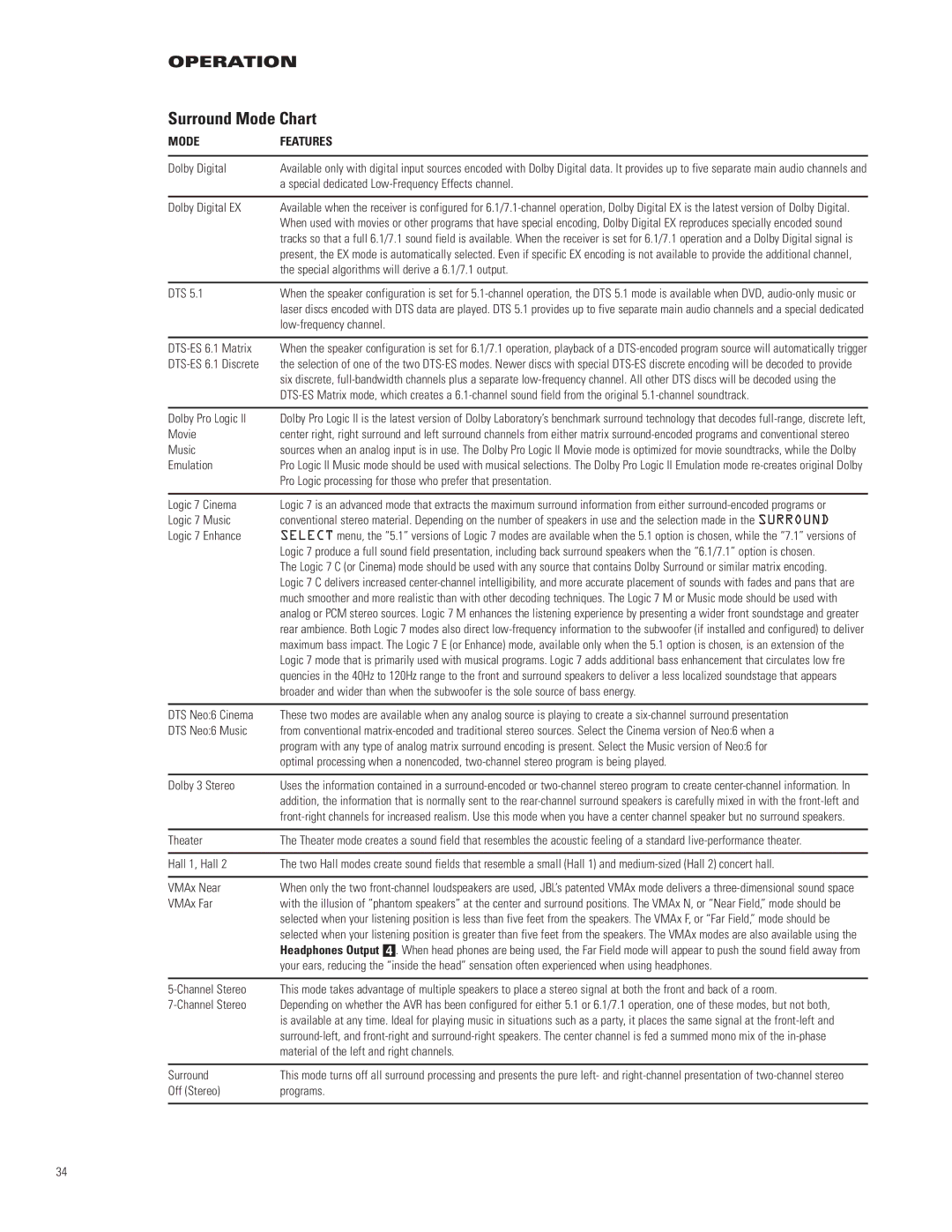
MODE | FEATURES |
| |
Dolby Digital | Available only with digital input sources encoded with Dolby Digital data. It provides up to five separate main audio channels and |
| a special dedicated Low-Frequency Effects channel. |
| |
Dolby Digital EX | Available when the receiver is configured for 6.1/7.1-channel operation, Dolby Digital EX is the latest version of Dolby Digital. |
| When used with movies or other programs that have special encoding, Dolby Digital EX reproduces specially encoded sound |
| tracks so that a full 6.1/7.1 sound field is available. When the receiver is set for 6.1/7.1 operation and a Dolby Digital signal is |
| present, the EX mode is automatically selected. Even if specific EX encoding is not available to provide the additional channel, |
| the special algorithms will derive a 6.1/7.1 output. |
| |
DTS 5.1 | When the speaker configuration is set for 5.1-channel operation, the DTS 5.1 mode is available when DVD, audio-only music or |
| laser discs encoded with DTS data are played. DTS 5.1 provides up to five separate main audio channels and a special dedicated |
| low-frequency channel. |
| |
DTS-ES 6.1 Matrix | When the speaker configuration is set for 6.1/7.1 operation, playback of a DTS-encoded program source will automatically trigger |
DTS-ES 6.1 Discrete | the selection of one of the two DTS-ES modes. Newer discs with special DTS-ES discrete encoding will be decoded to provide |
| six discrete, full-bandwidth channels plus a separate low-frequency channel. All other DTS discs will be decoded using the |
| DTS-ES Matrix mode, which creates a 6.1-channel sound field from the original 5.1-channel soundtrack. |
| |
Dolby Pro Logic II | Dolby Pro Logic II is the latest version of Dolby Laboratory’s benchmark surround technology that decodes full-range, discrete left, |
Movie | center right, right surround and left surround channels from either matrix surround-encoded programs and conventional stereo |
Music | sources when an analog input is in use. The Dolby Pro Logic II Movie mode is optimized for movie soundtracks, while the Dolby |
Emulation | Pro Logic II Music mode should be used with musical selections. The Dolby Pro Logic II Emulation mode re-creates original Dolby |
| Pro Logic processing for those who prefer that presentation. |
| |
Logic 7 Cinema | Logic 7 is an advanced mode that extracts the maximum surround information from either surround-encoded programs or |
Logic 7 Music | conventional stereo material. Depending on the number of speakers in use and the selection made in the SURROUND |
Logic 7 Enhance | SELECT menu, the “5.1” versions of Logic 7 modes are available when the 5.1 option is chosen, while the “7.1” versions of |
| Logic 7 produce a full sound field presentation, including back surround speakers when the “6.1/7.1” option is chosen. |
| The Logic 7 C (or Cinema) mode should be used with any source that contains Dolby Surround or similar matrix encoding. |
| Logic 7 C delivers increased center-channel intelligibility, and more accurate placement of sounds with fades and pans that are |
| much smoother and more realistic than with other decoding techniques. The Logic 7 M or Music mode should be used with |
