Page
Installing the Catalyst Software Suite
Installing the Catalyst Software Suite
Launching Catalyst Control Center Using the Start Menu
Launching Catalyst Control Center
Other Quick Launch Access Points
Launching Catalyst Control Center Using the System Tray
Launching Catalyst Control Center Using Hot Keys
Catalyst Control Center Dialog
Catalyst Control Center Dashboard
Basic View
Switch Views
Catalyst Control Center Views
Advanced View
Hotkeys Manager
Open Hotkeys Manager Click List active Hotkeys only
Create a list of active hot keys
See a list of active hot keys only
Sort hot keys
Display Profiles Manager
To access the Profiles Manager
Profiles Manager
Create a profile
Activate a profile
Click opens the following application, file or shortcut
Save a profile
Delete a profile
To access Preferences
Preferences
Hide or show Tooltips
Click Hide Splash Screen
Show or hide text that appears on the toolbar buttons
Hide the Catalyst Control Center Splash Screen
Change Catalyst Control Center language
Help
To access Help
Display help for the aspect or feature you are using
Display the online help
Create a Problem Report
Click Problem Report Wizard
Information Center
To access the Information Center
To access system information
Displays Manager
Catalyst Control Center Displays Manager
Enable Extended Mode
Access Displays Manager
Enable a secondary display device
Enable Clone Mode
Click Clone Main with display device in the pop-up menu
Enable Stretch Main Vertically
Enable Stretch Main Horizontally
Click Clone Main with display device
Select Swap display mapping
Swap displays in Extended Mode
Swap displays in all other modes
Change desktop size
Change display refresh rate
Force changes to a specific display setting
Apply your settings
Rotate the desktop
Discard your settings
Display Options
Select a refresh rate override
Determine how display devices are detected
Force TV detection
Restore default settings
Click Defaults
Monitor Properties
Enable Extended Display Identification Data Edid
Monitor Attributes
Digital Panel Properties
Attributes
Set Image Scaling
Click Attributes
Adjust the DVI Settings
Set Hue
Set Color Temperature
Avivo Color
Click Avivo Color
Add 720p mode to the Displays Manager Force button
Hdtv Support
Add an Hdtv format
Click Hdtv Support
Apply an Hdtv Format
Click Apply Format
Standard Settings
Adjust your Standard settings
Preview your changes
Set the Anti-Aliasing preference manually
Set Temporal anti-aliasing using SmoothVision HD
