Configuring
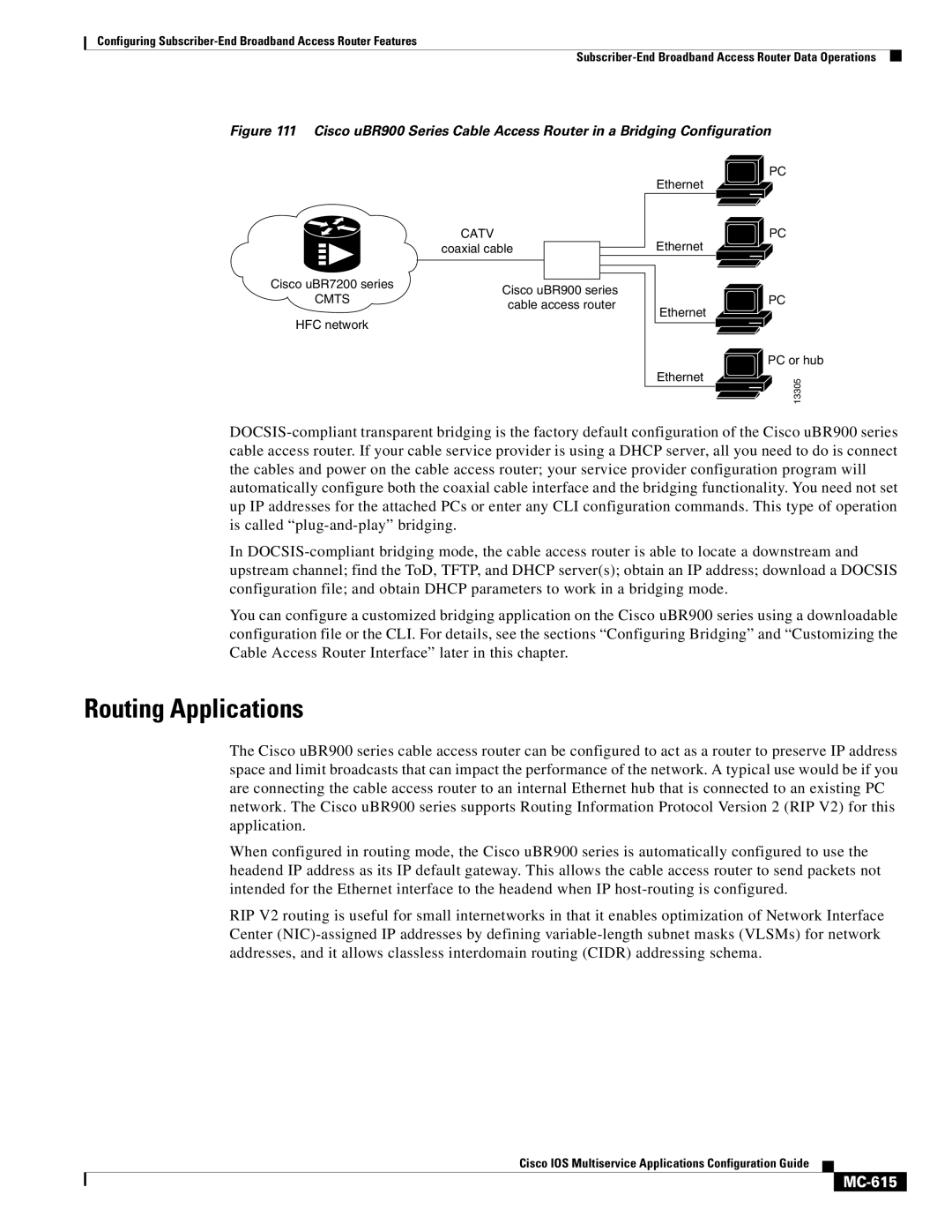
Figure 111 Cisco uBR900 Series Cable Access Router in a Bridging Configuration
Ethernet
PC
| CATV | |
| coaxial cable | |
Cisco uBR7200 series | Cisco uBR900 series | |
CMTS | ||
cable access router | ||
| ||
HFC network |
|
Ethernet
Ethernet
Ethernet
PC
PC
PC or hub
13305
In
You can configure a customized bridging application on the Cisco uBR900 series using a downloadable configuration file or the CLI. For details, see the sections “Configuring Bridging” and “Customizing the Cable Access Router Interface” later in this chapter.
Routing Applications
The Cisco uBR900 series cable access router can be configured to act as a router to preserve IP address space and limit broadcasts that can impact the performance of the network. A typical use would be if you are connecting the cable access router to an internal Ethernet hub that is connected to an existing PC network. The Cisco uBR900 series supports Routing Information Protocol Version 2 (RIP V2) for this application.
When configured in routing mode, the Cisco uBR900 series is automatically configured to use the headend IP address as its IP default gateway. This allows the cable access router to send packets not intended for the Ethernet interface to the headend when IP
RIP V2 routing is useful for small internetworks in that it enables optimization of Network Interface Center
Cisco IOS Multiservice Applications Configuration Guide