DERAILLEUR SYSTEMS
The derailleur system includes the front and rear derailleurs, the shift levers, and the derailleur control cables, all of which must function correctly for smooth gear shifting to occur. There are several different types of derailleur systems but all operate using similar principles. Your new bicycle may be fitted with a standard 'friction' type system where you will need to feel each gear shift into position. It may be fitted with an ‘index’ system (e.g. SIS) which links each different gear position to a positive click mechanism in the shifter, and makes shifting very simple and precise. A further development of SIS is the fully integrated system (e.g. STI) where the shift lever and brake lever mechanisms form an integrated unit with the system allowing both gear shifting and braking to occur at the same time.
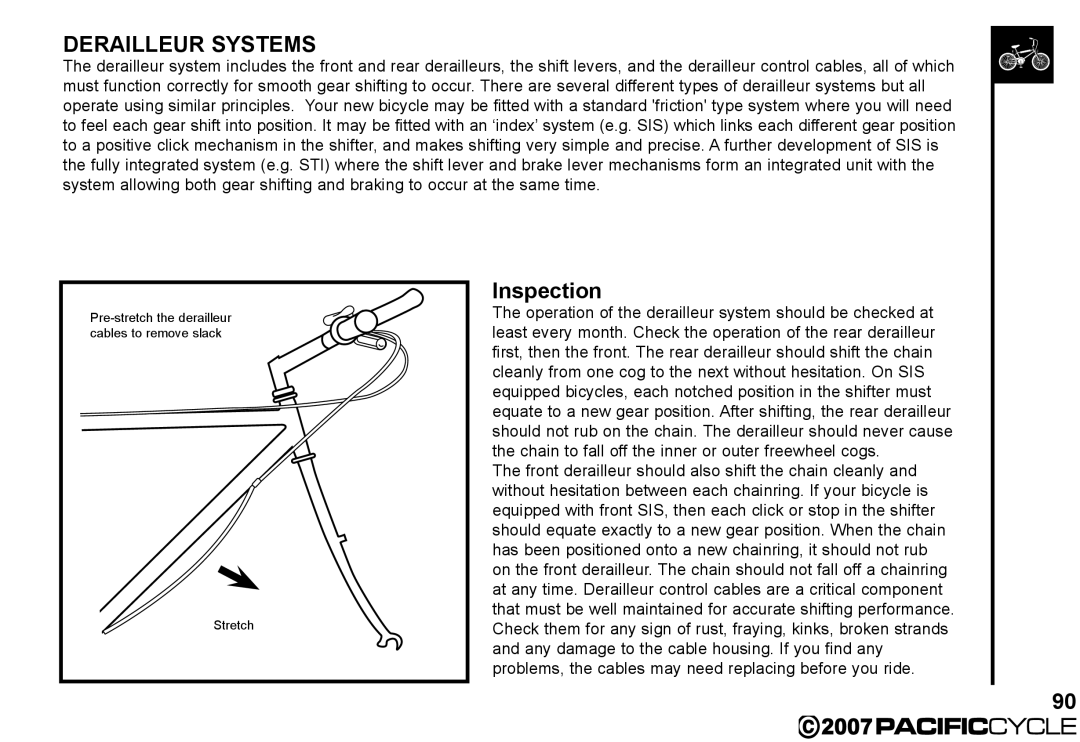
Stretch
Inspection
The operation of the derailleur system should be checked at least every month. Check the operation of the rear derailleur first, then the front. The rear derailleur should shift the chain cleanly from one cog to the next without hesitation. On SIS equipped bicycles, each notched position in the shifter must equate to a new gear position. After shifting, the rear derailleur should not rub on the chain. The derailleur should never cause the chain to fall off the inner or outer freewheel cogs.
The front derailleur should also shift the chain cleanly and without hesitation between each chainring. If your bicycle is equipped with front SIS, then each click or stop in the shifter should equate exactly to a new gear position. When the chain has been positioned onto a new chainring, it should not rub on the front derailleur. The chain should not fall off a chainring at any time. Derailleur control cables are a critical component that must be well maintained for accurate shifting performance. Check them for any sign of rust, fraying, kinks, broken strands and any damage to the cable housing. If you find any problems, the cables may need replacing before you ride.
90