REMOTE INTELLIGENT SENSOR - AREA MONITOR
3SYSTEM OPERATION AND FEATURES
3.1COMPLETE SAMPLING SEQUENCE
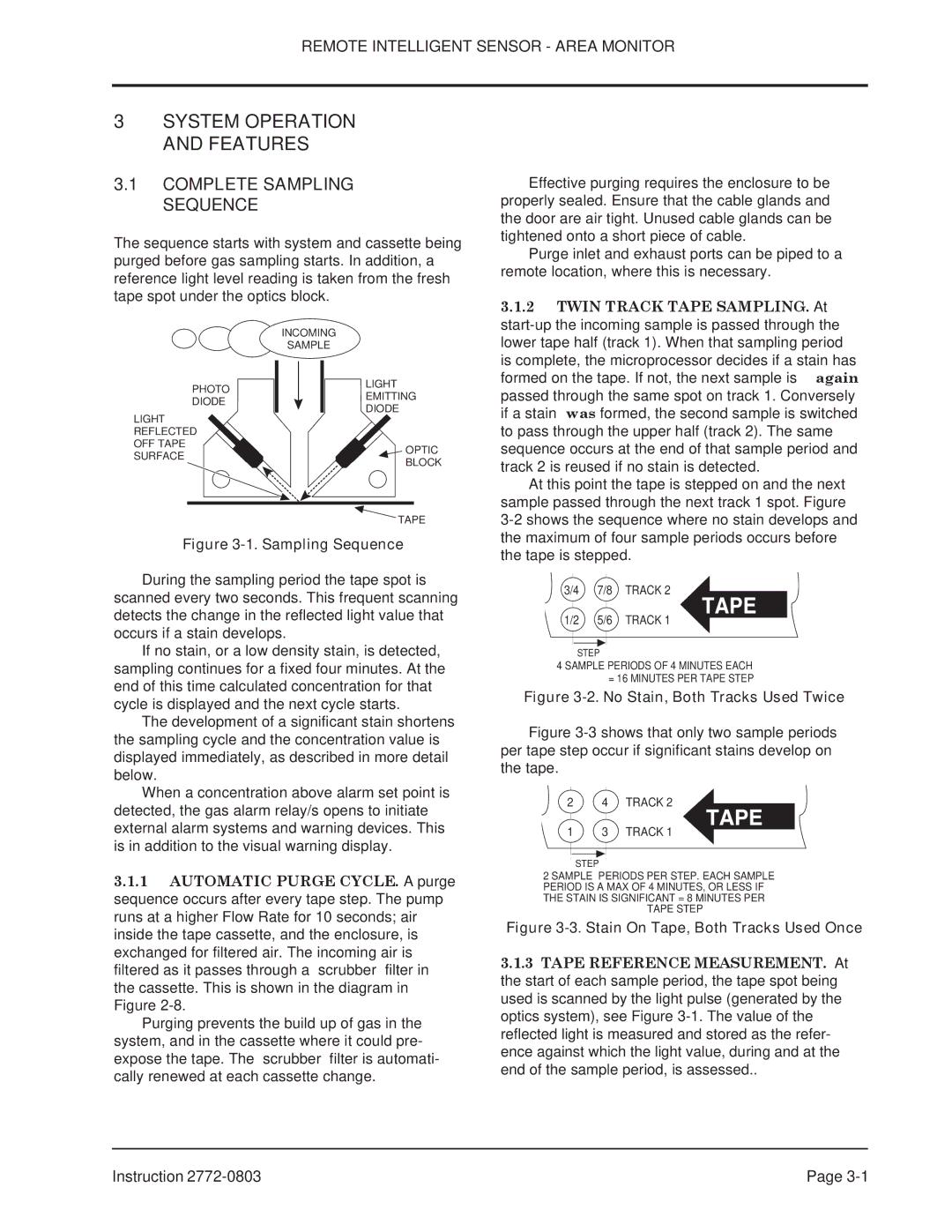
The sequence starts with system and cassette being purged before gas sampling starts. In addition, a reference light level reading is taken from the fresh tape spot under the optics block.
Effective purging requires the enclosure to be properly sealed. Ensure that the cable glands and the door are air tight. Unused cable glands can be tightened onto a short piece of cable.
Purge inlet and exhaust ports can be piped to a remote location, where this is necessary.
3.1.2 TWIN TRACK TAPE SAMPLING. At |
PHOTO
DIODE
LIGHT
REFLECTED
OFF TAPE
SURFACE
INCOMING
SAMPLE
LIGHT
EMITTING
DIODE
![]() OPTIC
OPTIC
BLOCK
lower tape half (track 1). When that sampling period |
is complete, the microprocessor decides if a stain has |
formed on the tape. If not, the next sample is again |
passed through the same spot on track 1. Conversely |
if a stain was formed, the second sample is switched |
to pass through the upper half (track 2). The same |
sequence occurs at the end of that sample period and |
track 2 is reused if no stain is detected. |
At this point the tape is stepped on and the next |
sample passed through the next track 1 spot. Figure |
TAPE
Figure 3-1. Sampling Sequence
During the sampling period the tape spot is scanned every two seconds. This frequent scanning detects the change in the reflected light value that occurs if a stain develops.
If no stain, or a low density stain, is detected, sampling continues for a fixed four minutes. At the end of this time calculated concentration for that cycle is displayed and the next cycle starts.
The development of a significant stain shortens the sampling cycle and the concentration value is displayed immediately, as described in more detail below.
When a concentration above alarm set point is detected, the gas alarm relay/s opens to initiate external alarm systems and warning devices. This is in addition to the visual warning display.
3.1.1AUTOMATIC PURGE CYCLE. A purge sequence occurs after every tape step. The pump runs at a higher Flow Rate for 10 seconds; air inside the tape cassette, and the enclosure, is exchanged for filtered air. The incoming air is filtered as it passes through a ‘scrubber’ filter in the cassette. This is shown in the diagram in Figure
Purging prevents the build up of gas in the system, and in the cassette where it could pre- expose the tape. The ‘scrubber’ filter is automati- cally renewed at each cassette change.
the maximum of four sample periods occurs before |
the tape is stepped. |
3/4 | 7/8 | TRACK 2 |
1/2 | 5/6 | TAPE |
TRACK 1 |
STEP
4 SAMPLE PERIODS OF 4 MINUTES EACH = 16 MINUTES PER TAPE STEP
Figure 3-2. No Stain, Both Tracks Used Twice
Figure 3-3 shows that only two sample periods per tape step occur if significant stains develop on the tape.
2 | 4 | TRACK 2 |
1 | 3 | TAPE |
TRACK 1 |
STEP
2 SAMPLE PERIODS PER STEP. EACH SAMPLE PERIOD IS A MAX OF 4 MINUTES, OR LESS IF THE STAIN IS SIGNIFICANT = 8 MINUTES PER
TAPE STEP
Figure 3-3. Stain On Tape, Both Tracks Used Once
3.1.3TAPE REFERENCE MEASUREMENT. At the start of each sample period, the tape spot being used is scanned by the light pulse (generated by the optics system), see Figure
Instruction | Page |