Error rate is the number of errors per operation. The algorithm that S.M.A.R.T. uses to record rates of error is to set thresholds for the number of errors and appropriate interval. If the number of errors exceeds the threshold before the interval expires, the error rate is considered to be unacceptable. If the number of errors does not exceed the threshold before the interval expires, the error rate is considered to be acceptable. In either case, the interval and failure counters are reset and the process starts over.
Predictive failures
S.M.A.R.T. signals predictive failures when the drive is performing unacceptably for a period of time. The firm- ware keeps a running count of the number of times the error rate for each attribute is unacceptable. To accom- plish this, a counter is incremented each time the error rate is unacceptable and decremented (not to exceed zero) whenever the error rate is acceptable. If the counter continually increments such that it reaches the pre- dictive threshold, a predictive failure is signaled. This counter is referred to as the Failure History Counter. There is a separate Failure History Counter for each attribute.
6.3.5Thermal monitor
Pulsar XT.2 drives implement a temperature warning system which:
1.Signals the host if the temperature exceeds a value which would threaten the drive.
2.Signals the host if the temperature exceeds a
3.Saves a S.M.A.R.T. data frame on the drive which exceeds the threatening temperature value.
A temperature sensor monitors the drive temperature and issues a warning over the interface when the tem- perature exceeds a set threshold. The temperature is measured at
The thermal monitor system generates a warning code of
This feature is controlled by the Enable Warning (EWasc) bit, and the reporting mechanism is controlled by the Method of Reporting Informational Exceptions field (MRIE) on the Informational Exceptions Control (IEC) mode page (1Ch).
The current algorithm implements two temperature trip points. The first trip point is set at the maximum temper- ature limit according to the drive specification. The second trip point is
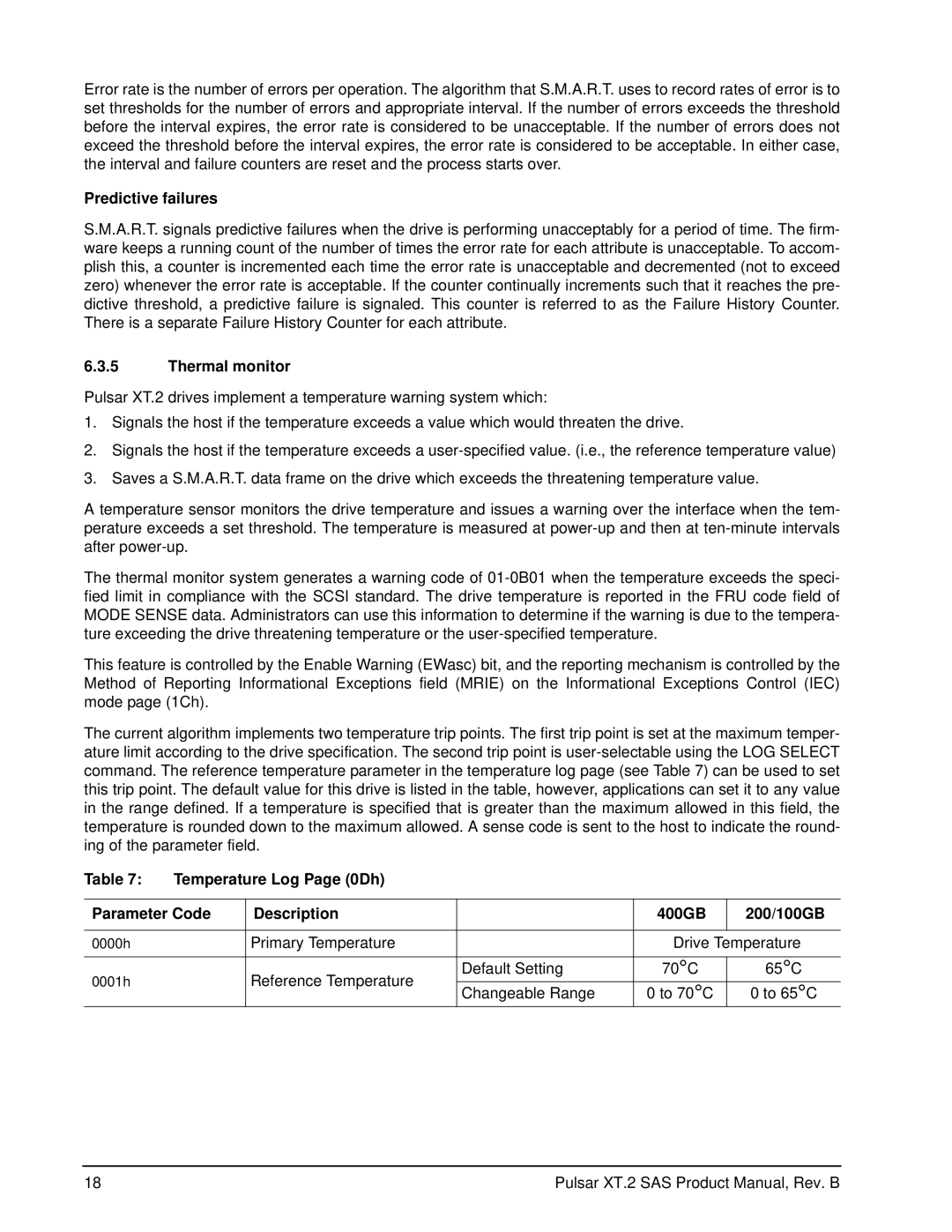
Table 7: | Temperature Log Page (0Dh) |
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
| |
Parameter Code | Description |
| 400GB | 200/100GB | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
0000h |
| Primary Temperature |
| Drive Temperature | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
0001h |
| Reference Temperature | Default Setting | 70°C | 65°C |
| Changeable Range | 0 to 70°C | 0 to 65°C | ||
|
|
| |||
18 | Pulsar XT.2 SAS Product Manual, Rev. B |