Anti-aliasing
Click Anti-aliasing
Click Transparent Anti-Aliasing
Set the level of adaptive anti-aliasing
Adaptive Anti-aliasing
Anisotropic Filtering
Set the Anisotropic Filtering preference manually
Click Anisotropic Filtering Select Enable High Quality AF
Set the Anisotropic Filtering to automated preference
Set higher quality Anisotropic Filtering
Disable Catalyst A.I
Set Catalyst A.I. settings
Catalyst A.I
Preview your changes
Mipmap Detail Level
Set the Mipmap detail level
Click Mipmap Detail Level
SmartShader
Select a SmartShader effect
Click SmartShader
All Settings
Click All Settings
Set the Anti-Aliasing preference manually
Set Wait for vertical refresh setting
Set the Catalyst A.I. setting
Click All Settings Scroll to Mipmap Detail Level
Click All Settings Scroll to Wait for vertical refresh
Set Enable geometry instancing
API Specific
Set Alternate pixel center for Direct 3D
Click API Specific
Set Support DXT texture formats for Direct 3D
Set Triple buffering for OpenGL
Color
Set Force 24-bit Z-buffer depth for OpenGL
Display Color page to configure Desktop
Color Desktop
Set Gamma, Brightness, and Contrast simultaneously
Click Reactivate ATI color controls button
Revert to last known All Channel settings
Reactivate your color settings
Set Color Gamma
Set Color Contrast
Display Color page to configure FullScreen 3D
Color FullScreen 3D
Avivo Video for Radeon Series starting from
Click Standard Settings
Select a Video Preset
Start the Video Wizard
Click Adjustments
Adjustments
Let the application control the video adjustments
Set Gamma
Set Contrast
Set Brightness
Select an Overlay Display when in Extended Mode
Video Overlay Theater Mode
Select an Overlay Display when in Clone Mode
Click Theater Mode
Deinterlacing
Set video aspect ratio
Select a deinterlacing mode
Click Deinterlacing
Adjust Gamma
Let the application control video adjustments
Click All Settings Scroll to Video Adjustments
Adjust Brightness
Adjust Saturation
Adjust Hue
Enable Windows Media Settings
Click All Settings Scroll to Theater Mode Settings
Click All Settings Scroll to Deinterlacing
Click Windows Media Video Acceleration
VPU Recover
Enable VPU Recover
Click Enable VPU Recover
Prepare an error report
CrossFire
CrossFire
Enable CrossFire
Click Enable CrossFire
Change motherboard Bios settings
CrossFire graphics card connections
Graphics cards with different amounts of memory
Card Reversal Recommended
3D client is active
CrossFire Is Currently Unavailable
