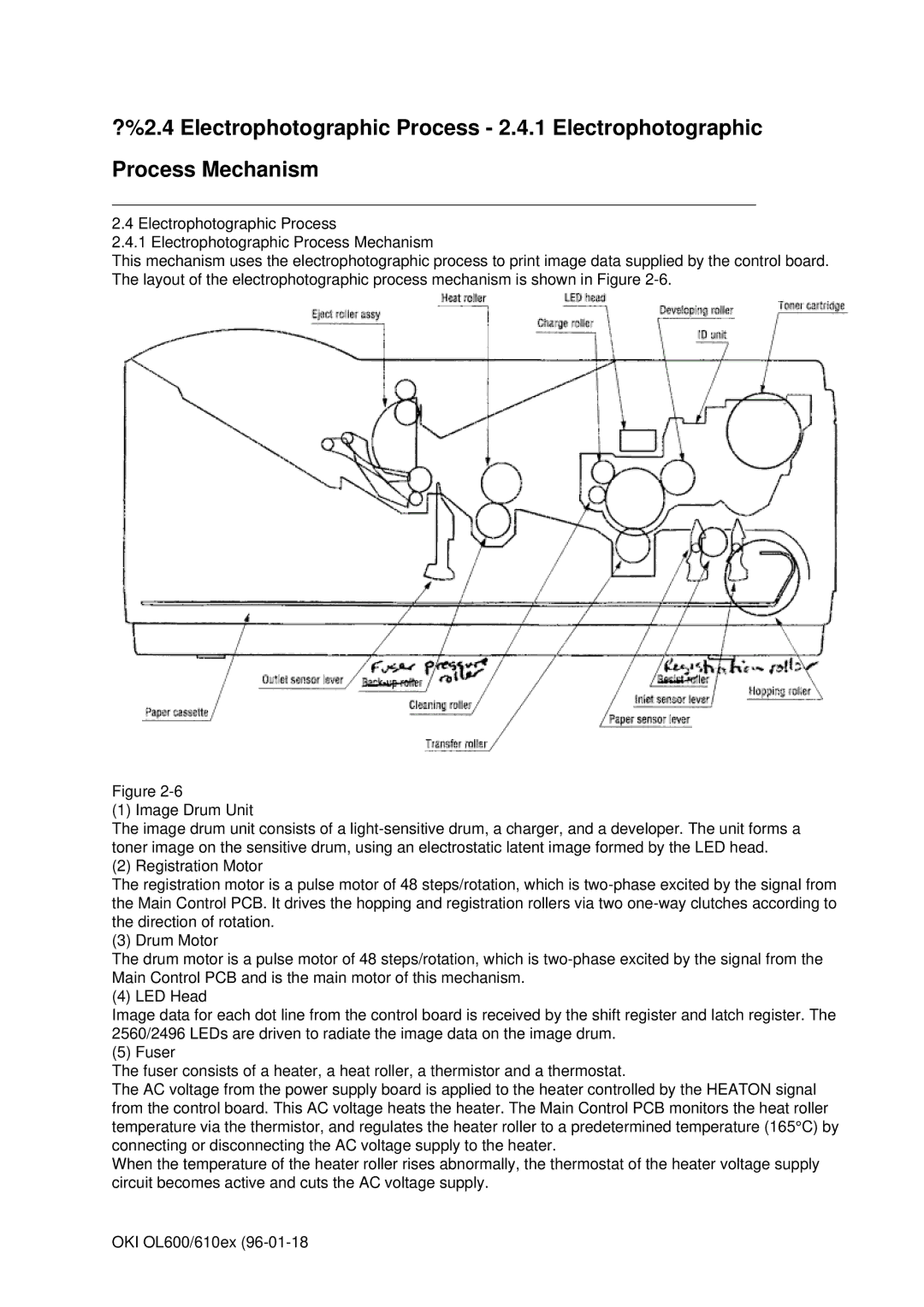
OL600E, OL610E, OL610EPS specifications
The Oki OL610EPS, OL610E, and OL600E are advanced line matrix printers renowned for their high-performance capabilities and durable design. These printers are ideal for high-volume printing environments where reliability and speed are crucial. They are often employed in sectors like manufacturing, logistics, and large-scale enterprises that require efficient document processing.One of the standout features of these models is their exceptional printing speed. The OL610EPS and OL610E can produce up to 1320 characters per second, while the OL600E offers a commendable output of up to 550 characters per second. This high-speed performance significantly boosts productivity, allowing businesses to handle large print runs with ease.
The printers incorporate Oki’s ribbon technology, which provides a longer ribbon life and reduces maintenance frequency. The OL610EPS boasts an impressive print head life, rated at 400 million characters, ensuring extended operation without the need for frequent replacements. This is particularly beneficial for businesses looking to minimize downtime and maximize efficiency.
Another key characteristic of the Oki OL610EPS, OL610E, and OL600E is their versatility in handling various media types. They can print on multi-part forms, labels, and envelopes, making them adaptable to a range of tasks. This multi-functionality is paired with a compact design, ideal for environments where space is limited.
In terms of connectivity, these printers feature various interfaces, including USB and parallel ports, ensuring compatibility with a wide range of systems. The OL610EPS and OL610E come equipped with advanced emulations such as IBM ProPrinter and Epson ESC/P, making integration into existing workflows seamless.
The durability of the Oki OL series is another notable attribute. Designed to withstand the rigors of continuous operation, these printers have robust construction that ensures longevity. The advanced thermal technology used in these models also contributes to lower power consumption, aligning with eco-friendly practices.
Furthermore, user-friendliness is a prominent aspect of Oki's design philosophy. The printers feature easy-access controls and a straightforward setup process, enabling quick operation and minimal training requirements for staff.
In conclusion, the Oki OL610EPS, OL610E, and OL600E line matrix printers stand out for their speed, versatility, and reliability. With advanced ribbon technology, robust construction, and user-friendly features, they are optimal solutions for businesses that demand efficient and high-quality printing capabilities.