MC-607
Configuring Subscriber-End Broadband Access Router Features
MC-608
Cisco IOS Software Feature Sets
Subscriber-end Overview
MC-609
Base IP Bridging Feature Set
Home Office Easy IP Feature Set
MC-610
Small Office Feature Set
Telecommuter Feature Set
MC-611
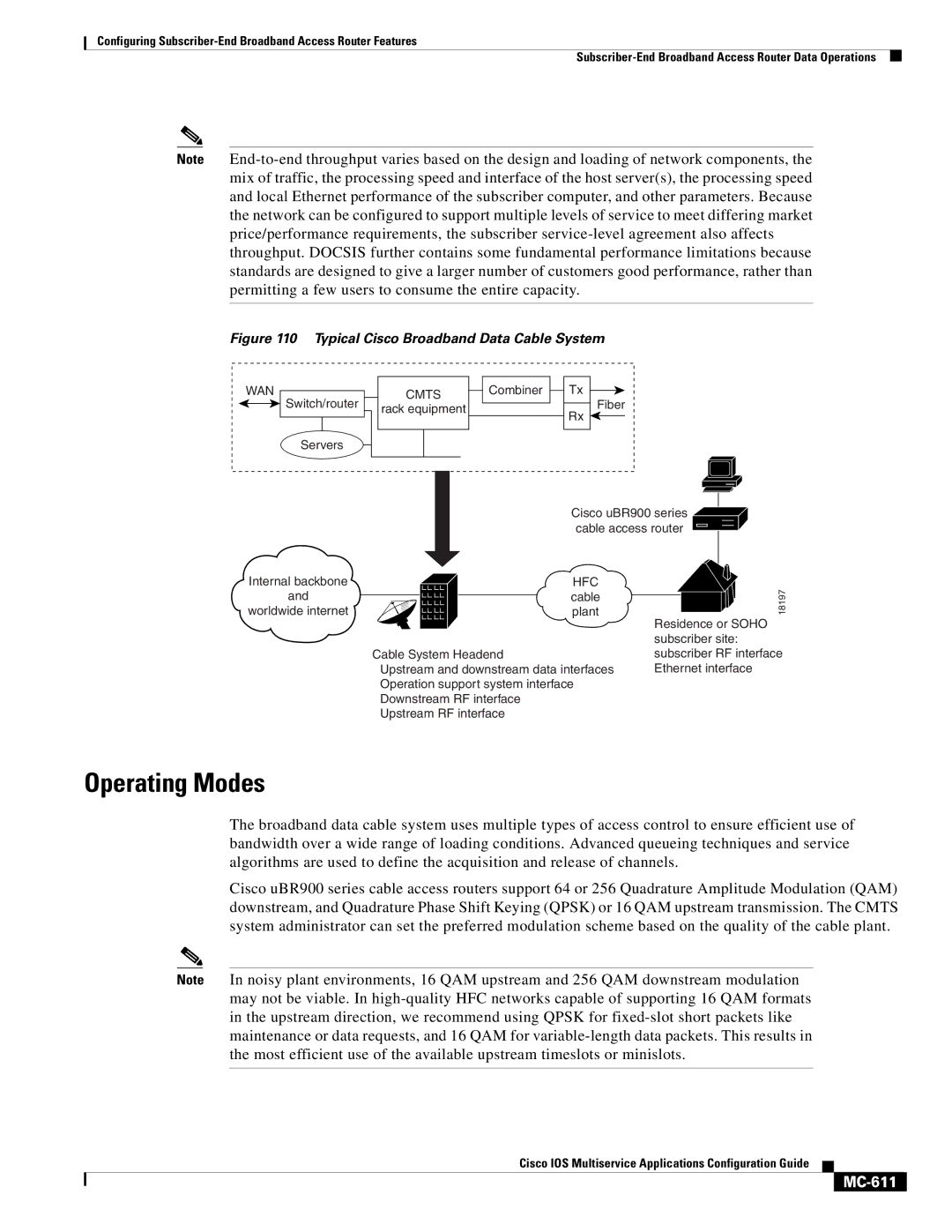
Operating Modes
MC-612
Data Specifications
Description Downstream Values Upstream Values
MC-613
Service Assignments
MC-614
Downstream and Upstream Data Transfer
Bridging Applications
MC-615
Routing Applications
Easy IP
L2TP Protocol
Dhcp Server
Network Address Translation and Port Address Translation
MC-617
Voice over IP Operations
Simplified VoIP over Cable Network
MC-618
MC-619
Voice Compression and Decompression
MC-620
Protocol Stack
Sgcp Protocol Stack
Subscriber-End Broadband Access Router Voice Specifications
Metric Value
MC-621
MC-622
Backup Pots Connection
MC-623
Docsis Baseline Privacy
IPSec Network Security
Firewall
Triple Data Encryption Standard
NetRanger Support-Cisco IOS Intrusion Detection
MC-624
MC-625
Subscriber-End Broadband Access Router Configuration Options
MC-626
MC-627
Event Description
MC-628
Sequence Event Description
MC-629
MC-630
MC-631
Cable Modem Initialization Flowchart
MC-632
Subscriber-End Broadband Access Router Basic Troubleshooting
Waitforlinkupstate
MC-633
UBR924# show controllers cable-modem 0 mac ?
MC-634
MC-635
Event 1-Wait for the Link to Come Up
Event 2-Scan for a Downstream Channel, then Synchronize
MC-636
Event 4-Start Ranging for Power Adjustments
Event 3-Obtain Upstream Parameters
MC-637
Event 5-Establish IP Connectivity
Event 7-Establish Security
Event 6-Establish the Time of Day
Event 8-Transfer Operational Parameters
Event 9-Perform Registration
MC-639
Event 11-Enter the Maintenance State
Event 10-Comply with Baseline Privacy
MC-640
Subscriber-End Broadband Access Router Configuration Tasks
MC-641
Configuring a Host Name and Password
Command Purpose
MC-642
Configuring Ethernet and Cable Access Router Interfaces
MC-643
Configuring Routing
MC-644
Verifying Routing
MC-645
Configuring Bridging
MC-646
MC-647
Reestablishing DOCSIS-Compliant Bridging
MC-648
Verifying DOCSIS-Compliant Bridging
MC-649
Customizing the Cable Access Router Interface
Using Multiple PCs with the Cable Access Router
MC-650
Basic Internet Access Bridging Configuration Example
MC-651
Basic Internet Access Routing Configuration Example
MC-652
IP Multicast Routing Configuration Example
MC-653
VoIP Bridging Using H.323v2 Configuration Example
MC-654
VoIP Routing Using H.323v2 Configuration Example
MC-655
NAT/PAT Configuration Example
MC-656
VoIP Bridging Using Sgcp Configuration Example
MC-657
IPSec Configuration Example
MC-658
L2TP Configuration Example
MC-659
MC-660

![]() cable access router
cable access router ![]()