Disabling CrossFire
Open the Profiles Manager
Viewing Your PC’s Display on a TV
Using TV Out
Connecting to a TV
To connect S-Video Out
Using a Monitor vs. Using TV Display
Using Games and Applications
Connecting to Hdtv
Using a TV as the Only Display
Viewing Text on a TV
Installing your ATI Hdtv video cable
ATI Hdtv Cable
Using Your ATI Hdtv Video Cable
Connecting to Hdtv
Are there specific Cmos motherboard settings for CrossFire?
What motherboards support CrossFire?
How are the graphics cards connected on a CrossFire system?
Which games/applications work with CrossFire?
Is a driver profile required to make CrossFire work?
On what basis are different rendering modes chosen?
What type of performance improvement is expected?
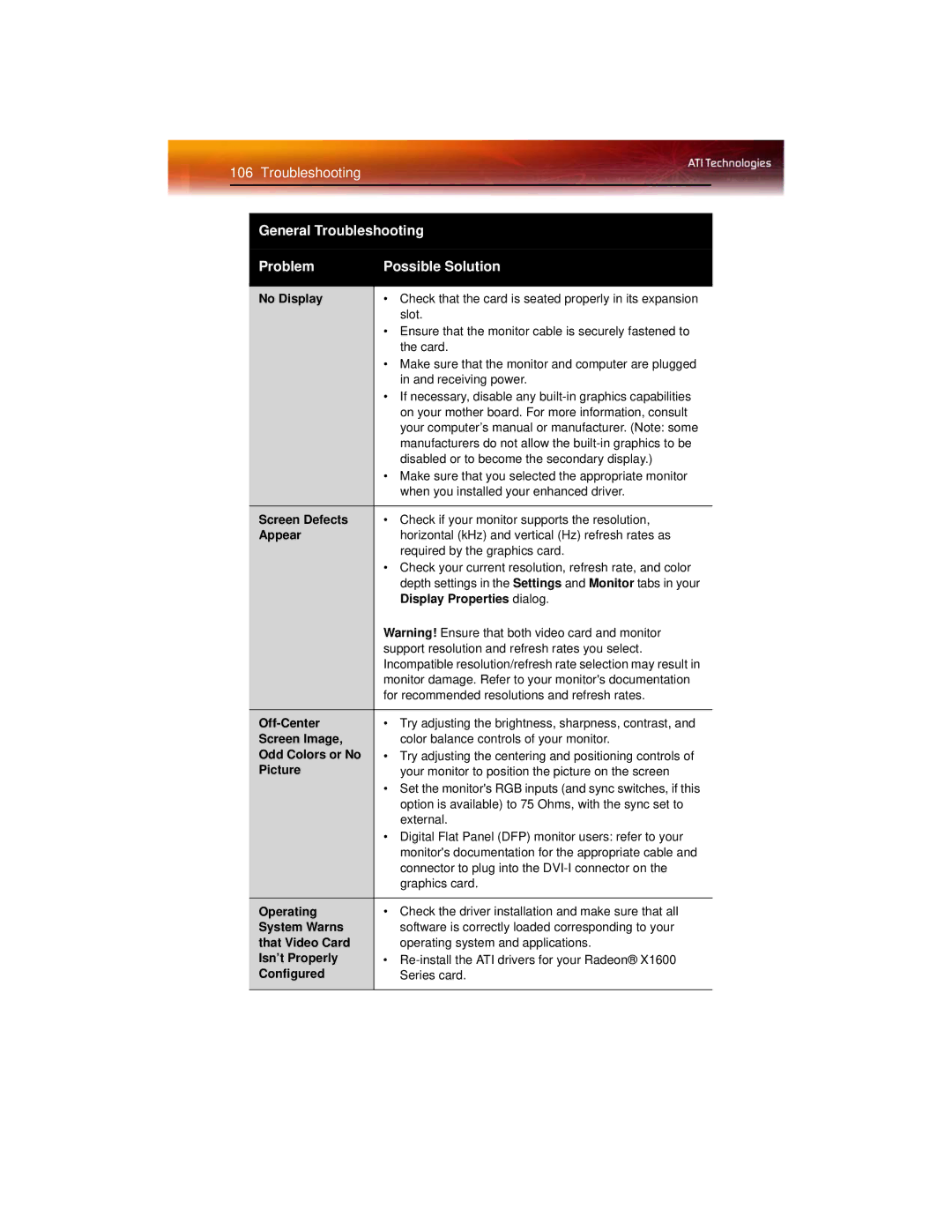
Troubleshooting
Reference
Screen Defects
CrossFire-Specific Troubleshooting
CrossFire-Specific Troubleshooting Problem Possible Solution
HDTV/HDTV Adapter Troubleshooting Problem Possible Solution
Product Registration Customer Care
Ati.com
Getting Additional Accessories
Compliance Information
FCC Compliance Information
CE Compliance Information
Electrical Safety
Industry Canada Compliance Statement
Informations de conformité de la CE
This product was manufactured by ATI Technologies Inc
Compliance Information
Pulldown
3Dc
Adaptive Anti-aliasing
Alpha Blending
Alternate Frame Rendering
Aspect
Anisotropic Filtering
Anti-aliasing
Aspect Ratio
Bit Depth
Back Buffer
Bilinear Filtering
Bitmap
Catalyst Control Center
Brightness
Buffer
Color Component
Compositing Engine
Component Video
Composite Video
Control Point
DirectX
Dashboard
Direct 3D
Dithering
Flat Shading
Fog
Frame Buffer
Frames Per Second
Gamma
Gouraud Shading
Hue
HydraVision
HyperZ HD
Lighting
Keyframe Interpolation
KTX Buffer Region Extension
Mipmapping
Offscreen Memory
OpenGL
ATI Overdrive
Pixel
PCI Express PCIe
Pipeline
Refresh Rate
Resolution
Scissor Mode
Saturation
Shadow Mask
SmartShader HD
SmoothVision HD
SuperTiling
Specular Highlight
Super Anti-aliasing
Video
Texture Mapping
Transition Minimized Differential Signaling Tmds
Texel
Texture Preference
VersaVision
Trilinear Filtering
Vector Adaptive Deinterlacing
Vertex Shader
Video Immersion
VGA Connector
VPU Recover
VideoShader HD
134
Index
Catalyst A.I , 62, 91, 102
CRT 4, 17, 109, 120, 121
Dot pitch 97, 121
Extended Mode 40, 41, 42, 80
Hdtv 97
Ntsc 115, 122, 125
Resolution 4, 21, 39, 46, 48, 51, 97, 106
Theater Mode 76, 80, 81, 84
TV 38, 41, 42, 43, 44, 46, 96, 97
Wizard 37, 76