Troubleshooting Guide
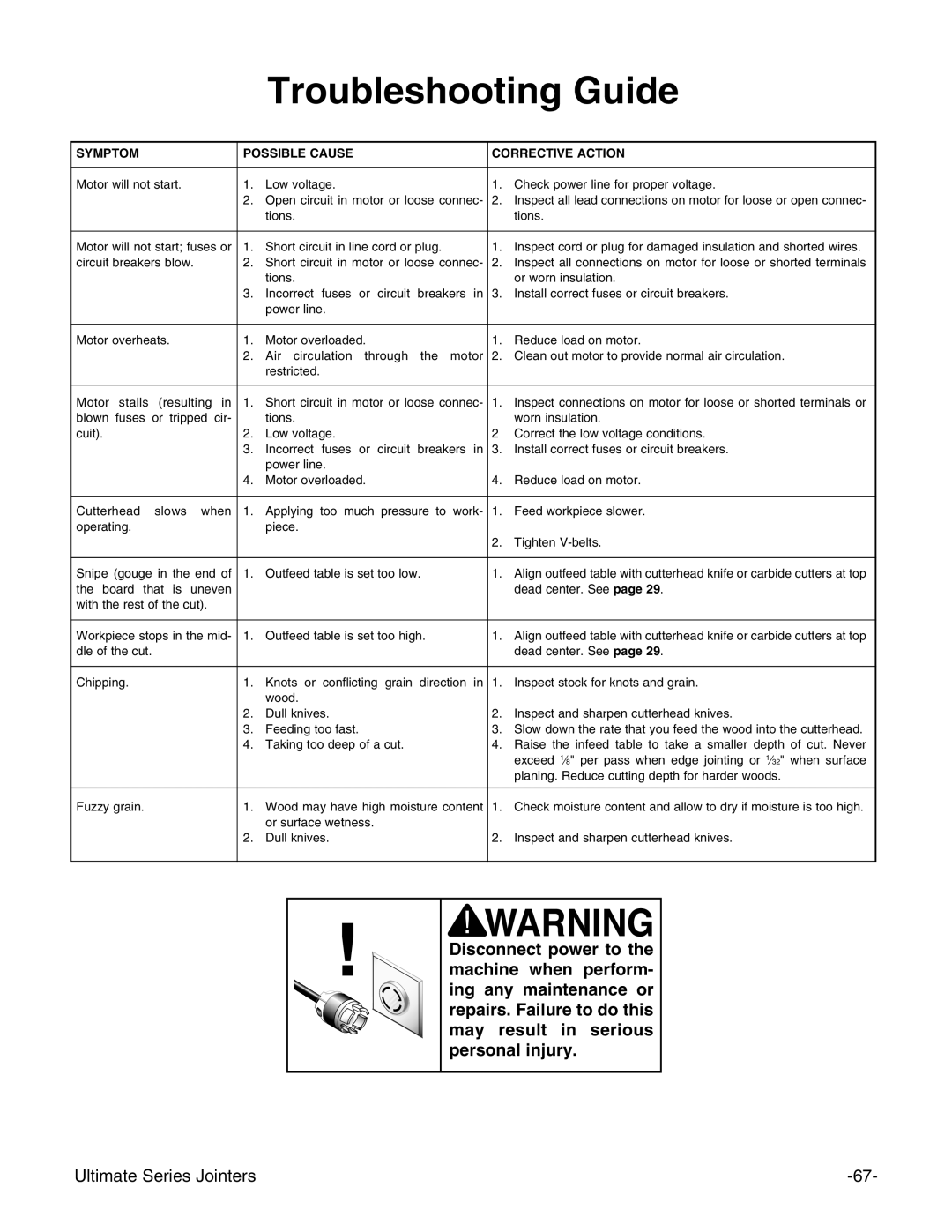
SYMPTOM |
| POSSIBLE CAUSE | CORRECTIVE ACTION | ||
|
|
|
|
| |
Motor will not start. | 1. | Low voltage. | 1. | Check power line for proper voltage. | |
|
| 2. | Open circuit in motor or loose connec- | 2. | Inspect all lead connections on motor for loose or open connec- |
|
|
| tions. |
| tions. |
|
|
|
|
| |
Motor will not start; fuses or | 1. | Short circuit in line cord or plug. | 1. | Inspect cord or plug for damaged insulation and shorted wires. | |
circuit breakers blow. | 2. | Short circuit in motor or loose connec- | 2. | Inspect all connections on motor for loose or shorted terminals | |
|
|
| tions. |
| or worn insulation. |
|
| 3. | Incorrect fuses or circuit breakers in | 3. | Install correct fuses or circuit breakers. |
|
|
| power line. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
Motor overheats. | 1. | Motor overloaded. | 1. | Reduce load on motor. | |
|
| 2. | Air circulation through the motor | 2. | Clean out motor to provide normal air circulation. |
|
|
| restricted. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Motor stalls | (resulting in | 1. | Short circuit in motor or loose connec- | 1. | Inspect connections on motor for loose or shorted terminals or |
blown fuses or tripped cir- |
| tions. |
| worn insulation. | |
cuit). |
| 2. | Low voltage. | 2 | Correct the low voltage conditions. |
|
| 3. | Incorrect fuses or circuit breakers in | 3. | Install correct fuses or circuit breakers. |
|
|
| power line. |
|
|
|
| 4. | Motor overloaded. | 4. | Reduce load on motor. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cutterhead | slows when | 1. | Applying too much pressure to work- | 1. | Feed workpiece slower. |
operating. |
|
| piece. |
|
|
|
|
|
| 2. | Tighten |
|
|
|
|
| |
Snipe (gouge in the end of | 1. | Outfeed table is set too low. | 1. | Align outfeed table with cutterhead knife or carbide cutters at top | |
the board that is uneven |
|
|
| dead center. See page 29. | |
with the rest of the cut). |
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
| |
Workpiece stops in the mid- | 1. | Outfeed table is set too high. | 1. | Align outfeed table with cutterhead knife or carbide cutters at top | |
dle of the cut. |
|
|
|
| dead center. See page 29. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Chipping. |
| 1. | Knots or conflicting grain direction in | 1. | Inspect stock for knots and grain. |
|
|
| wood. |
|
|
|
| 2. | Dull knives. | 2. | Inspect and sharpen cutterhead knives. |
|
| 3. | Feeding too fast. | 3. | Slow down the rate that you feed the wood into the cutterhead. |
|
| 4. | Taking too deep of a cut. | 4. | Raise the infeed table to take a smaller depth of cut. Never |
|
|
|
|
| exceed 1⁄8" per pass when edge jointing or 1⁄32" when surface |
|
|
|
|
| planing. Reduce cutting depth for harder woods. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Fuzzy grain. |
| 1. | Wood may have high moisture content | 1. | Check moisture content and allow to dry if moisture is too high. |
|
|
| or surface wetness. |
|
|
|
| 2. | Dull knives. | 2. | Inspect and sharpen cutterhead knives. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Disconnect power to the machine when perform- ing any maintenance or repairs. Failure to do this may result in serious personal injury.
Ultimate Series Jointers |