Network Tools
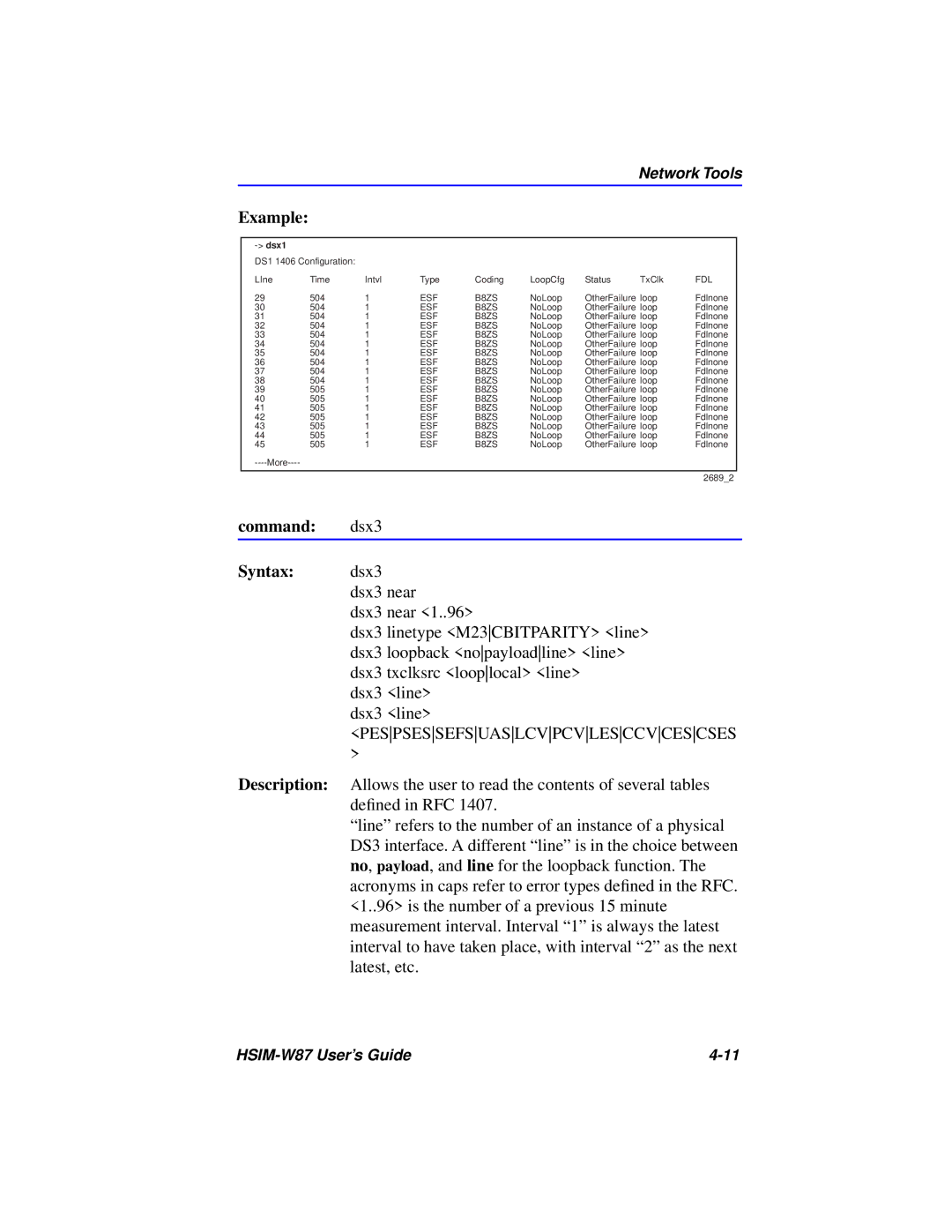
Example:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
DS1 1406 Configuration: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
LIne | Time | Intvl | Type | Coding | LoopCfg | Status | TxClk | FDL |
29 | 504 | 1 | ESF | B8ZS | NoLoop | OtherFailure loop | Fdlnone | |
30 | 504 | 1 | ESF | B8ZS | NoLoop | OtherFailure loop | Fdlnone | |
31 | 504 | 1 | ESF | B8ZS | NoLoop | OtherFailure loop | Fdlnone | |
32 | 504 | 1 | ESF | B8ZS | NoLoop | OtherFailure loop | Fdlnone | |
33 | 504 | 1 | ESF | B8ZS | NoLoop | OtherFailure loop | Fdlnone | |
34 | 504 | 1 | ESF | B8ZS | NoLoop | OtherFailure loop | Fdlnone | |
35 | 504 | 1 | ESF | B8ZS | NoLoop | OtherFailure loop | Fdlnone | |
36 | 504 | 1 | ESF | B8ZS | NoLoop | OtherFailure loop | Fdlnone | |
37 | 504 | 1 | ESF | B8ZS | NoLoop | OtherFailure loop | Fdlnone | |
38 | 504 | 1 | ESF | B8ZS | NoLoop | OtherFailure loop | Fdlnone | |
39 | 505 | 1 | ESF | B8ZS | NoLoop | OtherFailure loop | Fdlnone | |
40 | 505 | 1 | ESF | B8ZS | NoLoop | OtherFailure loop | Fdlnone | |
41 | 505 | 1 | ESF | B8ZS | NoLoop | OtherFailure loop | Fdlnone | |
42 | 505 | 1 | ESF | B8ZS | NoLoop | OtherFailure loop | Fdlnone | |
43 | 505 | 1 | ESF | B8ZS | NoLoop | OtherFailure loop | Fdlnone | |
44 | 505 | 1 | ESF | B8ZS | NoLoop | OtherFailure loop | Fdlnone | |
45 | 505 | 1 | ESF | B8ZS | NoLoop | OtherFailure loop | Fdlnone | |
2689_2
command: dsx3
Syntax: dsx3 dsx3 near
dsx3 near <1..96>
dsx3 linetype <M23CBITPARITY> <line> dsx3 loopback <nopayloadline> <line> dsx3 txclksrc <looplocal> <line>
dsx3 <line> dsx3 <line> <PESPSESSEFSUASLCVPCVLESCCVCESCSES
>
Description: Allows the user to read the contents of several tables defined in RFC 1407.
“line” refers to the number of an instance of a physical DS3 interface. A different “line” is in the choice between no, payload, and line for the loopback function. The acronyms in caps refer to error types defined in the RFC. <1..96> is the number of a previous 15 minute measurement interval. Interval “1” is always the latest interval to have taken place, with interval “2” as the next latest, etc.
|