Feature and Technical Overview | BlackBerry Enterprise Server process flows |
5.The BlackBerry Dispatcher compresses the content, encrypts it using the device transport key of the BlackBerry device, and sends the encrypted content to the BlackBerry Router.
6.The BlackBerry Router sends the encrypted content to the wireless network over port 3101.
7.The wireless network verifies that the PIN belongs to a valid BlackBerry device that is registered with the wireless network and sends the encrypted content to the BlackBerry device.
8.The BlackBerry device sends a delivery confirmation to the BlackBerry Router, and decrypts and decompresses the content so that the user can view it in the BlackBerry Browser.
If the BlackBerry MDS Connection Service does not receive a delivery confirmation within the flow control timeout limit, it sends a message to the wireless network to delete the pending content.
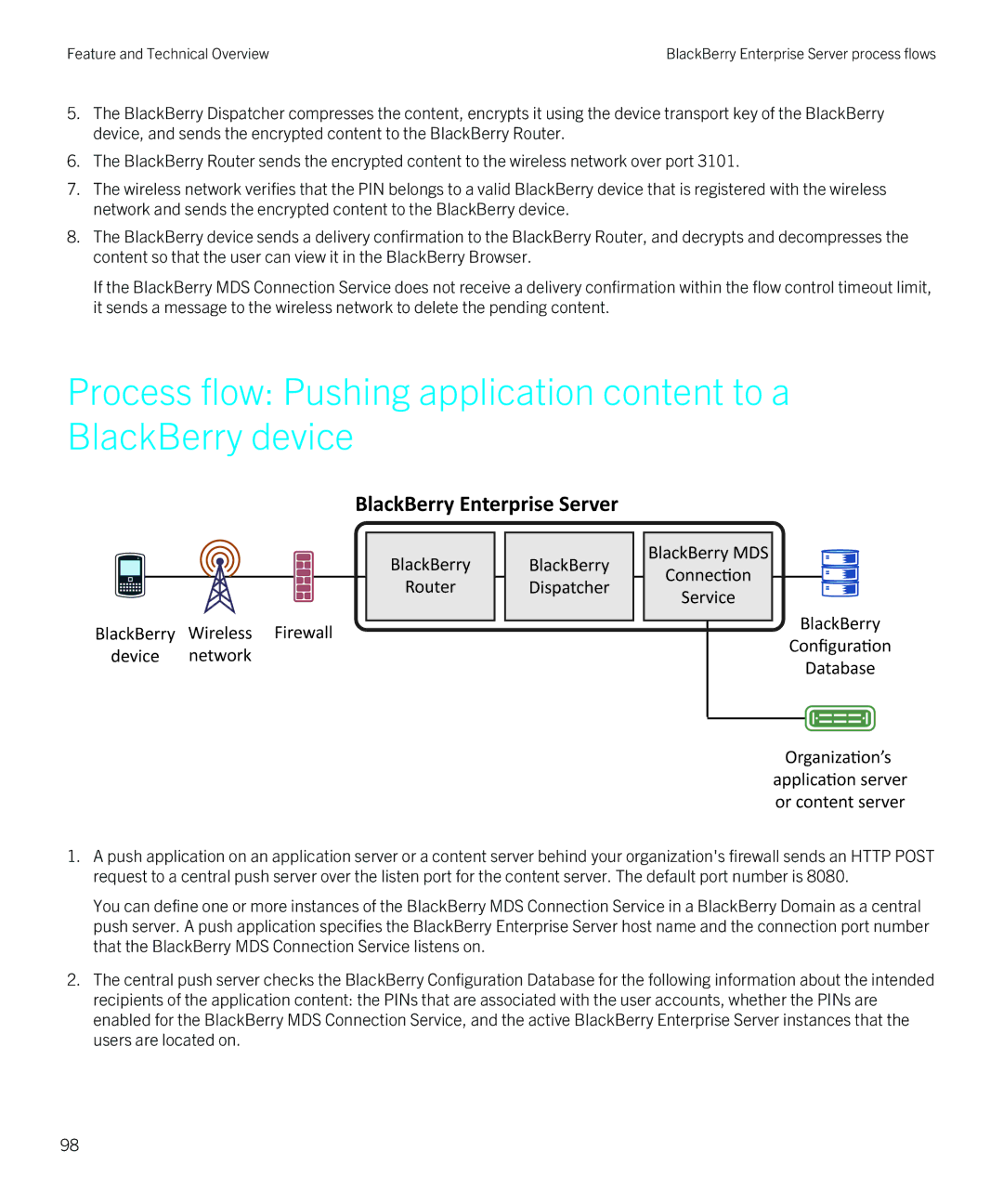
Process flow: Pushing application content to a BlackBerry device
1.A push application on an application server or a content server behind your organization's firewall sends an HTTP POST request to a central push server over the listen port for the content server. The default port number is 8080.
You can define one or more instances of the BlackBerry MDS Connection Service in a BlackBerry Domain as a central push server. A push application specifies the BlackBerry Enterprise Server host name and the connection port number that the BlackBerry MDS Connection Service listens on.
2.The central push server checks the BlackBerry Configuration Database for the following information about the intended recipients of the application content: the PINs that are associated with the user accounts, whether the PINs are enabled for the BlackBerry MDS Connection Service, and the active BlackBerry Enterprise Server instances that the users are located on.
98