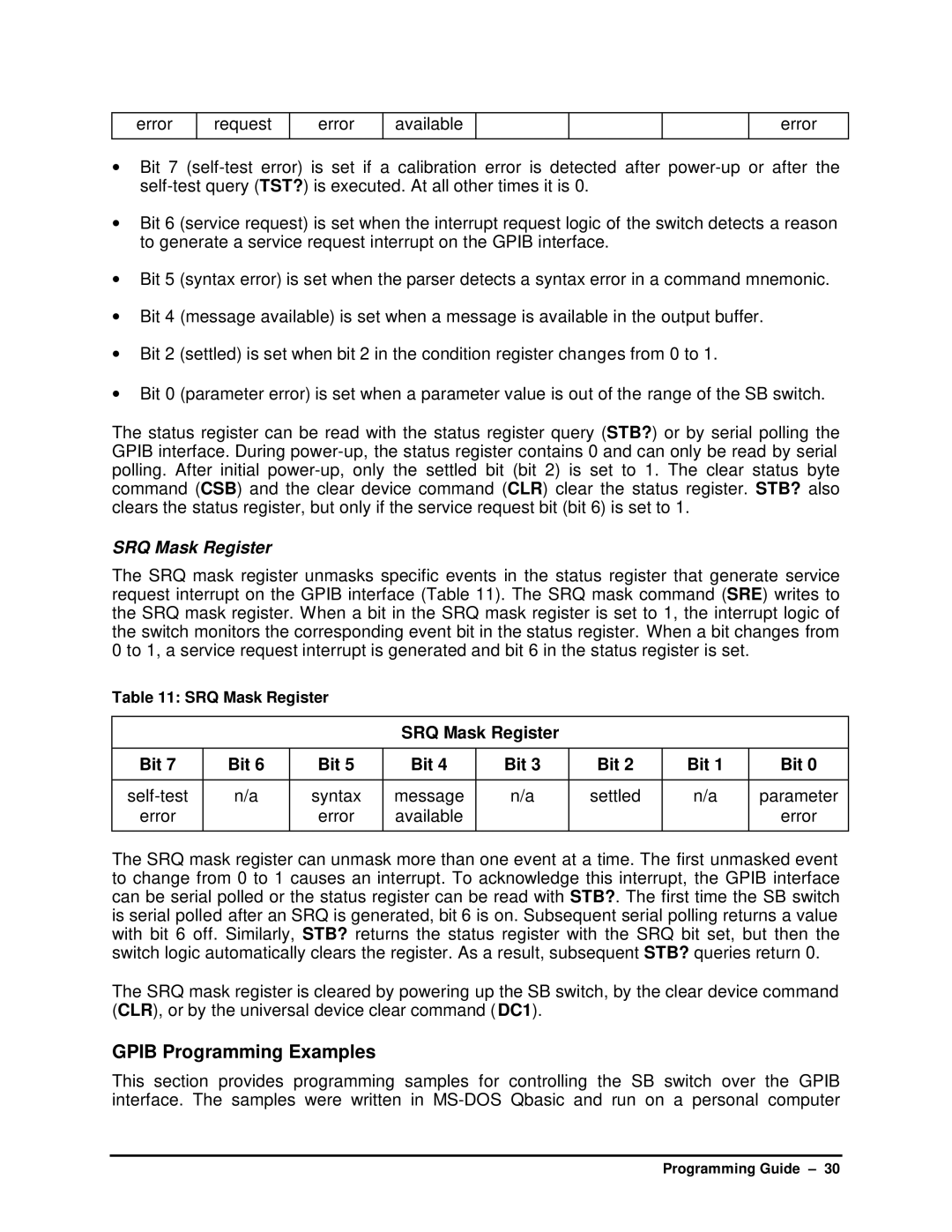
error
request
error
available
error
•Bit 7
•Bit 6 (service request) is set when the interrupt request logic of the switch detects a reason to generate a service request interrupt on the GPIB interface.
•Bit 5 (syntax error) is set when the parser detects a syntax error in a command mnemonic.
•Bit 4 (message available) is set when a message is available in the output buffer.
•Bit 2 (settled) is set when bit 2 in the condition register changes from 0 to 1.
•Bit 0 (parameter error) is set when a parameter value is out of the range of the SB switch.
The status register can be read with the status register query (STB?) or by serial polling the GPIB interface. During
SRQ Mask Register
The SRQ mask register unmasks specific events in the status register that generate service request interrupt on the GPIB interface (Table 11). The SRQ mask command (SRE) writes to the SRQ mask register. When a bit in the SRQ mask register is set to 1, the interrupt logic of the switch monitors the corresponding event bit in the status register. When a bit changes from 0 to 1, a service request interrupt is generated and bit 6 in the status register is set.
Table 11: SRQ Mask Register
SRQ Mask Register
Bit 7 | Bit 6 | Bit 5 | Bit 4 | Bit 3 | Bit 2 | Bit 1 | Bit 0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
n/a | syntax | message | n/a | settled | n/a | parameter | |
error |
| error | available |
|
|
| error |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
The SRQ mask register can unmask more than one event at a time. The first unmasked event to change from 0 to 1 causes an interrupt. To acknowledge this interrupt, the GPIB interface can be serial polled or the status register can be read with STB?. The first time the SB switch is serial polled after an SRQ is generated, bit 6 is on. Subsequent serial polling returns a value with bit 6 off. Similarly, STB? returns the status register with the SRQ bit set, but then the switch logic automatically clears the register. As a result, subsequent STB? queries return 0.
The SRQ mask register is cleared by powering up the SB switch, by the clear device command (CLR), or by the universal device clear command ( DC1).
GPIB Programming Examples
This section provides programming samples for controlling the SB switch over the GPIB interface. The samples were written in
Programming Guide – 30