| analog or PCM stereo sources. Logic 7 M enhances the listening experience by presenting a wider front soundstage and greater |
| rear ambience. Both Logic 7 modes also direct low-frequency information to the subwoofer (if installed and configured) to deliver |
| maximum bass impact. The Logic 7 E (or Enhance) mode, available only when the 5.1 option is chosen, is an extension of the |
| Logic 7 mode that is primarily used with musical programs. Logic 7 adds additional bass enhancement that circulates low fre |
| quencies in the 40Hz to 120Hz range to the front and surround speakers to deliver a less localized soundstage that appears |
| broader and wider than when the subwoofer is the sole source of bass energy. |
| |
DTS Neo:6 Cinema | These two modes are available when any analog source is playing to create a six-channel surround presentation |
DTS Neo:6 Music | from conventional matrix-encoded and traditional stereo sources. Select the Cinema version of Neo:6 when a |
| program with any type of analog matrix surround encoding is present. Select the Music version of Neo:6 for |
| optimal processing when a nonencoded, two-channel stereo program is being played. |
| |
Dolby 3 Stereo | Uses the information contained in a surround-encoded or two-channel stereo program to create center-channel information. In |
| addition, the information that is normally sent to the rear-channel surround speakers is carefully mixed in with the front-left and |
| front-right channels for increased realism. Use this mode when you have a center channel speaker but no surround speakers. |
| |
Theater | The Theater mode creates a sound field that resembles the acoustic feeling of a standard live-performance theater. |
| |
Hall 1, Hall 2 | The two Hall modes create sound fields that resemble a small (Hall 1) and medium-sized (Hall 2) concert hall. |
| |
VMAx Near | When only the two front-channel loudspeakers are used, JBL’s patented VMAx mode delivers a three-dimensional sound space |
VMAx Far | with the illusion of “phantom speakers” at the center and surround positions. The VMAx N, or “Near Field,” mode should be |
| selected when your listening position is less than five feet from the speakers. The VMAx F, or “Far Field,” mode should be |
| selected when your listening position is greater than five feet from the speakers. The VMAx modes are also available using the |
| Headphones Output 4. When head phones are being used, the Far Field mode will appear to push the sound field away from |
| your ears, reducing the “inside the head” sensation often experienced when using headphones. |
| |
5-Channel Stereo | This mode takes advantage of multiple speakers to place a stereo signal at both the front and back of a room. |
7-Channel Stereo | Depending on whether the AVR has been configured for either 5.1 or 6.1/7.1 operation, one of these modes, but not both, |
| is available at any time. Ideal for playing music in situations such as a party, it places the same signal at the front-left and |
| surround-left, and front-right and surround-right speakers. The center channel is fed a summed mono mix of the in-phase |
| material of the left and right channels. |
| |
Surround | This mode turns off all surround processing and presents the pure left- and right-channel presentation of two-channel stereo |
Off (Stereo) | programs. |
| |