Zhone Technologies, Inc. | IMACS Product Book, Version 4 |
|
|
Wireless Base Station Application
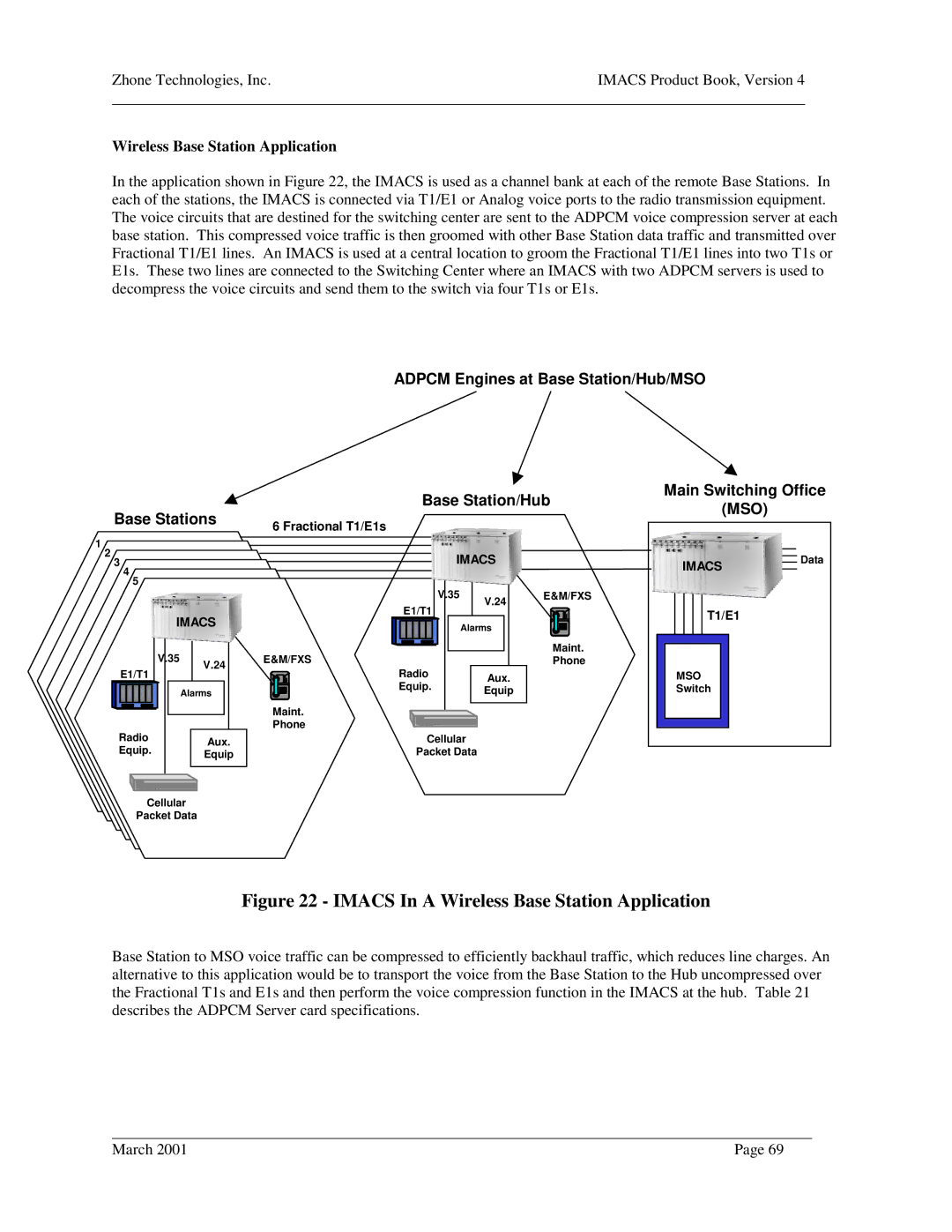
In the application shown in Figure 22, the IMACS is used as a channel bank at each of the remote Base Stations. In each of the stations, the IMACS is connected via T1/E1 or Analog voice ports to the radio transmission equipment. The voice circuits that are destined for the switching center are sent to the ADPCM voice compression server at each base station. This compressed voice traffic is then groomed with other Base Station data traffic and transmitted over Fractional T1/E1 lines. An IMACS is used at a central location to groom the Fractional T1/E1 lines into two T1s or E1s. These two lines are connected to the Switching Center where an IMACS with two ADPCM servers is used to decompress the voice circuits and send them to the switch via four T1s or E1s.
ADPCM Engines at Base Station/Hub/MSO
Base Stations
1 2 3 |
|
|
4 5 |
|
|
| IMACS | |
| V.35 | V.24 |
E1/T1 |
| |
|
| |
| Alarms | |
Radio |
| Aux. |
Equip. |
| |
| Equip | |
|
| |
Cellular |
| |
Packet Data |
| |
Base Station/Hub | Main Switching Office | |
(MSO) | ||
|
6 Fractional T1/E1s
| IMACS | IMACS | Data | |
|
|
|
| |
E1/T1 | V.35 | V.24 | E&M/FXS |
|
| T1/E1 |
| ||
Alarms |
| |||
|
|
| ||
E&M/FXS |
|
| Maint. |
|
|
| Phone |
| |
Radio |
| Aux. | MSO |
|
Equip. |
| Equip | Switch |
|
Maint. |
|
|
|
|
Phone |
|
|
|
|
Cellular |
|
|
| |
Packet Data |
|
|
| |
Figure 22 - IMACS In A Wireless Base Station Application
Base Station to MSO voice traffic can be compressed to efficiently backhaul traffic, which reduces line charges. An alternative to this application would be to transport the voice from the Base Station to the Hub uncompressed over the Fractional T1s and E1s and then perform the voice compression function in the IMACS at the hub. Table 21 describes the ADPCM Server card specifications.
March 2001 | Page 69 |