Dynamic DNS (DDNS) is a system that allows the domain name data held in a name server to be updated in real time. The most common use for this is in allowing an Internet domain name to be assigned to a computer (or router) with a dynamic IP address. This makes it possible for other sites on the Internet to establish connections to the machine without needing to track the IP address themselves. A common use is for running server software on a computer that has a dynamic IP address, as is the case with many consumer Internet service providers.
We recommend the free DDNS provider DYNDNS.ORG. Before you can use the DDNS feature, you need to set up an account with DYNDNS.ORG and create a domain name; e.g., myrouter.dyndns.org.
Host Name: Enter the domain/host name you have registered with DYNDNS.ORG. This must be the full domain name; e.g., mydomain.dyndns.org, and not mydomain. DDDNS Service Provider: Select “DynDns.org.”
User ID: Enter the DYNDNS username.
Password: Enter the DYNDNS password. Click “Add” to create the account.
Remember to first create an account and host name at http://www.dyndns.org. Once activated, the router will update the IP address automatically every time your ISP assigns a new address to you. That way, your DDNS domain name always points to your current public IP address.
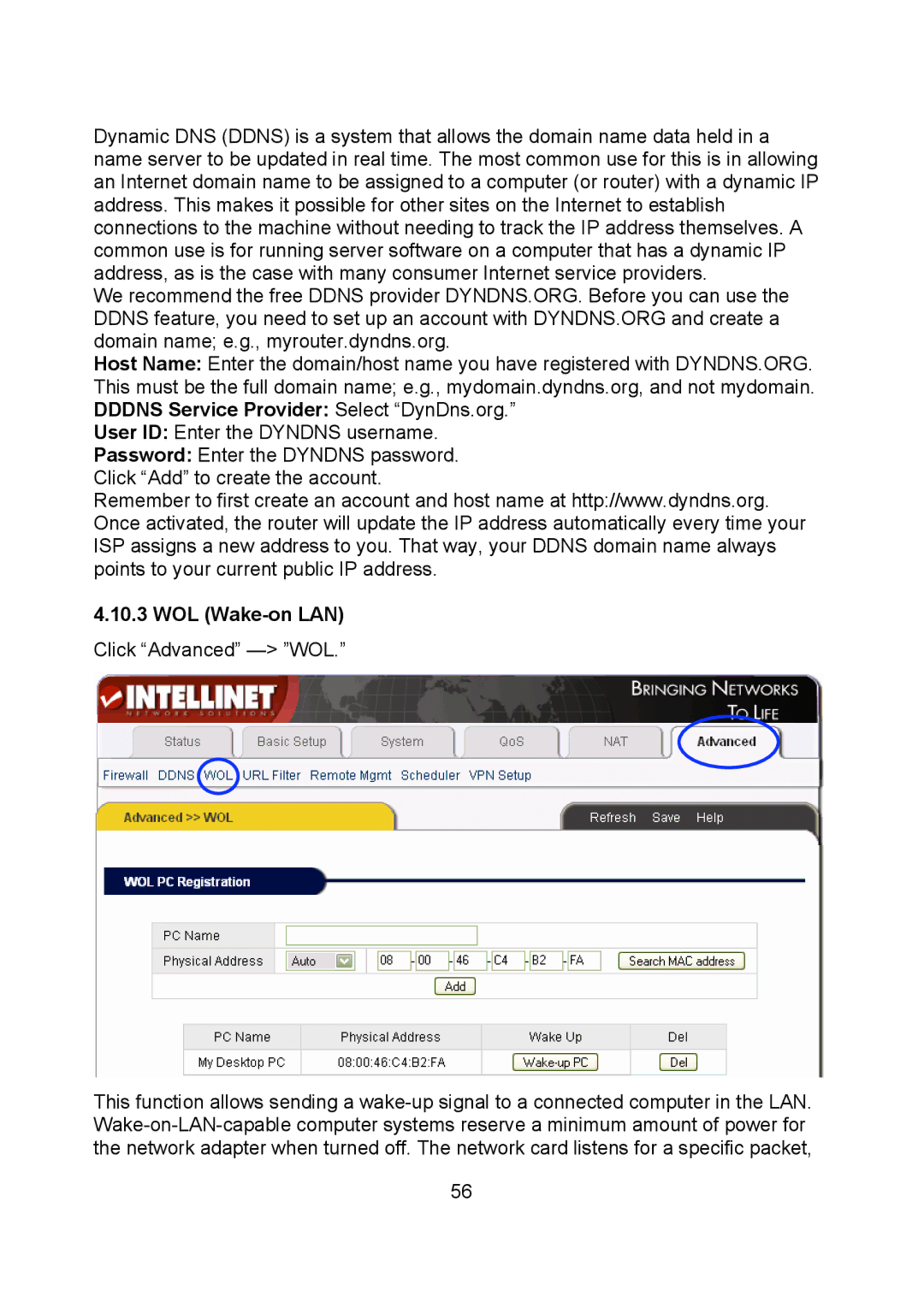
4.10.3 WOL (Wake-on LAN)
Click “Advanced” —> ”WOL.”
This function allows sending a
56