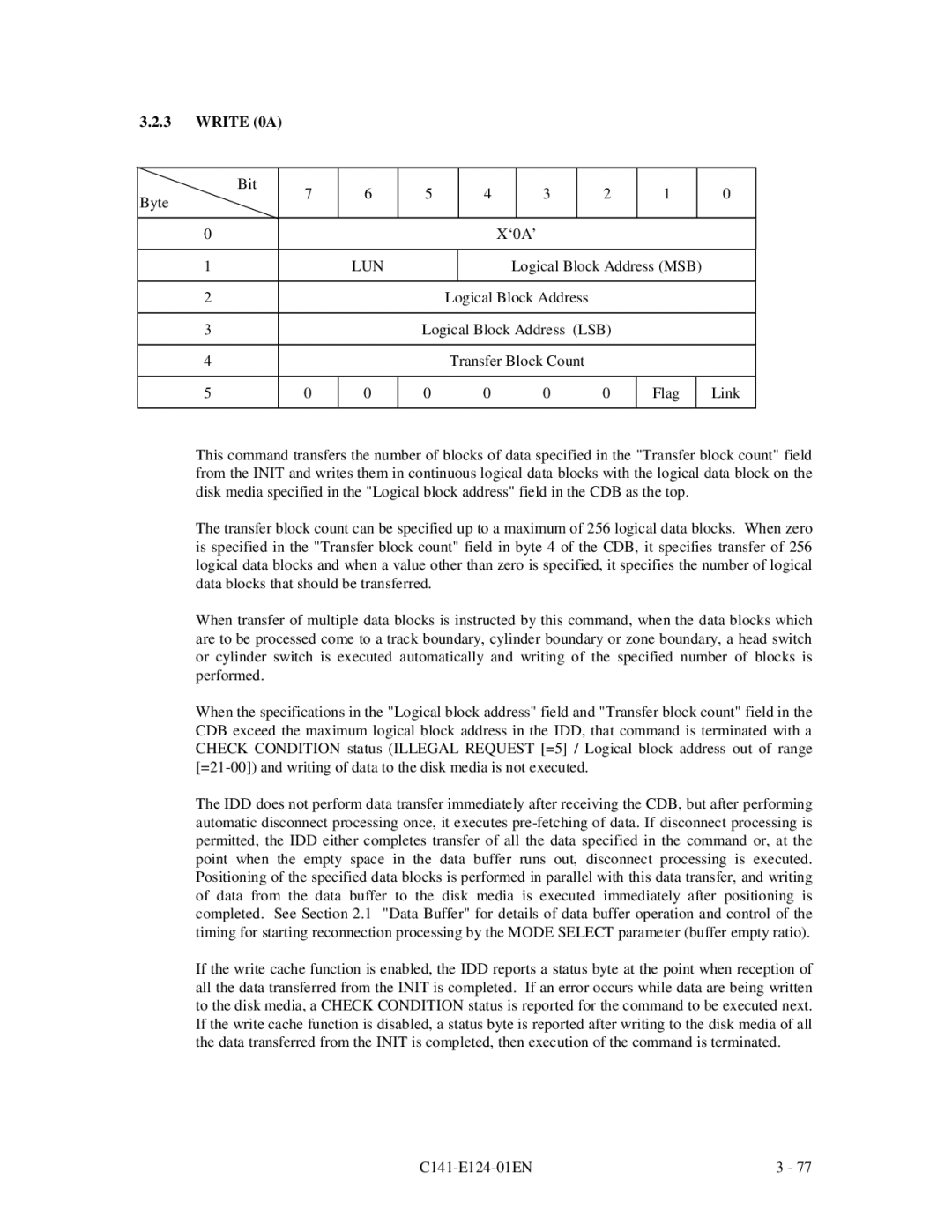
MAN3735, MAN3184, MAN3367, MAN3735 SERIES DISK DRIVES, MAN3367, MAN3184 specifications
Fujitsu's MAN3184, MAN3367, and MAN3735 series disk drives represent a significant advancement in storage technology, catering to the needs of businesses seeking reliability, performance, and high capacity. These drives are designed for enterprise environments, providing exceptional data integrity and speed essential for effective data management.The MAN3184 series is renowned for its high rotational speed of 10,000 RPM, which significantly enhances data access times. With a capacity of up to 18.4 GB, these drives are suitable for applications requiring quick read and write operations. The series employs an improved read/write head technology, which reduces latency and increases overall performance. This technology is complemented by advanced error correction mechanisms, ensuring the reliability necessary for critical data applications.
Transitioning to the MAN3367 series, these drives offer increased storage capacity and improved performance metrics. With capacities reaching up to 36.7 GB, they cater to growing data demands in modern enterprises. They also feature a 10,000 RPM spindle speed, ensuring that the drives can handle intensive workloads with ease. The MAN3367 drives include SCSI interface support, making them versatile and easy to integrate into various systems. The inclusion of intelligent caching algorithms allows for faster data retrieval, while built-in thermal management features ensure optimal performance, even under heavy usage.
The MAN3735 series takes performance up another notch, boasting higher capacities of up to 73.5 GB. These drives are particularly suited for environments that require high reliability and availability. The series utilizes a state-of-the-art SCSI Ultra160 interface, which maximizes data transfer rates, ultimately enhancing overall system efficiency. Additionally, the MAN3735 series employs advanced data protection technologies, including power loss protection and predictive failure analysis, which proactively minimizes potential downtime.
All these series of Fujitsu disk drives are built with a focus on durability and sustained performance. They are designed to operate seamlessly in high-demand environments, ensuring that organizations can rely on them for critical applications. Their compact design and energy-efficient operation make them an ideal choice for modern data centers looking to optimize space and reduce power consumption.
In summary, Fujitsu's MAN3184, MAN3367, and MAN3735 series disk drives deliver a blend of high capacity, performance, and reliability. These drives incorporate advanced technologies that address the evolving needs of enterprise storage solutions, making them a valuable asset for any organization aiming to enhance their data management capabilities.