Cisco Structured Wireless-Aware Network (SWAN) Implementation Guide
Cisco SWAN Framework Overview
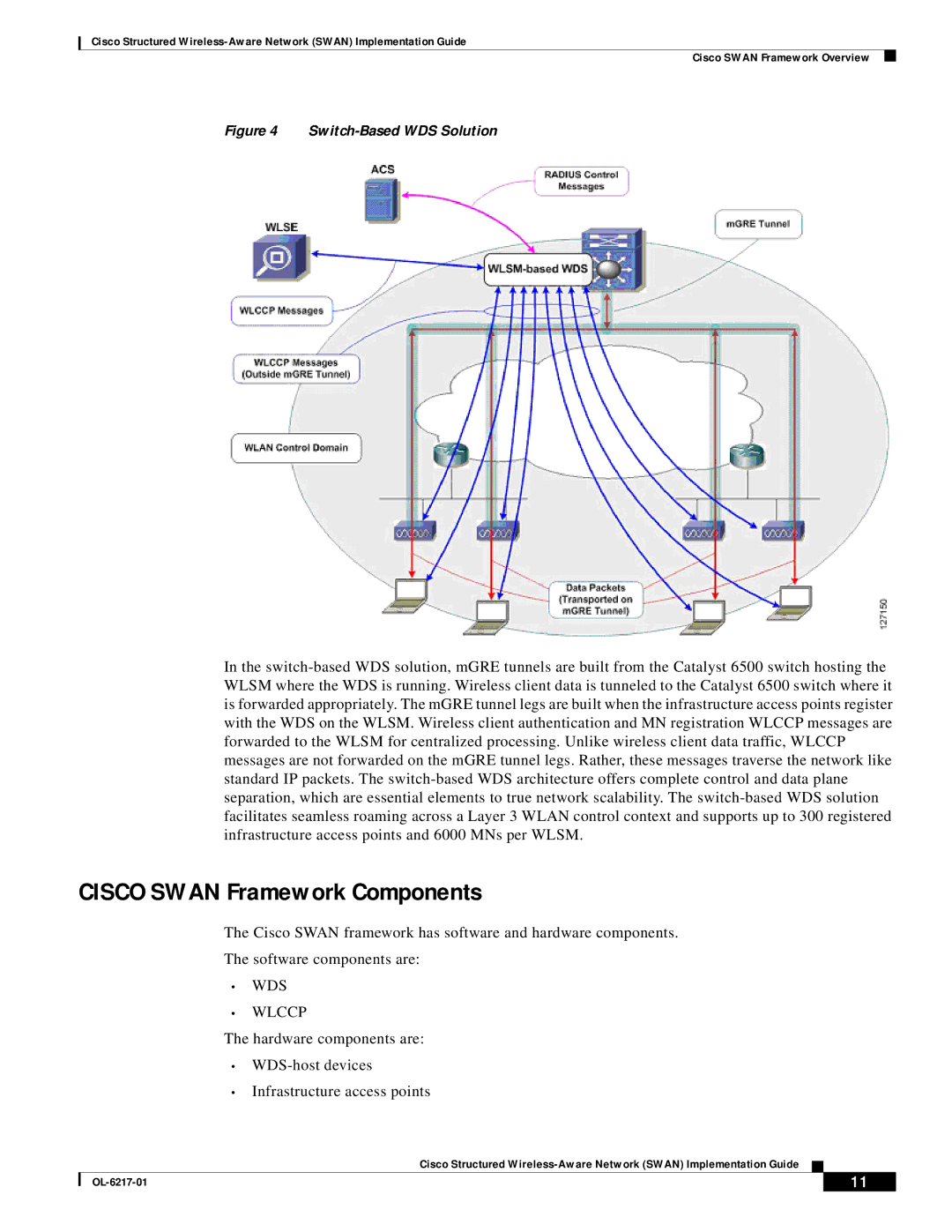
Figure 4 Switch-Based WDS Solution
In the switch-based WDS solution, mGRE tunnels are built from the Catalyst 6500 switch hosting the WLSM where the WDS is running. Wireless client data is tunneled to the Catalyst 6500 switch where it is forwarded appropriately. The mGRE tunnel legs are built when the infrastructure access points register with the WDS on the WLSM. Wireless client authentication and MN registration WLCCP messages are forwarded to the WLSM for centralized processing. Unlike wireless client data traffic, WLCCP messages are not forwarded on the mGRE tunnel legs. Rather, these messages traverse the network like standard IP packets. The switch-based WDS architecture offers complete control and data plane separation, which are essential elements to true network scalability. The switch-based WDS solution facilitates seamless roaming across a Layer 3 WLAN control context and supports up to 300 registered infrastructure access points and 6000 MNs per WLSM.
CISCO SWAN Framework Components
The Cisco SWAN framework has software and hardware components.
The software components are:
•WDS
•WLCCP
The hardware components are:
•WDS-host devices
•Infrastructure access points
Cisco Structured Wireless-Aware Network (SWAN) Implementation Guide