4-RAID Control-Web Interface
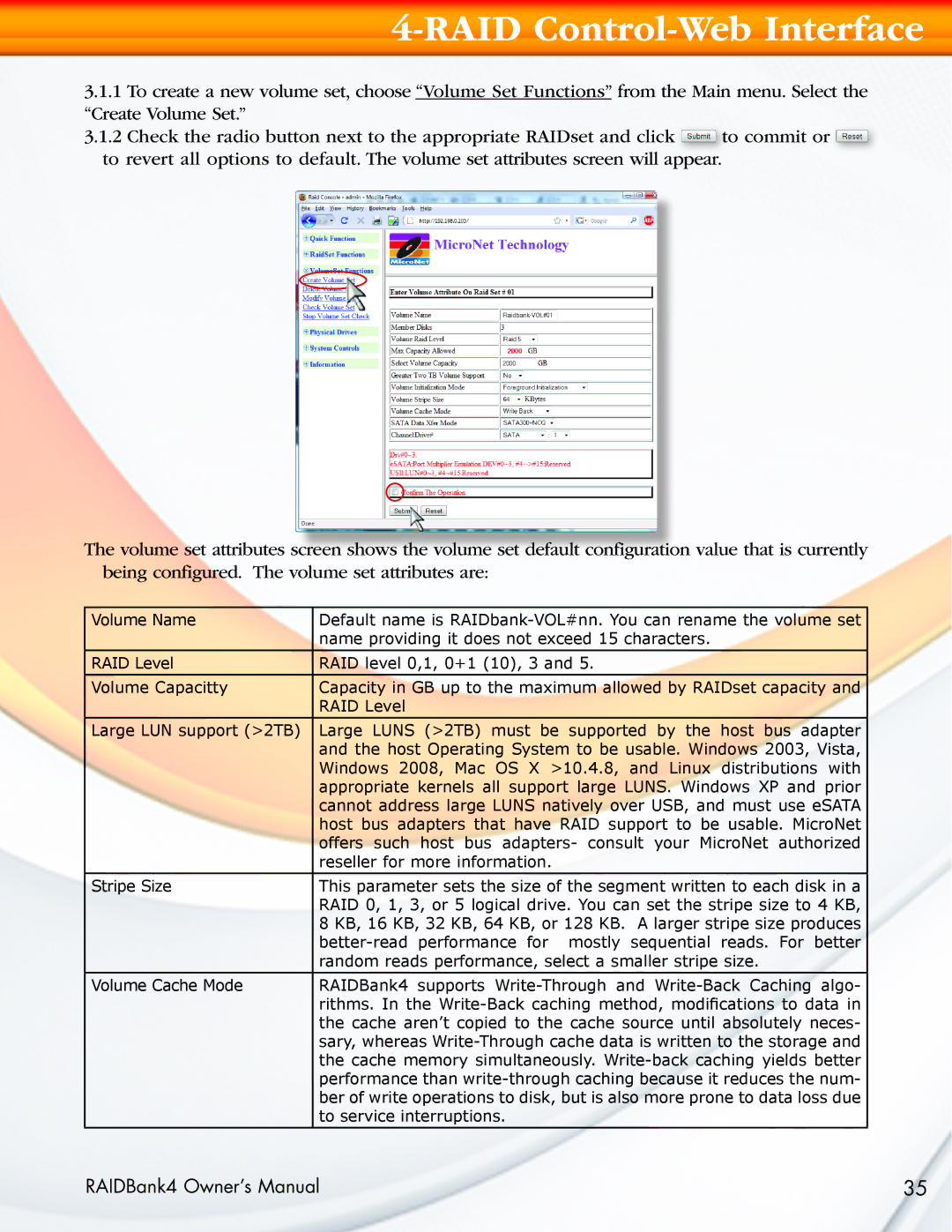
3.1.1To create a new volume set, choose “Volume Set Functions” from the Main menu. Select the “Create Volume Set.”
3.1.2Check the radio button next to the appropriate RAIDset and click ![]() to commit or
to commit or ![]() to revert all options to default. The volume set attributes screen will appear.
to revert all options to default. The volume set attributes screen will appear.
The volume set attributes screen shows the volume set default configuration value that is currently being configured. The volume set attributes are:
Volume Name | Default name is |
| name providing it does not exceed 15 characters. |
|
|
RAID Level | RAID level 0,1, 0+1 (10), 3 and 5. |
|
|
Volume Capacitty | Capacity in GB up to the maximum allowed by RAIDset capacity and |
| RAID Level |
|
|
Large LUN support (>2TB) | Large LUNS (>2TB) must be supported by the host bus adapter |
| and the host Operating System to be usable. Windows 2003, Vista, |
| Windows 2008, Mac OS X >10.4.8, and Linux distributions with |
| appropriate kernels all support large LUNS. Windows XP and prior |
| cannot address large LUNS natively over USB, and must use eSATA |
| host bus adapters that have RAID support to be usable. MicroNet |
| offers such host bus adapters- consult your MicroNet authorized |
| reseller for more information. |
|
|
Stripe Size | This parameter sets the size of the segment written to each disk in a |
| RAID 0, 1, 3, or 5 logical drive. You can set the stripe size to 4 KB, |
| 8 KB, 16 KB, 32 KB, 64 KB, or 128 KB. A larger stripe size produces |
| |
| random reads performance, select a smaller stripe size. |
|
|
Volume Cache Mode | RAIDBank4 supports |
| rithms. In the |
| the cache aren’t copied to the cache source until absolutely neces- |
| sary, whereas |
| the cache memory simultaneously. |
| performance than |
| ber of write operations to disk, but is also more prone to data loss due |
| to service interruptions. |
|
|
RAIDBank4 Owner’s Manual | 35 |