4.7 Servo Control
4.7.3 Servo frame format
As the servo information, the IDD uses the phase signal servo generated from the gray code and servo EVEN and ODD. This servo information is used for positioning operation of radius direction and position detection of circumstance direction.
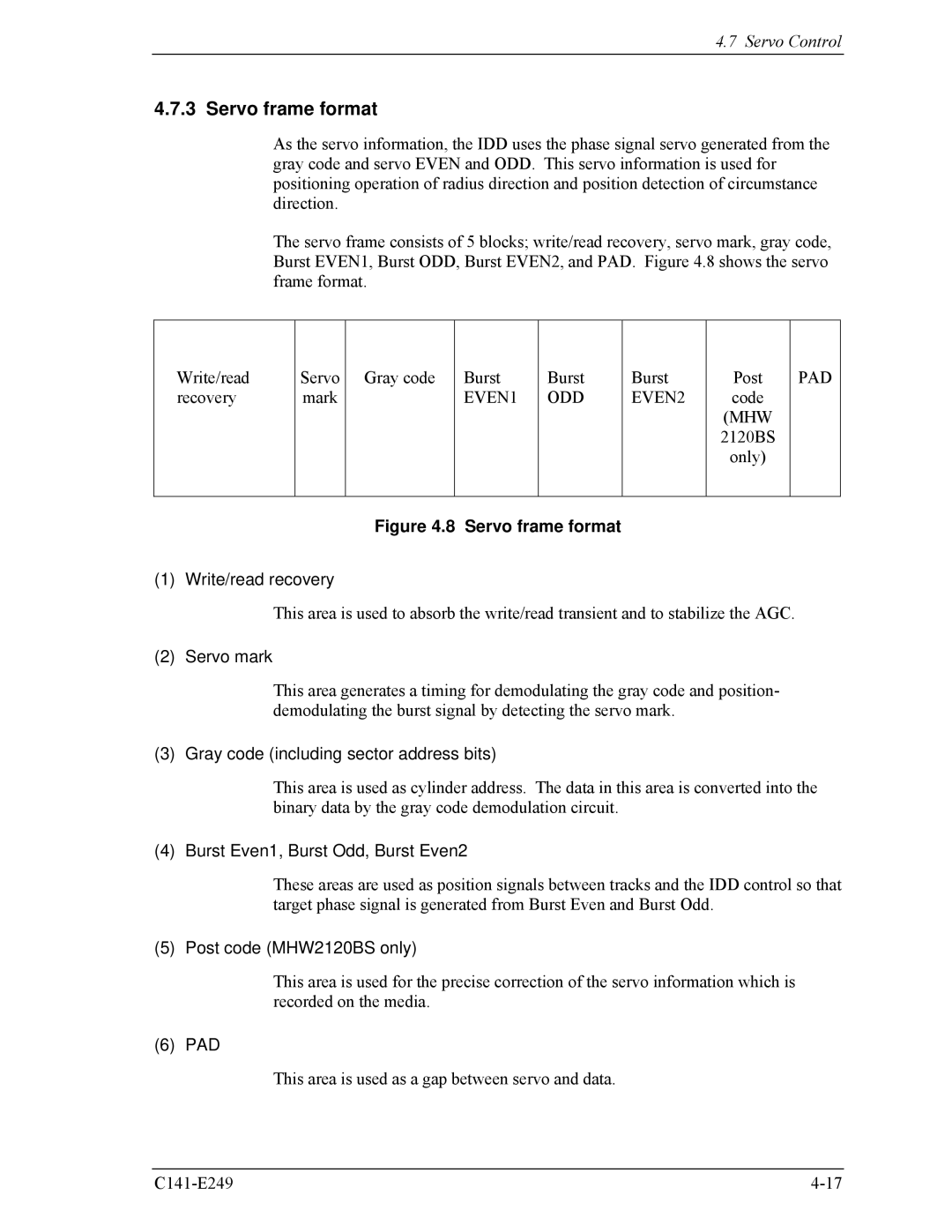
The servo frame consists of 5 blocks; write/read recovery, servo mark, gray code, Burst EVEN1, Burst ODD, Burst EVEN2, and PAD. Figure 4.8 shows the servo frame format.
Write/read | Servo | Gray code | Burst | Burst | Burst | Post | PAD |
recovery | mark |
| EVEN1 | ODD | EVEN2 | code |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| (MHW |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 2120BS |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| only) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Figure 4.8 Servo frame format |
|
|
| ||
(1) Write/read recovery
This area is used to absorb the write/read transient and to stabilize the AGC.
(2) Servo mark
This area generates a timing for demodulating the gray code and position- demodulating the burst signal by detecting the servo mark.
(3) Gray code (including sector address bits)
This area is used as cylinder address. The data in this area is converted into the binary data by the gray code demodulation circuit.
(4) Burst Even1, Burst Odd, Burst Even2
These areas are used as position signals between tracks and the IDD control so that target phase signal is generated from Burst Even and Burst Odd.
(5) Post code (MHW2120BS only)
This area is used for the precise correction of the servo information which is recorded on the media.
(6) PAD
This area is used as a gap between servo and data.