RS-232 SERIAL CONTROL COMMANDS
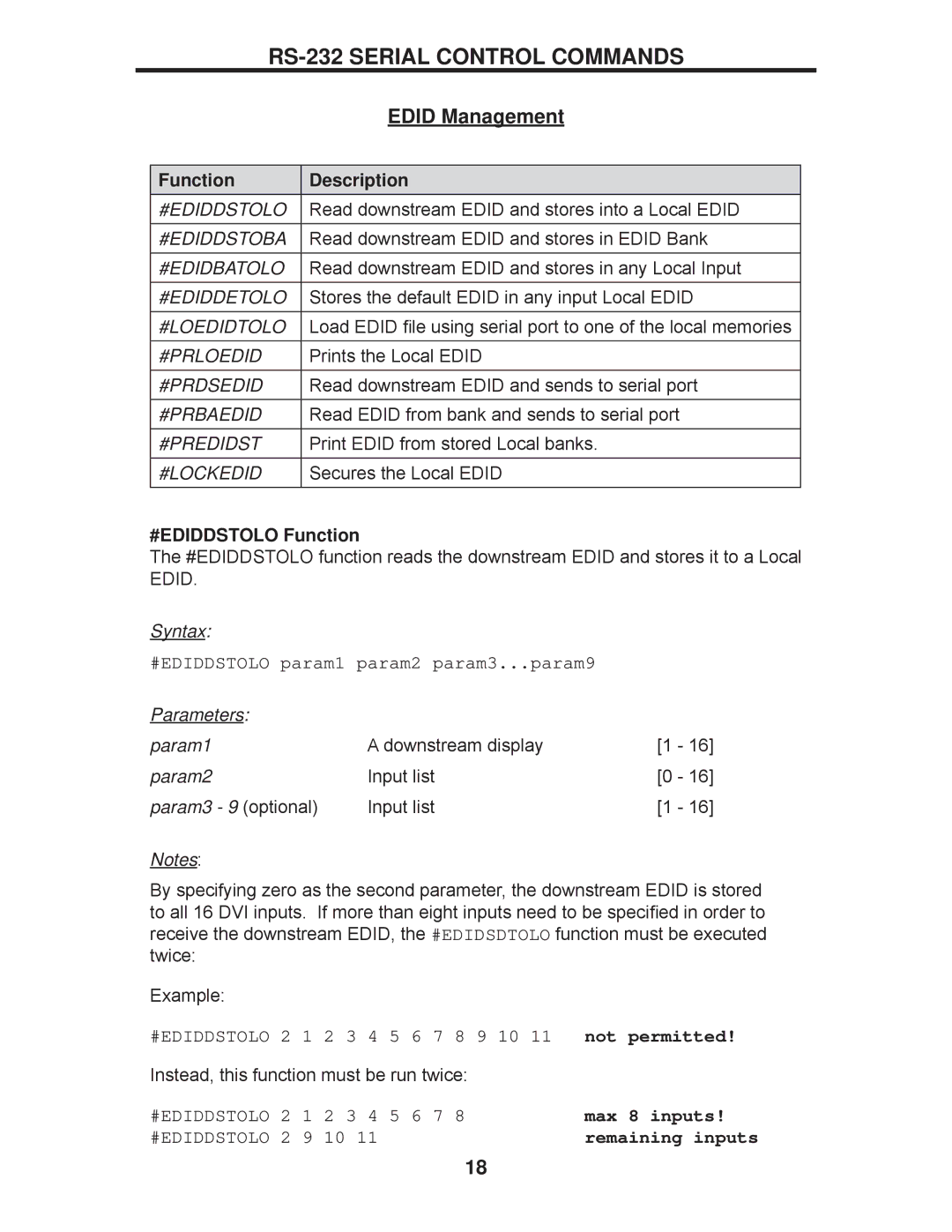
| EDID Management |
|
|
Function | Description |
#EDIDDSTOLO | Read downstream EDID and stores into a Local EDID |
#EDIDDSTOBA | Read downstream EDID and stores in EDID Bank |
#EDIDBATOLO | Read downstream EDID and stores in any Local Input |
|
|
#EDIDDETOLO | Stores the default EDID in any input Local EDID |
|
|
#LOEDIDTOLO | Load EDID file using serial port to one of the local memories |
|
|
#PRLOEDID | Prints the Local EDID |
|
|
#PRDSEDID | Read downstream EDID and sends to serial port |
|
|
#PRBAEDID | Read EDID from bank and sends to serial port |
#PREDIDST | Print EDID from stored Local banks. |
#LOCKEDID | Secures the Local EDID |
#EDIDDSTOLO Function
The #EDIDDSTOLO function reads the downstream EDID and stores it to a Local EDID.
Syntax:
#EDIDDSTOLO param1 param2 param3...param9
Parameters: |
|
|
param1 | A downstream display | [1 - 16] |
param2 | Input list | [0 - 16] |
param3 - 9 (optional) | Input list | [1 - 16] |
Notes:
By specifying zero as the second parameter, the downstream EDID is stored to all 16 DVI inputs. If more than eight inputs need to be specified in order to receive the downstream EDID, the #EDIDSDTOLO function must be executed twice:
Example:
#EDIDDSTOLO 2 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 not permitted!
Instead, this function must be run twice:
#EDIDDSTOLO | 2 | 1 | 2 3 4 | 5 6 7 8 | max 8 inputs! |
#EDIDDSTOLO | 2 | 9 | 10 11 |
| remaining inputs |
18